Hydrocarbon Structure, Naming and Energy
advertisement
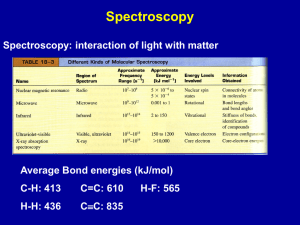
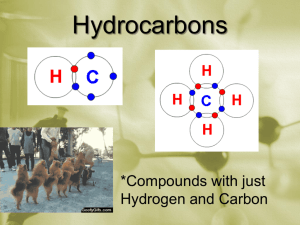
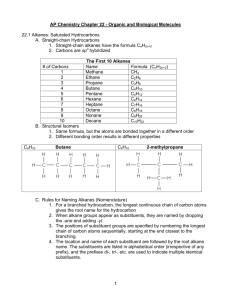
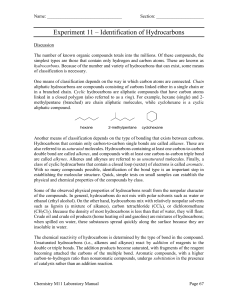
Hydrocarbon Structure, Naming and Energy ChemCom 2010 Review of Periodic Table • Organized by number of protons (atomic number) • Number of electrons is the same as the number of protons • Reactivity depends on VALENCE (outer shell) electrons • Number of valence electrons corresponds to group number Review of Chemical Bonding • Elements are looking for full outer shell • Combine in order to get full number of valence electrons • Carbon has 4 valence electrons • Hydrogen has 1 valence electron • Chemical energy is stored in the bonds between atoms Using the materials you and your partner have, make a hydrocarbon Count the number of C and the number of H Record them in the table on the board Alkanes – the most basic hydrocarbons Alkane names and formulas # Carbons Name Molecular Formula 1 Methane CH4 2 Ethane C2H6 3 Propane C3H8 4 Butane C4H10 5 Pentane C5H12 6 Hexane C6H14 7 Heptane C7H16 8 Octane C8H18 9 Nonane C9H20 10 Decane C10H22 What do you notice about the names of the alkanes? Energy Storage • Discuss the following with the person sitting in front or behind you. – Where is the energy? – Which have the most energy? How do we use hydrocarbons? • Coal – Heating – Electricity Generation • Oil – Heating – Electricity Generation – Transportation • Natural Gas – Heating – Electricity Generation – Transportation • Line up in the front of the room according to the first letter of your mother’s name. How do Hydrocarbons Form? • Put the cards in the proper order of formation • Once you think the order is correct have Ms. NH check • Once you have been confirmed as correct then grab your computer and write up the proper order for your notes • Now we know hydrocarbons are formed deep underground. • What are some way that you know of that we access the hydrocarbons deep underground? How do we access Hydrocarbons? • Close your computer screens – its video time! • Oil and Gas Drilling Video • Now in your own words, write a summary of what you saw in the video. • The oil that comes out of the ground is what we call CRUDE OIL • It is not useable straight from the ground, it must be processed How do we process Hydrocarbons? # Carbons Name Boiling Point 1 Methane -161.7 2 Ethane -88.6 3 Propane -42.1 4 Butane -0.5 5 Pentane 36.1 6 Hexane 68.7 7 Heptane 98.4 8 Octane 125.7 9 Nonane 150.8 10 Decane 174.0 Which alkanes would be gasses at room temperature (23)? Fractionating Tower The boiling points of the alkanes are used to separate the different fractions with a tower like the one shown to the left. Pull it all together • Explain what happens to one hydrocarbon from the time it becomes oil underground until it is fractionated into a something useful. Send your answer to me in an email. Please be sure to use proper grammar for full credit.