Alternator vs Generator Presentation
advertisement

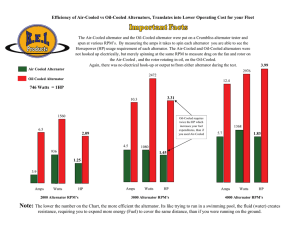
Alternator vs Generator Basic Theory Advantages/Disadvantages Inductance • Moving magnetic field in relation to conductor, generates electron flow • Electricity is generated • Faster movement, more flow • Larger field, more flow • Each conductor produces a fraction of output Generator • • • • • Windings spin within magnetic field RPM limited, low RPM, low output Magnetic strength has low variability Operates well at high engine RPM Generates it’s own field and flow from residual magnetism • It turns, it works Alternator • • • • • • Magnetic field spins within windings High variability in gauss Low RPM, strong magnet High RPM, weaker magnet Needs voltage to generate voltage Dead battery, no output Alternator/Generator • • • • • Wide range of RPM Lighter in weight More delicate Needs field current More complicated • • • • • Narrow RPM range Heavier for output Bulletproof Needs to turn Very simple system Electrical System • • • • • • Battery Alternator/Generator Distributing busses/ Breakers Switches Devices/Appliances Safeties Battery • • • • • • Battery voltage, 24 volts Stores energy for start/ ground ops Stabilizes against surges Charges back from alternator System voltage, 28 volts Why the difference? Distributing Busses • Direct power to devices • Circuit protection • In some cases, load shedding Switches • • • • Energize circuit Directly or remotely Remote, contactors, relays or solenoids Higher power items are remotely controlled • Switches themselves are high drain • Knowledge is power Devices/Appliances • • • • • • • Radios, lights, fans etc. High drain items Resistance heat and lights Transmitters Passive receivers In-Flight troubleshooting Transponder, DME or Comm radio Safeties • Circuit breakers/Fuses • Overloads • Alt. control unit/Alt. field current – Most are nuisance trips – Reset and continue – Do not reset 2nd time