Population - WordPress.com
advertisement

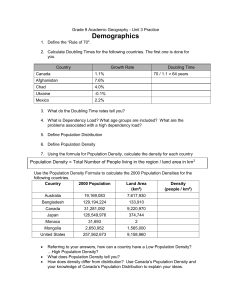
Population Population Biology and Human Population Essential Question: How many people can sustainably live on Earth? Objectives Students will: • Apply the power of exponential growth to population problems • Perform calculations involving doubling of populations (rule of 70) • Draw a J and S curve and explain the difference between them • Describe environmental resistance and discuss how it can lead to logistic growth Objectives, continued • Define and calculate: fertility rate, birth rate, life expectancy, death rate, population density, and survivorship • Compare and contrast density-dependent and density independent events • Explain the results of habitat fragmentation • Explain how genetic drift, founder effect, and bottleneck effect impact populations Dynamics • Exponential growth: Unlimited resources and lack of predators results in unrestricted increase in a population size • Biotic potential of a population is growth that would occur in absence of interfering factors • Such organisms are generalists: quantity of individuals ensures survival of some Classic J-curve World Population Doubling Time Change First doubling: 1 – 2 billion Second doubling: 2 – 4 billion Third doubling: 2.5 – 5 billion Fourth doubling: 3 – 6 billion What is happening to doubling time? _________ years _________ years _________ years _________ years Population doubling • Exponential growth results in doubling of the population. • Example: The human population doubled from 2.5 billion to 5 billion between 1950 and 1990 – 40 years • 70 ÷ r = Doubling time, where r is the percentage growth rate. This is called the RULE OF 70. (It comes from the natural log of 2, which is .70) • Apply the rule: If the world population doubled in 40 years, what was the growth rate between 1950-1990? • Use: Doubling time is used by countries to predict the need for resources and infrastructure and to aid in planning. Limits • Carrying capacity – maximum number of individuals an ecosystem can support • Some species naturally limit their population growth when resources are limited • Logistic growth curve – appears as an S, illustrates population size limited by resource availability • Other species experience oscillating cycles of growth and decline J-curve Oscillation curves Predator and prey populations often oscillate. Think about it. Host and parasite populations oscillate in a similar manner. Be familiar with this concept. Overshoot / Crash Some species overreproduce which can lead to a population crash – case study St. Matthew Island Reproductive Strategies r and K strategists - K strategists - r strategists Factors that change population • Nutrition, climate, soil, water are required • Fecundity: the ability to reproduce • Natality: production of new individuals • Total Fertility Rate: measure of offspring produced in an average female’s life time • Crude Birth Rate: number of births / thousand individuals • Life expectancy: the number of years an individual is expected to live • Life span: the longest period of time an organism reaches Factors that change population • Population density: number of individuals per square mile or kilometer • Mortality rate: death rate of a population • Crude Death Rate: number of deaths / thousand • Immigration: population growth by individuals coming in • Emigration: population decrease by individuals exiting • Migration: movement of populations • Replacement Rate: the number of offspring required for a couple to replace themselves (accounts for deaths) Factors that regulate population DENSITY INDEPENDENT • Abiotic factors • Natural disasters, weather, climate change over time DENSITY DEPENDENT • Biotic factors • Predator-prey, territoriality • Stress, crowding, disease Conservation Biology • What is Conservation Biology? A multidisciplinary science that has developed to address the loss of biological diversity. • Why should we be concerned about conserving biodiversity? For the first time in Earth’s history, a single species, Homo sapiens, could cause a mass extinction. The main cause of loss of biodiversity is loss of habitat caused by human activities. • What is Phytoremediation? The use of plants and soil bacteria to reduce the concentrations of toxic chemical compounds in the environment. Phytoremediation is widely accepted as a costeffective environmental restoration technology. • Is it possible to restore rainforests? • How to save endangered species Demographic transition • Theory of growth and change in population and its characteristics as a result of industrialization • 4 distinct phases • Modeled with a graph in which you can see the following three changes over time: • birth rate • death rate • actual population Demographic transition graph Population on the Y axis, Time on the X axis. Phase analysis • Why are birth and death rates high in Phase I (Preindustrial)? • Why does death rate plummet in Phase II (Early Transitional)? • Why does birth rate begin to decrease in Phase III (Transitional)? • Why does the population remain high in Phase IV (Industrial) when birth and death rates are low? • Is there a Phase V? What might it look like? Phase analysis 1 Thanksgiving Population Project Research one country’s demographics and report on: 1. Population 2. Birth rate 3. Death rate 13. State the 4. Infant mortality rate Demographic Transition 5. Life expectancy 6. Growth rate 2013 / 1995 Phase your country is in. 7. Education levels 14. Cite evidence to 8. Primary Industries (1-3) support your assertion. 9. Employment levels 10. Income per capita 11. Government Type 12. Key current events (1-3) Rubric • Information: concise, up to date, accurate, complete • Illustrations: demographic transition, population age structure diagram, photos showing life in your country • Audience: Presentation is professional, interesting, compelling…. makes audience want to write an award-winning screenplay with this country as a setting…. (or visit, or join the Peace Corps) Logistics • FORMAT? • Add a page to APESlahs2013.wordpress.com • Poster • Power point • Where to get info? • http://populationpyramid.net/ • https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-worldfactbook/ • How many students per presentation? Due date: Monday, December 2 Email or text me with questions Thanksgiving HW • Define all terms in this ppt • Population Math Problems B 1-5 • Read and summarize 3 articles on Conservation Biology • Population Project • Meet Wednesday, November 27 from 10-noon Resources • http://www.worldometers.info/world-population/ • http://www.census.gov/popclock/ • http://worldof7billion.org/ • http://www.worldof7billion.org/index.php/student _video_contest • http://populationpyramid.net/ • https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/theworld-factbook/