Slides 3 - start [kondor.etf.rs]
![Slides 3 - start [kondor.etf.rs]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010042273_1-46762134bc93b52f370894d59a0e95be-768x994.png)
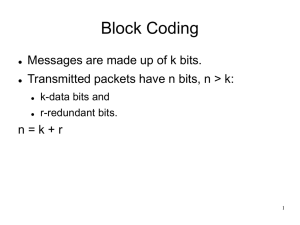
The Data Link Layer
Functions of the Data Link Layer
•
Provide service interface to the network layer
•
Frame delineation
•
Dealing with transmission errors
•
Error detection and correction codes
•
Positive and negative acknowledgements
•
Timers
•
Regulating data flow
•
Slow receivers not swamped by fast senders
Functions of the Data Link Layer
Relationship between packets and frames.
Data Link Layer Services
•
Unacknowledged connectionless service
•
Acknowledged connectionless service
•
Acknowledged connection-oriented service
Frame Delimiting
•
Character count
•
Flag bytes with byte stuffing
•
Starting and ending flags, with bit stuffing
Framing
A character stream. (a) Without errors. (b) With one error.
Framing
(a) A frame delimited by flag bytes.
(b) Four examples of byte sequences before and after stuffing.
Framing
Bit stuffing
(a) The original data.
(b) The data as they appear on the line.
(c) The data as they are stored in receiver’s memory after destuffing.
Error Detection and Correction
•
Error-Correcting Codes
•
Error-Detecting Codes
Hamming Distance
•
Hamming distance between codewords X and
Y, is the number of ones in X
Y
•
The number of detected bit errors is d if d +1 is the minimum Hamming distance between two codes.
•
The number of corrected bit errors is d if 2 d +1 is the minimum Hamming distance between two codes.
Error Correction
•
Codeword Y is calculated from generation matrix G , and block of data X :
Y = XG =[ x
1
, x
2
,…, x m
]· G mxn
•
At the receiver side the syndrom is found that detects and correct an error using check parity matrix H :
S = Y’H T
Error correction
•
For generation and parity check matrices it should hold
GH T =0
•
If
G =[ I m
| P ]
Then
H =[P T | I n-m
]
•
Here I is unity matrix, n is the codeword length, and m = n-k is the data block length
Error correction: Hamming Code
•
In Hamming code the codeword length is 2 m -1 -1, the number of added bits is 2 m -1 m -1
•
Parity check matrix comprises all possible column vectors. For example for m =4
H
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
Error Detection Code: CRC
•
Data block and codeword represented by polynomials.
•
If data block is X(x)=b
0
+b
1 x+…+b m -1 x m -1 , codeword is Y(x)=X(x)x k -mod(X(x), G(x)), where
G(x) is a generator polynomial of order k .
•
At the receiver side, codeword polynomial is divided by G(x). If the reminder is non-zero, an error is detected.
Error-Detecting Codes
Calculation of the polynomial code checksum.
Elementary Data Link Protocols
•
An Unrestricted Simplex Protocol
•
A Simplex Stop-and-Wait Protocol
•
A Simplex Protocol for a Noisy Channel with Frame Sequence Numbers
Sliding Window Protocols
•
A One-Bit Sliding Window Protocol
•
A Protocol Using Go Back N
•
A Protocol Using Selective Repeat
Sliding Window Protocols
A sliding window of size 1, with a 3-bit sequence number.
(a) Initially.
(b) After the first frame has been sent.
(c) After the first frame has been received.
(d) After the first acknowledgement has been received.
Sliding Window Protocols
Pipelining and error recovery. Effect on an error when
(a) Go back N (Wrec=1)
(b) Selective Repeat
Sliding Window Protocol Timers
Simulation of multiple timers in software.
A Sliding Window Protocol Using Selective Repeat
Wrec ≤ (S max
+1)/2 a) Initial situation with a window size seven.
b) After seven frames sent and received, but not acknowledged.
c) Initial situation with a window size of four.
d) After four frames sent and received, but not acknowledged.
Example Data Link Protocols
•
HDLC - High-level Data Link Control
•
PPP – Point-to-Point Protocol
High-Level Data Link Control
Frame format for bit-oriented protocols.
High-Level Data Link Control
Control field of
(a) An information frame.
(b) A supervisory frame.
Type: RECEIVE READY, REJECT, RECEIVE NOT READY,
SELECTIVE REPEAT
(c) An unnumbered frame.
Type: DISCONNECT, SNRP (set normal response mode),
SABM (set asynchronous balanced mode), FRAME REJECT
The Data Link Layer in the Internet
A home personal computer acting as an internet host.
PPP – Point to Point Protocol
The PPP full frame format for unnumbered mode operation.
Protocol: Link Control Protocol (LCP), Network Control Protocol (NCP),
IP, IPX, Appletalk, CLNP
PPP – Point to Point Protocol
A simplified phase diagram for bring a line up and down.
PPP – Point to Point Protocol
The LCP frame types.