Chapter 12 - Garnet Valley School District
advertisement

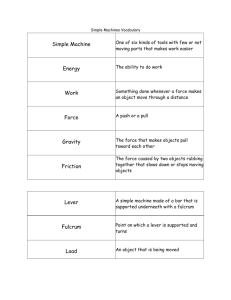
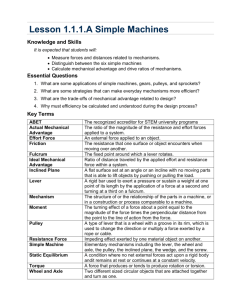
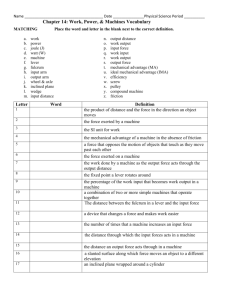
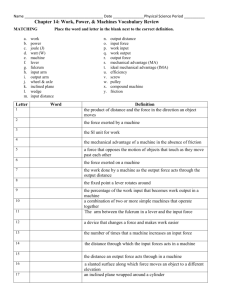
Chapter 12 Flash Cards 20 index cards Work • When force is exerted on an object causing it to move in the same direction • Work = F x D • Joule (J) = N•m Joule • The amount of work you do when you apply a force of 1N to move an object 1m. • 1N m = 1J • Power • The amount of work done on an object in a unit of time • Power = Work/Time J/s • Unit is the Watt (W) Machine • A device that makes work easier by changing the amount of force you exert, the distance over which you exert the force, or the direction in which you exert the force. Input Force • The force you exert on a machine. • Also called effort. Output Force • The force that the machine exerts on an object. • Also called resistance. Input Work • The input force times the input distance. Output Work • Output Force x Output Distance • Always less than Input Work Mechanical Advantage • The Number of times a machine multiplies your input force. Output Force • MA = Input force Efficiency • Compares the output work to the input work. Expressed as a percent. Output Work • Efficiency = x 100% Input Work Inclined Plane • A machine that consists of a flat sloped surface. • Ex: ramp Length of Incline • MA = Height of Incline H L Wedge • A machine that is thick at one end and tapers to a thin edge at the other end. length of wedge W • MA = width of wedge L Ex: axe, Knife, Teeth Screw • An inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder. • MA increases as the threads get closer together. • Ex: jar lid, car jack. Fulcrum and Lever • A lever is a rigid bar that pivots or rotates on a fulcrum. • A Fulcrum is a fixed point for a lever to pivot on. Fulcrum 1st Class Lever • A lever that has the fulcrum between the input (effort) and output (resistance) E R F • Always changes direction of force. The closer to the resistance, the more it multiplies your force. • Ex: crow bar, see-saw, scissors. 2nd Class Lever • A lever that has the output force (resistance) between the input (effort) and fulcrum. R E F • Input and output forces are in the same direction. The closer the output is to the fulcrum, the more MA you get. • Ex: Door, wheel barrow, nutcracker. 3rd Class Lever • A lever that has the input (effort) between the output (resistance) and the fulcrum. R F E • Usually multiplies distance by decreasing the force. • Ex: baseball bat, hockey stick, fishing rod. Wheel and Axle • A machine that has two circular or cylindrical objects fastened together that rotate on a common axis. radius of the wheel • MA = radius of the axle • Ex: screwdriver, steering wheel, door knob. Pulley • A machine made of a grooved wheel with a rope. 4 supporting ropes • MA = the number of supporting ropes holding the object. • Ex: flagpoles, cranes, sails. ¼F 1 2 34 Compound Machine A machine that utilizes (makes use of) two or more simple machines. MA is the product (multiply) of the MA of the machines that make it up. Ex: can opener, apple peeler.