Effective Training Methods - RBAP-MABS
advertisement

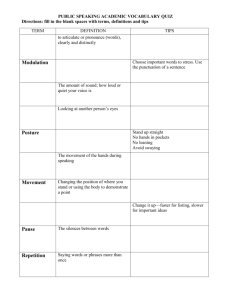
Effective Training Methods MABS Technical Resource Specialists Training and Accreditation Program Objectives • At the end of the session, the participants are expected to have learned the following: – Different training delivery methods – Appropriate methods to use for a certain type of training activity – Good Posture – Good gestures Training Delivery Methods: Lecture Advantages: Easy to prepare & deliver Suitable to a large audience Convey info in a short-time Time-frame easy to determine Disadvantages: Minimal participation Trainer-centered than traineecentered Tends to bore audiences Requires thorough planning Poor audience learning retention Tip: Plan the opening, main body and closing sections of the lecture. Group Discussion Advantages: More participative than lecture Surface values and opinions well Democratic in approach Distribution of learning responsibility Disadvantages: Not effective for large group Requires good facilitator Time management may be a problem May engender conflict/dominance Tips: Be clear on what needs to be done from the start. Summarize towards the end. Lecture-Discussion Combine lecture with interactive discussion with trainees. It improves the lecture by asking questions that make the audience think about ideas or concepts being presented. Allows individual participation even with large training programs. Role Play Advantages: Provides meaningful firsthand experience. Develops understanding of opposing views Fun, innovative, entertaining Highly creative and imaginative Elicits broad discussion during processing Disadvantages: Situations limited to simple ones Difficult to use properly Tip: Always use observers On-the-Job Training/Coaching A one-on-one continuous mentoring approach Advantages: Developmental Individualized Readily applicable on the job Holistic and realistic Feedback process is continuous Disadvantages: Time-consuming and costly Needs skilled mentor Used only in limited circumstances Good rapport between mentor and understudy is essential Tips: Clarify expectations at the start. Provide structure, feedback and assessment Demonstration A show-tell-follow-check approach to learning Advantages: Direct, easy,clear to follow Learning by example Realistic, readily applicable Suitable in skill or technical training Job-related Disadvantages: Not everyone can be accommodated in hands-on Tip : Follow the telldo-ask-practice approach Case Study Controlled Group Discussion Based on a Written Text Advantages: Suitable for right or wrong situations Maximum participation Applicable on the job Disadvantages: Needs effective case text More time needed to read, discuss, answer and report. Tips: Pre-test the case when possible Provide not only text but guide questions/ tasks Fit contents to trainees needs/ organizations Games and Simulations Animated activities to generate fun in learning Disadvantages: Advantages: Learning may be Fun and enjoyable sidetracked Allows full Learning outcomes vary in participation consistency Surfaces values and Some are unparticipative attitudes well Which Training Methods Should You Use? To transfer knowledge: Group discussion Lecture Group or individual exercises Forums Panel Discussions Film, video, etc. To practice problemsolving: Case studies Brainstorming Discussion Groups Exercises, etc. Which Training Methods Should You Use? To develop skills: demonstrations for manual skills role playing for interpersonal skills peer teaching programmed instructions, etc. To change attitudes: role playing individual exercises demonstrations campaigns, etc. SOME TIPS FOR INSTRUCTORS/ TRAINORS Tips for Instructors Before the Session: 1.As instructor, dress appropriately (i.e. no slippers, shorts, revealing outfits) to command credibility. For clothing, very bright colors are not recommended as this may distract participants from the course material. Tips for Instructors 2. Arrive well in advance of the participants to check the following room conditions and equipment: Table and chairs sufficient and set up as desired (consider a U-shape for maximum viewing and interaction). Copies of training schedule and materials. Ensure appropriate air circulation in the room. Refreshments (i.e. drinks, snacks) Test equipment. Overhead projector machine in place and working. (Be sure the cord is out of the way. Tape it down where people may walk.) Tips for Instructors 3. Know your subject thoroughly Write it out and reduce it to cards Write opening and closing sentences 3. Be conscious of time. Your invitation to the participants should include course duration, as well as, what time the course will start and end. During the training, make sure you are within the time limits of each module. Tips for Instructors During discussions: 1. Discussions are an important aspect of adult learning; they encourage involvement and reflection and result in better understanding and retention of information. Tips for Instructors 2. Give each participant an opportunity to express his or her views, but be sure to keep the discussion on tract. Ask for ideas and offer suggestions If there is a lull in the discussion, or nobody know what quite to add, you can provide an idea or example of your own. Draw people out when they are reluctant to participate Tips for Instructors Maintain or enhance self-esteem. Listen and respond with empathy Example: After someone speaks up, you might want to add confidence by saying something like “that’s a good point,” or “good idea!” 3. Check for understanding. Clarify when questions may be asked (either during or after presentation.) 4. Manage time by presenting the agenda beforehand so participants know what to expect. Use a timer to remind or signal you to wind up each session. Presentation Techniques Use of Overhead Projector 1. Once you focus the projector before participants arrive you should not have to adjust it again. When you think the machine is in focus, walk to the back of the room and look at the screen to check if the acetates can be seen clearly. 2. While you are teaching, do not stand directly in front of the screen, or the image will be projected on you as well. Stand to one side of it, and do not turn around to look at it. Presentation Techniques Use of Overhead Projector 3. If you wish to point out something on a particular overhead, do so by using a pen or other object to point to the appropriate area on the transparency itself, on the bed of the projector. Postures Posture and the way a presenter conducts himself on the platform is an important part of a good presentation. Stand up straight and face the audience head-on. Keep posture open with arms relaxed and hanging down at your sides. Hold head up high with your chin up. Trainer Gestures Gestures, a form of body language, are also a part of your overall visual picture. They are visual reinforcements of the words and ideas the trainer is trying to communicate to his audience. They include hand, arm, and head movements and can enhance your presentation or detract from it. Effective Gestures Effective gestures are spontaneous but not distracting Movements are broad and flowing, not fast and jerky Nodding of head and smiling are effective ways to emphasize a point Gestures to Avoid • Finger pointing and fist raising can be interpreted as hostile or threatening • Crossing hands behind the back • Crossing arms over chest believing it appears relaxed and confident. • Hands inside the pocket • Clasping hands in folded position Common Trainer Problems What’s wrong? No eye contact • • • • Participants feel alone and neglected. You look scared and uncomfortable. Students lose trust in the trainer. You lose credibility and appear dishonest. • No personal connection is made. They Can’t Hear You • Audiences withdraw when they can’t hear the trainer. • Listening to a trainer speaking too loudly conjures up uncomfortable childhood memories of being yelled at; it’s demeaning. • When you speak too loudly, you may spit on trainees. • Speaking too loudly or too softly is irritating and interferes with learning. This is My Life • You run the risk of entering the Tangent Zone. • Participants perceive your ego to be bigger that Mt. Everest. • Program focus gets lost. • It feels like you’re wasting their time. • Or, maybe you just like to hear yourself to talk. Speech Tics • • • • • • “Speech tics” are annoying to the audience. Repetitive sounds get old and boring fast. Trainees get easily distracted. They will start counting your “speech tics.” Some people will make fun of you. You decrease your believability Silly Screw-ups • • • • • Your credibility is shot. You appear absent-minded. Your organization skills are questioned. Time is wasted fixing the mistakes. If the video is wrong, you have to fill that time with something else. Getting in their Faces • This behavior can be threatening/antagonistic. • Participants may become embarrassed. • It violates their comfort zones. • There is potential for starting fights. • It distracts from what is being said. • You might spit on others and swap germs. • It’s too intimate (and intimidating) for some. Cutting off Questions • You don’t listen to questions. • You begin to answer questions before askers are finished. • You disregard questions and keep going. • You say, “We’ll get to that later.” and hope you will. • You act like their questions are beneath the dignity of an answer. • You tell them to ask questions at the end, and then run out time. Slideswiping • The overhead projector, as a training tool, is abused. • Participants are likely to go sleep. • Swiping slides is a lazy way to present information. • Retention and application are reduced. How to Overcome Stage Fright 1. Plan as if your life depended on it. 2. Get rid of last-minute butterflies. 3. Transform anxiety to excitement 4. Practice, practice, practice Other Tips • • • • • • Mix your media Correlate training with reality Have data at your fingertips Play-it-by ear Friendly facial expression Keep your sense of humor