Lecture-7(Topology)
advertisement

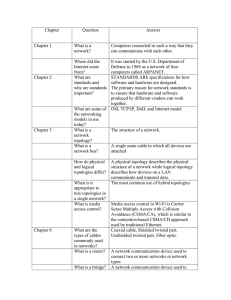
TOPOLOGY: Network Topology Defines how various computers or nodes they are connected to each other or It is the physical arrangement of links in the networks or The topology of a network is defined as the geometric representation of the relationship of all the links and linking devices to one another, is called as topology. TYPES OF TOPOLOGY: According to the geometric representation of relationship the topologies are categorized into 6 types these are follows Mesh Topology Star Topology Tree Topology Ring Topology Bus Topology Hybrid Topology MESH TOPOLOGY: In mesh topology, every device has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other device i.e Each node is connected to every other node by direct links. In a fully connected mesh topology contains n devices then it has n(n-1)/2 physical channels and (n-1) input/output ports Advantages: Carries own data. Robust(if one link becomes unusable. it does not effect the whole system) Security and Privacy Point to point links make fault identification easy. Disadvantage: More number of Input ports required Installation & reconfiguration are difficult. STAR TOPOLOGY: In star topology each device has a dedicated point-to-point link to a central controller called hub. so the devices are not directly linked to one another. Controller act as likes an exchange Advantage: Cheaper then mesh Easier to Install ,maintain and reconfigure Robust Requires less cable Easy fault identification Disadvantage: If hub goes down, then the entire Network becomes defunct ion. BUS TOPOLOGY: A bus topology uses multipoint philosophy. Along cable called bus acts as backbone to all nodes. All nodes on the bus topology have equal access to the trunk. This is accomplished using short drop cables or direct T-connectors or Nodes are connected to bus cable by drop lines & taps Drop line: connection running between device & main cable Tap :it is a connect or that connects node with metallic core of bus via drop line Systems connect to this backbone using T connectors or taps As signal transverse across the bus ,some of the energy convert ed into heat energy,thus weakening of signals Therefore this topology cannot be used for very large no of computers Advantage: Cheap and easy to implement. Less number of cables required Easy to extend a network by adding cable with a repeater and allows it to travel a longer distance. Disadvantages: A break in the cable will prevent all systems from accessing the network. Network disruption when computers are added or removed RING TOPOLOGY: In ring topology each system connected to its adjacent neighbours A signal is passed along the ring in one direction, from device to device, until it reaches its destination. If a node wants to send something to distant node then it goes through some intermediate nodes. Which acts like repeaters reproducing the incoming bits stream with full signal on outgoing lines. Advantage: if a node not receiving signal for a long time it can issue an alaram. Easy to reconfigure and install. Disadvantages: a single break in the cable can disrupt the entire network traffic is only in one direction Dual-ring Network Topology : The type of Network Topology in which each of the nodes of the network is connected to two other nodes in the network, with two connections to each of these nodes, and with the first and last nodes being connected to each other with two connections, forming a double ring. The data flows in opposite directions around the two rings, although, generally, only one of the rings carries data during normal operation, and the two rings are independent unless there is a failure or break in one of the rings. Advantages : Very orderly network where every device has access to the token and the opportunity to transmit Performs better than a star topology under heavy network load Disadvantages : Moves, adds and changes of devices can affect the network Much slower than an bus network under normal load. HYBRID TOPOLOGY: This topology is the combination of different topologies. In this case bus,star and ring topologies are used to create hybrid topology. Advantage: Workgroup efficiency and traffic can be customized. Combine the benefits of several different types of topologies. Disadvantages: Device on one topology cannot be places into another topology with out some hard ware changes. TREE TOPOLOGY(hierarchical): In this topology not every device plugs directly to central hub. Majority of device are conneted to secondary hub that in turn conneted to central hub. Here two types of hub is used one is central hub is called active hub. It contains repeaters which regenerates the received bit pattern before sending them out. But another hub is called passive hub which provides simple physical connection between attached devices. Advantage: It allows more devices to be attached to single hub and can therefore increase the signal can travel between devices. Point-to-point wiring for individual segments Disadvantage: If the active hub fails then the networks goes down. More difficult to configure and wire than other topologies