Centrifugal Pump Performance Experiment
advertisement

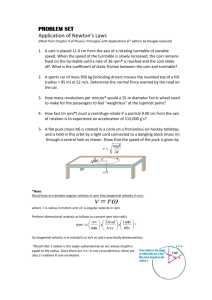
Centrifugal Pump Performance Experiment Presented by: Steven King ME 498 Senior lab November 16, 2004 Overview of Presentation Objectives Methodology and Background Experimental Setup Discussion of Results Conclusions and Recommendations Objectives Become familiar with centrifugal pump operation Analyze the principles of fluid flow at 5 different shaft speeds Evaluate pump performance Methodology and Background Key Equations B (1) Cd 0.907 6.53 ReD (2) RED Vt 2 D1 (3) (4) Vt C d Q Cd AtVt Assumptions: Β= .75, ρ=998, and μ=9.55x10-4 ΔP and was recorded during experiment. 0 (5) 2 P2 P1 V2 2 V12 Hp Z 2 Z1 2g g P 1 4 Methodology and Background Cont. Key Equations Continued (6) W pump QP2 P1 (7) pump QP2 P1 T Affinity Laws Q2 Q1 N2 N1 N2 Hp 2 Hp1 N1 2 N2 P2 P1 N1 3 Experimental Setup Overall System Schematic Experimental Setup Cont. Experimental Setup Cont. = 2 in = 1.5 in Venturi Flow Meter Results Uncertainty Values for Experiment wQ = 38.0% wη = 39.7% Affinity Law Results Value found from Experiment Q (m3/s) 1165 RPM % Difference 5.61E-03 5.30E-03 5.55 P (W) 435.8 470.8 7.43 Hp (m) 7.92 9.06 12.58 7.49E-03 6.96E-03 7.12 P (W) 906.1 1066.4 15.03 Hp (m) 12.33 15.6 20.96 Q (m3/s) 1530 RPM Calculated Using Affinity Laws Results Cont. Pump Head vs. Flow Rate 20 18 2 y = -130514x + 273.53x + 17.664 2 R = 0.999 16 Pump Head (m) 14 12 y = -109848x2 + 75.198x + 14.49 R2 = 0.9972 10 y = -123314x2 + 197.32x + 10.708 R2 = 0.9945 8 2 y = -37652x - 285.26x + 8.3396 2 R = 0.9714 6 900.2 RPM 992.8 RPM 4 2 y = -54121x - 192.77x + 7.0513 2 R = 0.9559 2 1165 RPM 1352 RPM 1530 RPM 0 1.5E-03 2.5E-03 3.5E-03 4.5E-03 5.5E-03 Flow Rate (m^3/s) 6.5E-03 7.5E-03 8.5E-03 Results Cont. Pump Efficiency vs. Flow Rate 0.8 y = -9353.1x2 + 165.91x - 0.0087 R2 = 0.9985 0.7 0.6 Pump Efficiency 2 y = -19075x + 183.32x + 0.0023 2 R = 0.9955 0.5 y = -9886.8x2 + 151.87x - 0.0003 R2 = 0.9989 0.4 y = -15468x2 + 165.33x + 0.0014 R2 = 0.9976 0.3 y = -15032x2 + 166.37x - 0.0027 R2 = 0.9987 900.2 RPM 992.8 RPM 0.2 1165 RPM 1352 RPM 1530 RPM 0.1 0.0 0.0E+00 1.0E-03 2.0E-03 3.0E-03 4.0E-03 5.0E-03 Flow Rate (m^3/s) 6.0E-03 7.0E-03 8.0E-03 Results Cont. Pump Efficiency vs. Pump Power to Fluid 0.8 0.7 2 y = -2E-06x2 + 0.0021x - 0.0003 R2 = 0.9996 y = -2E-07x + 0.001x + 0.0032 2 R = 0.9992 0.6 Pump Efficiency 2 y = -3E-06x + 0.0027x + 0.0008 2 R = 0.9985 2 y = -1E-06x + 0.0015x - 0.0017 2 R = 0.9988 2 y = -4E-08x + 0.0008x + 0.0009 2 R = 0.9999 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 900.2 RPM 992.8 RPM 1165 RPM 0.1 1352 RPM 1530 RPM 0.0 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 Pump Power (Watts) 700 800 900 1000 Results Cont. Pump Power to Fluid vs. Flow Rate 1000 y = -1E+07x2 + 214130x - 15.3 R2 = 0.9978 900 Pump Power (Watts) 800 y = -1E+07x2 + 168878x - 8.0432 R2 = 0.9984 700 600 y = -8E+06x2 + 126678x - 4.5836 R2 = 0.9983 500 400 y = -5E+06x2 + 85850x - 0.3415 R2 = 0.999 300 900.2 RPM 200 y = -5E+06x2 + 73781x - 0.2309 R2 = 0.999 100 992.8 RPM 1165 RPM 1352 RPM 1530 RPM 0 0.0E+00 1.0E-03 2.0E-03 3.0E-03 4.0E-03 5.0E-03 Flow Rate (m^3/s) 6.0E-03 7.0E-03 8.0E-03 Conclusions and Recommendations All R2 were above .95 with most being above .99 The best overall efficiency was approximately 70% for an RPM of 1530 The use of pressure gauges and dynamometer that are less affected by vibration would improve results A more accurate method of recording voltage and current would also improve the results