L1ppt
advertisement

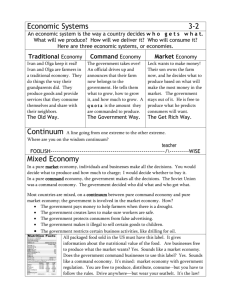
Basics of Economics An Introduction Bell Ringer • There are 14 students, yet I only have ten pieces of candy. • How do I decide who gets a piece? • Hand out candy. • Offer a choice: instead of candy you can have one point extra credit. • But first, depending on your choice, what will you give up? Essential Questions • What is economics? • Why does scarcity and opportunity cost dictate economic choices? • What are the three basic production questions asked in order to deal with scarcity and opportunity cost? • How do different nations answer the three production questions? • Why are the factors of production an important aspect of the three production questions? Economics • Economics is the study of how people, societies, industries, and governments choose to use resources. • Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individual households and firms in making decisions on the allocation of limited resources – Typically, it applies to markets where goods or services are bought and sold. – Microeconomics examines how these decisions and behaviors affect the supply and demand for goods and services, which determines prices, and how prices, in turn, determine the quantity supplied and quantity demanded of goods and services. Economics • Macroeconomics is a branch of economics dealing with the performance, structure, behavior, and decisionmaking of an economy as a whole, rather than individual markets. – This includes national, regional, and global economies. – Macroeconomists study aggregated indicators such as GDP, unemployment rates, and price indices to understand how the whole economy functions. Founding Principles "Economics is the science which studies human behavior as a relationship between given ends and scarce means which have alternative uses." -- Lionel Robbins, An Essay on the Nature and Significance of Economic Science (London: MacMillan, 1932) Scarcity Opportunity Cost • • is the fundamental economic problem of having seemingly unlimited human wants and needs in a world of limited resources – – It states that society has insufficient productive resources to fulfill all human wants and needs. Alternatively, scarcity implies that not all of society's goals can be pursued at the same time; trade-offs are made of one good against others. • • Trade off is when you give up one thing for another. It therefore, heavily impacts how the thr • • the value of the next-highest-valued alternative use of that resource. If, for example, you spend time and money going to a movie, you cannot spend that time at home reading a book, and you cannot spend the money on something else. If your next-best alternative to seeing the movie is reading the book, then the opportunity cost of seeing the movie is the money spent plus the pleasure you forgo by not reading the book. The impact of scarcity and opportunity cost • People and the economy have to make decisions about what to produce and what to buy under the condition of scarcity • Producers make what they think consumers will buy so the resources they use and the price associated with them are determined by the perceived profit that can be made • Consumers have to decide between wants and needs in order to determine what to spend their limited resources on. – Wants: things they are not necessarily to sustain life – Needs: things necessary to life; i.e. food, shelter, water. In a PURE MARKET ECONOMY there is no government involvement in economic decisions. The government lets the market answer the three basic economic questions: 1. What will be produced? Consumers decide what should be produced in a market economy through the purchases they make. 2. How will it be produced? Production is left entirely up to businesses. Businesses must be competitive in such an economy and produce quality products at lower prices than their competitors. 3. For whom to produce? In a market economy, the people who have more money are able to buy more goods and services. Capitalism features private ownership of businesses and marketplace competition. It is the same as a free enterprise system ,laissez faire, and market economy The political system most frequently associated with capitalism is democracy. The Four Factors of Production • • • • Land, labor, capital & entrepreneurship Used to answer the basic economic questions Are the resources (essential ingredients) of economic activity Goal of economic activity = productivity o Amount of goods & services the economy creates o Depends on how producers combine the 4 factors Four Factors Capital • • • Has a few meanings Entrepreneurship • Financial capital • An investment resource used in production o Invests in new businesses or expands already existing businesses Capital goods: o o Products that can be used in the production of different products but that are not part of the new product Examples: machinery, buildings, stocks of raw materials • • Human resource that brings land, labor, and capital together by starting, operating, and expanding businesses Create productivity through their enterprise Operate businesses to make a profit o Reward for the economic risk of entrepreneurs Four Factors Land • • • An economic resource as property Landowners earn money from property through: o o o Charging Rent Leasing Selling Land adds natural resources to production o o •• • • Labor Renewable Resources: trees Nonrenewable Resources: minerals, fossil fuels Provided by workers Also known as human capital o A person’s potential for economic productivity Some potential comes naturally: o o Talent for drawing Being good at math What helps develop human capital? o o o Education Training Good Habits of Character Productivity •• •• •• • • Economies strive to achieve maximum productivity Definition: the relationship between the 4 factors that go into production & the goods and services that come out of production Increases to the extent that input creates more output In general a society’s degree of productivity determines its average standard of living The level of wealth, comfort, material goods and necessities available to a certain socioeconomic class in a certain geographic area. Increased by the efficient use of production An economy is efficient when the cost of producing a given good or service is as low as possible and equal to its price In an efficient economy, resources are used in ways that maximize their intended values Actions that make the economy more efficient increase its overall wealth • In a PURE COMMAND ECONOMY there is complete government involvement in economic decisions. The government answers the three basic economic questions: 1. What? In a command economy, government officials decide what will be produced and in what amount. 2. How? Production is left entirely up to the government. The government owns the means of production. Businesses and property belong to the government. 3. For whom? In a command economy, the government decides for whom to produce without considering market demand. A command economy is designed to keep a few people from becoming rich while the rest of society struggles or winds up in poverty. Communism is a pure command economy. •In this system, land, property, and businesses are in the hands of the government. •The state owns the factors of production, and government officials decide the answers to the basic economic questions. Economic Systems • There are no PURE market economies. • There are no PURE command economies. Mixed Economies Nearly all modern world economies have characteristics of both market and command economic system. They are called mixed economies. Mixed Economy Mixed economies are not totally command or totally market. They have elements of both. However, some mixed economies lean more towards free markets and some tend to lean more toward command structures. Mixed Economy The United States is not totally a market economy. It is a mixed economy. Example 1: The economy of the United States is based on private enterprise. However, some industries (for example, power companies and railroads in some areas) are under collective ownership. Example 2: The United States government is involved in the economy through laws and regulations governing businesses, and it provides socialistic programs, such as welfare, Medicaid, and Medicare. Example 3: The government monitors how stocks are traded, outlaws monopolies, and will intervene if inflation gets out of control. HOWEVER, the United States government tries to let the market operate as freely as possible. Mixed Economy China is not a totally command economy It is a mixed economy. It places strict controls on its economy, and many of the larger industries are owned by the state. In recent years, though, China’s desire to compete economically in the world has led it to allow some private ownership and business. It is possible to look at economic systems along a continuum. Typically, the continuum runs from a Pure Command Economy to a Pure Market Economy. On a continuum, from Pure Command Economy to Pure Market Economy, economic freedom runs from none to total. On notebook paper, draw and label this continuum. 1. Place the economy of the United States on your continuum. 2. Place the economy of Cuba on your continuum. 3. Place the economy of the People’s Republic of China on your continuum. •On this continuum, the economy of the United States would be placed closer to the right-hand side of the line than the left-hand side. •China would be placed much closer to the left-hand side of the scale. •Cuba would be placed closer to China than the United States. (Of course, the placements on the continuum could change if political or economic changes are made in these countries.) As you can see, when studying different economic systems, it is good to view them on a continuum. Quick review: On this continuum where would you place the China? Cuba? Where do you think you should place Mexico? Task: In a well-written paragraph, explain why the United States economy is placed where it is placed on this continuum. Why the United States is placed where it is on this continuum? The economy of the United States is not a pure market but instead is a mixed economy leaning toward market. The United States has some market elements in the economy. The United States also has some elements of a traditional economic system . For example, goods are often exchanged or bartered at a flea market. The United States also has some command elements. For example, the U. S. government controls the production of some goods (like nuclear weapons) or decides who will get some goods (such as food stamps). Traditional • A traditional economy is defined by three characteristics – It is based on agriculture, fishing, hunting, gathering or some combination of the above. – It is guided by traditions. – It may use barter instead of money • Typically located in third world nations that are considered to have emerging economies • All economies are thought to have evolved from traditional roots • Is not usually placed on a continuum Application • Think of a resource that is scarce in your personal life: it could be a tangible or intangible resource – Why is it scarce? – How do you determine its utilization? – What is the opportunity cost associated with this above decision? Application • Go to http://www.heritage.org/index/country/brazil • Determine the type of economy for the following nations: – Brazil – Hong Kong – Venezuela – Estonia • For each provide evidence for your answer. • Finally, place each on a market continuum.