POWER DISTRIBUTION FOR THE ATLAS EXPERIMENT
advertisement

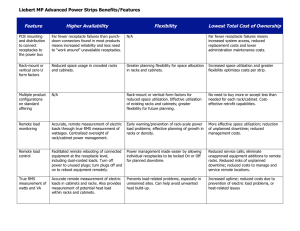
RACK POWER SUPPLY AND CONTROL as proposed by ST-EL. J. Pedersen, ST-EL Presentation,J.C.O.B., 05.06.2002 1 , SUMMARY Introduction Power equipment ALICE and LHC-B. ATLAS and CMS. Control possibilities Cost Conclusion , 2 INTRODUCTION The aim: ST-EL provides a state of the art power supply with adequate monitoring. The experiments can control the power distribution to their racks. The experiments can define trip conditions for the racks through an “External interlock” The experiments can view the status of the power distribution of the racks 3 , POWER DISTRIBUTION EQUIPMENT ALICE and LHC-B. Recuperate existing HAZEMEYER switchboards. Relatively voluminous, cabling through false floor. ATLAS and CMS. Use new “CANALIS” style distribution equipment. An isolated bus-bar system. Very dense construction, thus well suited for installation in areas of limited space. Routed in steel housing, thus very low field emissions. , 4 , , POWER AVAILABILITY Basic assumption: The racks will be fed from the normal supply, i.e. neither diesel nor UPS back up. If a short-break supply ( diesel back-up ) or a no-break supply ( UPS with or without diesel back-up is required, this will come with a price tag attached to it. The experiments should analyse their needs for back-up carefully. , 7 RACK POWER EQUIPMENT Try to avoid single phase switch mode power supplies with simple capacitive input stages. This type of equipment means heavy 3rd harmonic pollution of the power network. It requires de-rating of the power equipment and may require filtering: Increased cost If possible, use three phase or single phase equipment with sinusoidal input current and a power factor close to 1. 8 , CONTROL POSSIBILITIES The control interface equipment between ST-EL and the experiments will be based on a PLC solution. The experiment will be able to command the individual feeders ON/OFF. ST-EL will not retain a command possibility. The experiment will be able to monitor the status of each feeder The experiment will be able to use an external interlock ( A 48 V, potential free contact, normally closed, open on fault ) , 9 COST Cost is incurred by: Re-vamping of the HAZEMEYER equipment Purchase of CANALIS-type equipment Installation and cabling*) work HOW MUCH WILL IT COST? I DO NOT KNOW ! ANYWAY, YOU WILL HAVE TO PAY FOR IT *) ALICE and LHC B mainly , 10 POTENTIAL PROBLEMS Will the equipment work properly in high magnetic fields? Field emission by the power distribution; This is seen as a possible problem by certain people in ATLAS. ST-EL believes that a bus-bar system as described here, can alleviate these fears. 11 , CONCLUSION ST-EL can supply a powering system for the experimental electronics racks that seem to fulfil the requirements of the experiments. ST-EL will have to: Establish an overview of existing HAZEMEYER equipment and cost the re-vamping of it. Launch a call for tenders for “CANALIS” like equipment Estimate installation costs To allow ST-EL to do this in a sensefull way the experiments will have to define their needs, including needs for safe power! 12 ,