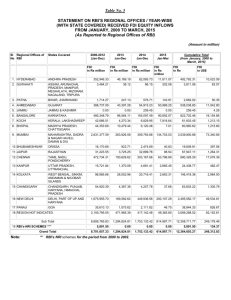
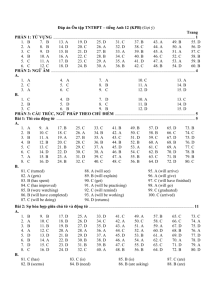
Foreign Direct Investment
advertisement

Chapter 7 Foreign Direct Investment Chapter Preview • Characterize global FDI flows and patterns • Discuss each theory that tries to explain FDI • Identify important management issues in the FDI decision • Explain why home and host nations intervene in FDI flows • List the methods that nations use to promote and restrict FDI © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 2 Foreign Direct Investment Purchase of physical assets or significant amount of ownership of a company in another country to gain some measure of management control By contrast, portfolio investment does not involve obtaining a degree of control in a company © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 3 Growth of World FDI vs. GDP © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 4 Reasons for FDI Growth Increasing globalization International mergers and acquisitions Entrepreneurship and small firms © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 5 Value of Cross-Border M&As © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 6 Worldwide FDI Flows World FDI inflows Developed (58%), developing (36%) European Union: 33% of world FDI 70,000 multinationals Developing nations China: 9% of world FDI All of Africa: 3% of world FDI © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e with 690,000 affiliates Chapter 7 - 7 International Product Life Cycle A company begins by exporting its product and later undertakes foreign direct investment as a product moves through its life cycle © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 8 Market Imperfections (Internalization) Company undertakes FDI to internalize a transaction that is being made inefficient by a market imperfection Trade barriers (e.g., tariffs) Specialized knowledge (e.g., managerial ability) © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 9 Eclectic Theory A firm undertakes FDI when location, ownership, and internalization advantages combine to make a location appealing Location advantage Ownership advantage Internalization advantage (optimal location) (special asset) (efficiency) © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 10 Market Power A firm undertakes FDI to establish a dominant presence in an industry Market power = Greater profits Vertical integration Extends company’s activities into stages of production that provide its inputs (backward integration) or absorb its outputs (forward integration) © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 11 Management Issues and FDI Control • Partnership requirements • Benefits of cooperation Production costs • Rationalized production • Cost of R&D Purchase-or-build decision Customer knowledge Following clients © Prentice Hall, 2008 Following rivals International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 12 Balance of Payments National accounting system that records all payments to entities in other countries and all receipts coming into the nation Current account Capital account Records transactions involving the import and export of goods and services, income receipts on assets abroad, and income payments on foreign assets inside the country © Prentice Hall, 2008 Records transactions involving the purchase or sale of assets (including assets such as property and shares of common stock in a company) International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 13 Why Host Intervenes in FDI Initial FDI boosts economy Balance of Payments + FDI may decrease import demand FDI may generate exports Access technology Obtain resources and benefits Access management skills + Create employment © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 14 Why Home Intervenes in FDI FDI – Removes resources from the nation – Can eliminate an export market – Might eliminate domestic jobs + May improve national competitiveness + Can offshore ‘sunset’ industries © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 15 Host Promotion Methods Financial incentives Infrastructure improvements Low or waived taxes Low-interest loans Improved seaports, roads, telecommunications networks © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 16 Host Restriction Methods Ownership restrictions Performance demands Prohibit investment in certain industries or businesses Local content reqmnt. Technology transfers Export targets © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 17 Home Promotion Methods Insurance on assets abroad Loans and loan guarantees Tax breaks on profits earned abroad © Prentice Hall, 2008 Special tax treaties Persuade other nations to accept FDI International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 18 Home Restriction Methods Higher tax rates on foreign income Sanctions on specific nations © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 19 Chapter Review • Characterize global FDI flows and patterns • Discuss each theory that tries to explain FDI • Identify important management issues in the FDI decision • Explain why home and host nations intervene in FDI flows • List the methods that nations use to promote and restrict FDI © Prentice Hall, 2008 International Business 4e Chapter 7 - 20