Quiz 1 answers
advertisement

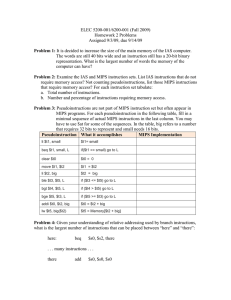
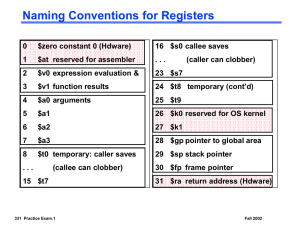
1. a) b) Given the importance of registers, what is the rate of increase in the number of registers in a chip over time? Very fast: They increase as fast as Moore’s law Very slow: They only increase as the instruction set changes Ans: (b) • Moore’s law projects the doubling of transistors every couple of years and has nothing to do with registers. • The number of registers will change only if instruction set architecture is changed. Because machine code has only 5 bits to represent each register, so it would require a substantial change (a new ISA) 2. Define the R-format instruction: a) b) c) d) e) What are the various fields? What is the basic lay-out? What does each field represent? Are all of the bits used / needed for each field? Given an example of an R-format instruction in MIPS assembler and the corresponding machine code Fields • • • • • Example: Op-code: operation code add r1, r2, r0 Rs, Rt: source registers 000000 00010 00000 00001 00000 100000 Rd: destination register SA: shift amount Funct-code: function specifier 3. Define the I-format instruction: a) b) c) d) e) What are the various fields? What is the basic lay-out? What does each field represent? Why this instruction format needed as opposed to the Rformat? Give an example of an I-format instruction in MIPS assembler and the corresponding machine code Fields • • • • Op-code: operation code Rs: source register Rt: destination register Immediate: 2’s complement constant Example: addi r1, r2, 1 001000 00010 00001 0000000000000001 4. What is the range of addresses for conditional branches in the MIPS ISA? PC 4 4 2 address PC 4 4 (2 1) 15 15 5. Answer the following questions as true or false: a) The beq instruction always modifies the program counter register b) The add instruction does not modify the PC c) The jal instruction always modifies the PC d) The instruction beq r1,r2,1 will advance the PC by one byte if [r1]=[r2] e) The instruction beq r1,r2,1 will advance the PC by one word if [r1]=[r2] Ans: • T. PC = PC+4 even if r1 <> r2 • F. PC = PC+4 • T. Unconditional branch • F. PC = PC+4 + 4 x 1 • F. PC = PC+4 + 4 x 1 6. Find the shortest sequence of core MIPS instruction to determine the absolute value of a two’s complement integer. Please the result into r3. There are several possible answers to this question. However, in general, all involve the following two steps: 1. 2. Convert the number to a positive value if it is negative, which can be done by multiplication, xor, nor, etc… Move the value to r3 7. Write out the truth table, the logic equation and draw the gates for the Sum bit of a 1-bit adder Cin Sum Sum bit is 1 if an odd number of the three inputs 1 →XOR the three inputs a Cout b half adder