Foundations of Economics
advertisement

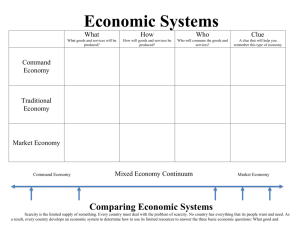
Economics 101 Strand 5: Concept 1: PO 1-4 Mr. Mosqueda Wants & Choices Economics is the study of CHOICES (as they pertain to PRODUCERS, CONSUMERS and the GOVERNMENT) Everybody wants different things Clothing, food, shelter, etc Wants change over time (toys, etc) Depends on society, cultures, climate, interests, etc… Wants can be long or short term Willy Wonka: I Want It Now! VIDEO CLIP Productive Resources The price/cost of the items we want depend on three factors: Factors of production LAND (Resources from the Earth, unaltered by man) LABOR (People’s effort, skills and knowledge) CAPITAL (Man-made resources used over and over– eg., computers, machines, etc. Production to Consumption The GOODS and SERVICES produced are then sent to the consumers to be: BARTERED without money PURCHASED with money (savings) (This is called consumption) The Consumption Problem Productive resources (land, labor and capital) and goods and services are limited Human wants and needs are unlimited Resulting in SCARCITY Making Choices There are never enough resources to produce all the goods and services people want (SCARCITY) As a result, people must make CHOICES about what want they want to satisfy Making Choices Because things are scarce, buyers (consumers) and sellers (producers) have to make ECONOMIC CHOICES (resulting in OPPORTUNITY COSTS) Costs (what you have to give up in order to get what you want, eg. Money, time, etc.) OPPORTUNITY COST: the highest valued benefit given up when a choice is made If the opportunity cost is worth it, then you should consume it! What does it mean to study Economics? Based on consumer choice and opportunity costs, economists must answer three basic questions: WHAT goods and services will be produced? HOW will the goods and services be produced TO WHOM will the goods and services be distributed? The Study of Economics By answering these questions most efficiently creates the need for SPECIALIZATION and INTERDEPEDENCE resulting in trade Economics: DECSISION-MAKING under SCARCITY Independent Practice Answer Questions 2-6 on page 357, use Chapter 13, Section 1 (PP 349-357) for help if needed. What you don’t finish in class, will be HOMEWORK! Types of Economies People do not make economic decisions all by themselves Communities working together to produce, distribute and consume products is called an ECONOMY There are 3 types of economies Traditional, Market and Demand Traditional Economies Traditional economies rely on people working together to help the whole community EX: Ancient tribes of hunters, families, etc. All men hunting to “produce” enough food for the entire tribe, all resources are shared by the entire community Pure traditional economies are rare today Command Economies Government owns and controls the factors of production and makes economic decisions for the entire community Government decides what people “need” or “want” and distributes it to the people Socialism (USSR), North Korea, China, Kings Market Economy Opposite of a Command Economy Private individuals produce factors of production and are free to make their own choices about production, distribution and consumption Relies on competition to produce high quality at low prices (Walmart, Target, etc) People are free to do as they wish in order to make money Very little government control Also known as Free Enterprise or Capitalism Entrepreneurs create and run companies and small businesses USA Market Economy Disadvantages Benefits 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Makes people rich Competition produces high quality at low costs Encourages creativity More choices for consumers Encourages hard work 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. People can take advantage of system Greedy Can easily get out of control Rich get richer, poor get poorer Government may have a difficult time intervening if necessary Market Economy Adam Smith Father of Capitalism Book: The Wealth of Nations Absentminded Frequently walked into things Horrible cook Sleepwalker/Daydreamer Had prolonged conversations with himself Independent Practice Answer Questions 2-5 on page 369, use Chapter 13, Section 2 (PP 363-369) for help if needed. What you don’t finish in class, will be HOMEWORK!