Ativity 1, 2, 3
advertisement

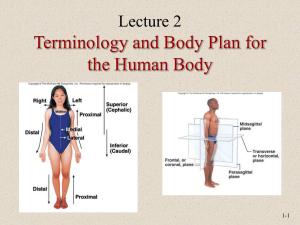
LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1 Credit: Portland Community College Edited 2009 Anatomy • Gross anatomy: the study of body structures visible to the naked eye (without a microscope) • Microscopic anatomy: • Cytology: Analysis of the internal structures of individual cells • Histology: examination of tissues (groups of specialized cells that work together to perform a specific function. 2 Anatomical Position • Anytime you describe structures relative to one another, you must assume this standard position: • Body erect • Feet slightly apart • Palms facing forward • Thumbs point away from body 3 Anterior Landmarks 4 Posterior Landmarks 5 Anatomical Locations • • • • • • • • • • Abdominal: abdominal region Acromial: the point of the shoulder Antebrachial: forearm Antecubital: anterior surface of the elbow Axillary: armpit Brachial: upper arm Buccal: cheek of the face Calcaneal: heel of the foot Carpal: wrist Cephalic: head 6 Anatomical Locations • • • • • • • • • • • Cervical: neck Deltoid: round part of the shoulder Digital: fingers and toes Dorsum: back Femoral: thigh Frontal: forehead Gluteal: buttocks Hallux: big toe Inguinal: groin Lumbar: lower back Mammary: breast 7 Anatomical Locations • • • • • • • • • • Mental: chin Nasal: Nose Occipital: base of the skull Olecranal: elbow Oral: mouth Orbital: bony eye socket Otic: ear Palmar: palm of hand Patellar: Kneecap Pedal: Foot 8 Anatomical Locations • Pelvic: pelvis region • Perineal: area between anus and external genitals • Plantar: sole of foot • Pollex: thumb • Popliteal: behind the knee • Pubic: genital region • Sacral: lower back between the hips • Scapular: shoulder blade • Tarsal: ankle • Thoracic: chest 9 Body Orientation and Direction • These are relative positions • Proximal/distal • Used to describe locations on the arms and legs • GI tract • Medial/lateral • Medial is closer to the midline • Farther away from the midline 10 Body Orientation and Direction • Dorsal: Back • Ventral: Front • Superior or Cephalad is toward the head • Inferior or Caudal is toward the feet • Anterior: most forward • Posterior: toward the backside 11 Planes of the Body 12 Dorsal Body Cavity • Dorsal cavity protects the nervous system • Contains Brain and Spinal Cord 13 Cavities • Thoracic Cavity • Heart & Lungs • Subdivided into the mediastinum and plural cavities • Lower border is the diaphragm • Abdominal Cavity • Stomach, Liver, Intestines • Pelvic Cavity • Reproductive organs Bladder, Rectum 14 Serous Membranes • Serous Membranes have two layers 1. Parietal serosa lines internal body walls 1. Visceral serosa covers the internal organs • Serous fluid separates the serosae 15 Serous Membranes 16 Serous Membranes of the Heart 17 Quadrants • RUQ • Liver • LUQ • Spleen • RLQ • Appendix • LLQ • Sigmoid colon 18 Abdominopelvic Regions 19 Lab Activity 2 Organ Systems Martini Chapter 1, Pages 9-10 Integumentary System • Structures: Skin, hair, sweat and oil glands • Function: • • • • • Forms external body covering Protects deeper tissues from injury Involved in vitamin D synthesis Prevents desiccation, heat loss, and pathogen entry Site of pain and pressure receptors 21 Skeletal System • Structure: 206 bones of the human body • Function: • Protects and supports body organs • Provides a framework that muscles can use to create movement • Hematopoiesis (synthesis of blood cells) • Mineral storage • Bone contains 99% of the body’s store of calcium 22 Muscular System • Structures: The 600+ muscles of the body • Function: • • • • Locomotion Manipulation of the environment Maintaining posture Thermogenesis (generation of heat) 23 Nervous System • Structures: Brain, Spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. • Function: • Fast-acting control system of the body • Monitoring of the internal and external environment and responding (when necessary) by initiating muscular or glandular activity • Information Assessment 24 Endocrine System • Structures: Hormone Secreting Glands • Pituitary, Thyroid, Thymus, Pineal, Parathyroid, Adrenal, Pancreas, Small Intestine, Stomach, Testes, Ovaries, Kidneys, Heart • Functions: • Long-term control system of the body • Regulates growth, reproduction, and nutrient use among other things. 25 Cardiovascular System • Structures: • Heart, Blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries) • Functions: • The heart pumps blood thru the blood vessels. • Blood provides the transport medium for nutrients (glucose, amino acids, lipids), gases (O2, CO2), wastes (urea, creatinine), signaling molecules (hormones), and heat. 26 Lymphatic/Immune System • Structures: • Lymphatic vessels, Lymph nodes, Spleen, Thymus, Red bone marrow • Functions: • Returning “leaked” fluid back to the bloodstream • Disposal of debris • Attacking and resisting foreign invaders (pathogens i.e., disease-causing organisms) • Absorption of fat from the digestive tract 27 Respiratory System • Structures: • Nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs • Functions: • Constantly supply the blood with O2, and remove CO2 • Regulate blood pH 28 Digestive System • Structures: • Oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gallbladder • Functions: • Ingestion and subsequent breakdown of food into absorbable units that will enter the blood for distribution to the body’s cells 29 Urinary System • Structures: • Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra • Functions: • Removal of nitrogenous wastes • Regulation of body’s levels of water, electrolytes, and acidity 30 Reproductive System • Structures: • Male: • Testes, scrotum, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra, prostate gland, seminal vesicles, penis • Female: • Ovary, uterine tube, uterus, cervix, vagina, mammary glands • Functions: • Making Babies 31 The End 32