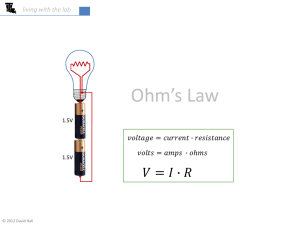
B. the unit of electric charge
advertisement

UNIT 3 ELECTRICITY (CHAPTERS 7-9) Complete the follow questions There are quizzes provided towards the end of the booklet Name: Goal • Review your understanding of the laws of static charge. 1 What to Do Complete the following sentences using the following terms. Each term may be used more than once. attracts, repels, positive, neutral, negative 1. 2. 3. 4. A negative charged is repelled by a _______________________ charge. A positive charge ______________________a negative charge. A charged object ______________________a neutral object. A negative object attracts an unknown object. The unknown object could be _____________________ or ________________________. 5. A positive object ________________________ a positive object. Use the diagram below to answer question 6. 6. A positively charged object is attached to a table as shown. Use an arrow to indicate the direction of the force on the negative (), positive (+), and neutral (no sign) charges placed near the object on the table. 7. Use the words “increased” or “decreased” to complete each of the following statements. (a) To increase the electric force between two charged objects, the distance separating the two charges should be ________________________. (b) To increase the electric force between two charged objects, the amount of charge on one or both objects should be ________________________. (c) To decrease the electric force between two charged objects, the distance separating the two charges should be ________________________. (d) To decrease the electric force between two charged objects, the amount of charge on one or both objects should be ________________________. Goal • Represent charging by induction and charging by conduction. 2 What to Do Answer the following questions. 1. In terms of the movement of charge, what is the difference between charging by induction and charging by conduction? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 2. The following diagram of a charged rod and a neutral solid object can help you answer questions 2–3. Use () to represent negative charges and (+) to represent positive charges. 3. Identify which of the diagrams in question 2 shows charging by: conduction _____________________induction ________________________ 3 Goal • Represent charging by induction and charging by conduction. What to Do Answer the following questions. 1. In terms of the movement of charge, what is the difference between charging by induction and charging by conduction? _____________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 2. The following diagram of a charged rod and a neutral solid object can help you answer questions 2–3. Use () to represent negative charges and (+) to represent positive charges. 3. Identify which of the diagrams in question 2 shows charging by: conduction _____________________induction ________________________ 4 Goal • Practise drawing circuit diagrams. What to Do For each of the following circuit illustrations, draw its corresponding circuit diagram and answer the questions that follow. 1. Circuit A 2. Circuit B 3. Circuit C 1. Circuit diagram 2. Circuit diagram 3. Circuit diagram 1. (a) Is this circuit open or 2. (a) Is this circuit open or closed? __________ closed? __________ (b) If this is a closed (b) If this is a closed circuit, what is the circuit, what is the source of the potential source of the difference? _________ potential difference? What is the load? _________ What is _______________ the load? _________________ 5 3. (a) Is this circuit open or closed? __________ (b) If this is a closed circuit, what is the source of the potential difference? _________ What is the load? _________________ Goal • Practise calculating current. What to Do Calculate the current in each of the following circuit diagrams. The current at the source is represented by Is 1. I2 = ______ 2. I3 = ______ 3. I5 = ______ ______ I3 = ______ I5 = ______ 6 Goal • Practise potential difference calculations. What to Do Calculate the missing potential difference in each of the following circuit diagrams. The voltage at the source is represented by Vs [Vs] Diagrams 1. V1 = ______ 2. VS = ______ 3. V1 = ______ 7 Goal • Review your understanding of how to use Ohm’s law. What to Do Answer the following questions. 1. What is the resistance of a toaster if a current of 12.5 A flows through it when it is connected to 120 V? __________________________________________________ 2. A light bulb has a resistance of 90 What current flows through the bulb when it is connected to 120 V? __________________________________________________ 3. A current of 0.50 A flows through a light bulb that has a resistance of 18 What is the voltage across this light bulb? __________________________________________________ 4. A flashlight bulb has a resistance of 4.0 What current passes through the bulb if it is connected to 3.0 V? __________________________________________________ 5. What potential difference is necessary to produce a current of 0.60 A in a load that has a resistance of 25 __________________________________________________ 6. The current through a load in a circuit is 2.5 A. If the potential difference across the load is 75 V, what is the resistance of the load? __________________________________________________ 7. (a) An 80 V potential difference is measured across a light bulb that has a resistance of 16 What is the current through this light bulb? __________________________________________________ (b) If the light bulb was replaced by a bulb with twice the resistance, what would be the new current through the bulb? __________________________________________________ 8. A 25 mA current flows through a 300 lamp. What is the voltage across the lamp? __________________________________________________ 8 Goal • Practise using the resistor colour code. What to Do Use the resistor colour code table to answer the following questions. Colour black brown red 0 1 2 Numeric value orange yellow green blue 3 4 5 6 violet grey 7 8 white 9 1. Give the value of each resistor indicated by the colour bands. 1st band colour 2nd band colour 3rd band colour (a) blue green red (b) violet black yellow (c) green blue brown (d) brown red black (e) grey violet orange (f) red brown red Resistor Value () 2. A current of 0.20 A flows through a resistor when connected to a 46 V power supply. (a) What is the value of this resistor? ________________________________________________________ (b) What are the first three bands of colour on this resistor? __________________________________________________________________ 3. A current of 2.5 mA flows through a resistor when connected to a 16 V power supply. (a) What is the value of this resistor? _______________________________________________ (b) What are the first three bands of colour on this resistor? _____________________________________________________________________ 9 Goal • Review your understanding of series circuits. What to Do Circle the best term in the parentheses to correctly complete each statement. 1. A series circuit has (more than one, only one) path for current to travel. 2. In a series circuit, the current at one location in the circuit is (equal to, different from) the current at another location in the circuit. 3. If two different resistors are connected in series, the voltage across one resistor will be (equal to, different from) the voltage across the second resistor. 4. By adding a resistor in series with an original resistor, the total resistance of the circuit (increases, decreases). 5. The sum of the voltages across each of the resistors in a series circuit is (equal to, different from) the voltage supplied by the battery. Find the unknown voltage at V, and current at A, in each of the following circuits. 6. Voltage = _________ Current = _________ 7. Voltage = _________ Current = _________ 10 Goal • Review your understanding of parallel circuits. What to Do Circle the best term in the parentheses to correctly complete each statement. 1. A parallel circuit has (only one, more than one) path for current to travel. 2. Two different resistors are connected in parallel. The current through one of the resistors will be (equal to, different from) the current through the other resistor. 3. If two different resistors are connected in parallel, the voltage across one resistor will be (equal to, different from) the voltage across the second resistor. 4. By adding a resistor in parallel with an original resistor, the total resistance of the circuit (increases, decreases). 5. The total current entering the junction of a parallel circuit must be (equal to, different from) the sum of the currents through each branch of the parallel circuit. Find the unknown voltage at V, and current at A, in each of the following circuits. 6. Voltage = _________ Current = _________ 7. Voltage = _________ Current = _________ 11 Goal • Draw labelled circuit diagrams. What to Do Use information from Chapter 9 to help you draw the circuit diagrams described below. Be sure to use the proper circuit symbols, and label your drawings. Description Diagram 1. Draw a circuit diagram consisting of a 9.0 V battery, an ammeter, and a 25 resistor in series. Include a voltmeter that is measuring the potential difference across the resistor. 1. 2. Draw a circuit diagram consisting of a battery made up of two 1.5 V cells, one closed switch, two lamps, and an ammeter in series. Show the direction in which the current flows. 2. 3. Draw a circuit diagram consisting of a battery made up of four 1.5 V cells, one closed switch, one lamp, two 0.50 resistors in series, and a voltmeter. Show the direction in which the current flows. 3. 12 Goal • Practise interpreting circuit diagrams. What to Do 1. Describe what will happen in the circuit shown above if… (a) the switch is closed ___________________________________________________________ (b) the switch is closed and the first bulb is removed __________________________________ (c) the switch is closed and the fifth bulb is removed __________________________________ 2. Calculate the missing quantities for the circuit below. 3. Calculate the missing quantities for the circuit below. 13 Goal • Calculate electrical power and energy. What to Do Answer the following questions. Show all your work. 1. A current of 5.0 A flows through a flashlight bulb when it is connected to 6.0 V. What is the power of this bulb? ___________________________________________________________________ 2. A 600 W electric heater is connected to a 120 V source. What current flows through the heater? ___________________________________________________________________ 3. A 2.5 A current flows through a 100 W lamp. What is the voltage across the lamp? ___________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the current through a 6.0 W light bulb when it is connected to a 1.5 V battery? ___________________________________________________________________ 5. (a) A 40 W light bulb is connected to a power supply and draws a current of 0.75 A. What is the voltage of the power supply? _________________________________________________________________ (b) If the 40 W light bulb is replaced by a 100 W light bulb, how much current will flow through the 100 W bulb? ________________________________________________________________ 6. What is the power, in watts, of an unknown device if a current of 35 mA flows through the device when it is connected to 3.0 V? ___________________________________________________________________ 7. How much energy, in joules, is consumed by a 120 W light bulb if it is left on for 15 min? ___________________________________________________________________ 8. How much energy, in joules, is consumed by a 1400 W hair dryer if it is used for 10 min? ___________________________________________________________________ 9. How much energy, in joules, is consumed by a 200 W stereo if it is left on for 4.0 h? __________________________________________________________________ 14 Goal • Practise calculating the cost of energy. What to Do Answer the questions below. Show all your work. 1. A meter reader determines that a business has used 3550 kW h of energy in two months. If electricity costs 10¢ per kW h, calculate the bill. 3. A 730 W toaster and 1200 W electric frying pan are plugged into the same 100 V outlet. How much will it cost to operate the two appliances at 8¢ per kW h if they are used for 20 h? 15 2. An electric heater draws 1100 W of power. Electricity costs 8¢ per kW h. How much does it cost to operate the heater 3.0 h a day for 30 days? 4. A toaster is used an average of 5.0 h a month. The toaster draws 8.0 A of current from a 110 V outlet. If electricity costs 8¢ per kW h, how much will it cost to operate the toaster for one year? Goal • Check your understanding of Chapter 7. What to Do Circle the letter of the best answer. 1. Static electricity refers to charges that A. travel through a conductor B. exist on a neutral object C. can be collected and held in one place D. power your computer 2. Which of the following correctly identifies the charges on the particles of an atom? Proton Electron Neutron A. positive neutral negative B. negative positive neutral C. neutral negative positive D. positive negative neutral 3. Which of the following statements describes a solid neutral object becoming positively charged? A. Protons have been removed from this object. B. Electrons have been removed from this object. C. Protons have been added to this object. D. Electrons have been added to this object. 4. A object that contains 5 million electrons can still be neutral because A. electrons have no charge B. the electrons are spread out evenly in the object C. it also contains 5 million protons D. the object is an insulator 5. Static charge can apply a force without touching the other object. This type of force is called A. action-at-a-distance force B. long distance force C. contact force D. imaginary force 16 6. Which of the following is true of charged objects? A. Like charges attract and opposite charges repel. B. Like charges repel and neutral objects are repelled by charged objects. C. Like charges repel and opposite charges attract. D. Like charges attract and neutral objects are attracted to charged objects. 7. Which of the following would increase the force between two charged objects? A. increasing the distance between the objects B. increasing the charge on the objects C. decreasing the charge on the objects D. none of the above 8. Which of the following best describes a neutral solid object that is charged by conduction? A. The electrons in the neutral solid object relocate when a charged object is brought near. B. The protons in the neutral solid object relocate when a charged object is brought near. C. The electrons in the neutral object transfer onto a positively charged object. D. The protons in the neutral object transfer onto a negatively charged object. 9. Which of the following best describes a neutral solid object that is charged by induction? A. The electrons in the neutral solid object relocate when a charged object is brought near. B. The protons in the neutral solid object relocate when a charged object is brought near. C. The electrons in the neutral object transfer onto a positively charged object. D. The protons in the neutral object transfer onto a negatively charged object. 10. An electroscope that is charged positive would have its metal leaves separated. A negatively charged rod is brought close to, but not touching the knob of the positive electroscope. The metal leaves would A. move farther apart B. move closer together C. not move D. become negatively charged 17 Match the Term on the left with the best Descriptor on the right. Each Descriptor may be used only once. Term _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 11.electroscope 12.Van de Graaff generator 13.acetate 14.conductor 15.grounding 16.coulomb Descriptor A. materials that allow electrons to travel freely B. the unit of electric charge C. device used to produce large amounts of static charge D. allowing charge to flow into Earth’s surface E. materials that do not allow electrons to travel freely F. device used to detect static charge G. acquires a negative charge by friction Short Answer Questions 17. Two charged objects are positioned 5 cm away from each other. Describe the change in the force between these two objects when (a) the charge on one of the objects is increased (b) the distance between the objects is increased to 10 cm (c) the charge on both of the objects is decreased Use the following diagram of a neutral solid object to answer question 18. 18. Use () to represent electrons and (+) to represent protons to complete the diagrams. (a) A positive rod is positioned near the original object. (b) A positive rod is touched to the original object. 18 Goal • Check your understanding of Chapter 8. What to Do Circle the letter of the best answer. 1. The amount of electric energy stored in charge depends on which two factors? A. current, amount of voltage B. current, amount of resistance C. voltage, amount of charge D. voltage, amount of resistance 2. Which combination of materials could be used to produce the best electrochemical cell? A. two silver electrodes and an acidic solution B. an aluminum electrode, a copper electrode, and an acidic solution C. two silver electrodes and water D. an aluminum electrode, a copper electrode, and water 3. Which of the following is not a common energy source used to produce electrical energy? A. friction B. thermocouples C. piezoelectric crystals D. elastic 4. Which of the following is not an electric load? A. battery B. light bulb C. resistor D. buzzer 5. Which statement correctly defines the difference between static electricity and current electricity? A. Static electricity is the flow of positive charge, whereas current electricity is the flow of negative charge. B. Static electricity is the flow of charge in a circuit, whereas in current electricity the charge stays in one place. C. Static electricity is the flow of negative charge, whereas current electricity is the flow of positive charge. D. In static electricity, the charge stays in one place, whereas current electricity is the flow of charge in a circuit. 6. Conventional current is defined as A. the flow of charge from positive to negative B. the flow of charge from negative to positive C. the flow of electrons D. the current caused by sources other than batteries 19 7. An electric device that slows down current and changes electrical energy into other forms is called a A. battery B. conductor C. resistor D. switch Use the resistor colour coding chart to answer-question 8. Colour Numeric value black brown red orange yellow green blue violet grey white 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 8. Calculate the resistance of a resistor with the following three bands of colours: blue, yellow, red. A. 4600 B. 64 200 C. 6400 D. 642 9. What is the purpose of an ohmmeter? A. to measure current B. to measure voltage C. to measure resistance D. to measure charge 10. A current of 2.0 A flows through a 12 resistor. What is the voltage across this resistor? A. 2. 0 V B. 6.0 V C. 12 V D. 24 V 20 Match the Term on the left with the best Descriptor on the right. Each Descriptor may be used only once. Term _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 11.voltmeter 12.ammeter 13.current 14.voltage 15.resistance 16.circuit Descriptor A. amount of charge passing a given point per second B. device used to measure current. C. a complete path for current to travel D. device used to measure potential difference E. slows down the movement of charge F. the flow of positive charge G. amount of electric potential energy per unit of charge. Short Answer Questions 17. Draw a circuit diagram for the following circuit. 18. Calculate the following using Ohm’s law. (a) A light bulb is connected to a 9.0 V battery. The current through the light bulb is measured to be 300 mA. What is the resistance of the light bulb? _______________________________________________________________ (b) A 16 V source is connected to a 2.5 k load. What is the current through this load? Give your answer in both amperes (A) and milliamperes (mA). _______________________________________________________________ 19. You are given a load of an unknown resistance. Describe how you would determine this load’s resistance using a battery, voltmeter, ammeter, and connecting wires. ___________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 21 Goal • Check your understanding of Chapter 9. What to Do Circle the letter of the best answer. 1. Two identical resistors are connected in series to a battery. How does the current through the second resistor compare to the current through the first resistor? A. half the current B. twice the current C. the same current D. no current 2. Two identical resistors are connected in parallel to a battery. How does the voltage across the second resistor compare to the voltage across the first resistor? A. half the voltage B. twice the voltage C. the same voltage D. half the voltage of the battery 3. A load is connected to a battery. If a second identical load is added in series to the first, what happens to the total resistance of the circuit and the current leaving the battery? A. Total resistance increases and the current increases. B. Total resistance increases and the current decreases. C. Total resistance decreases and the current increases. D. Total resistance decreases and the current decreases. 4. A load is connected to a battery. If a second identical load is added in parallel to the first, what happens to the total resistance of the circuit and the current leaving the battery? A. Total resistance increases and the current increases. B. Total resistance increases and the current decreases. C. Total resistance decreases and the current increases. D. Total resistance decreases and the current decreases. 5. Which of the following units would be used if measuring a large amount of energy? A. joule B. watt C. coulomb D. kilowatt-hour 22 6. Which one of the following best represents a series pathway? A. walking from home to school B. running a lap on an oval running track C. going through the checkouts at a large grocery store D. driving across Canada 7. In the circuit shown below, what would be the readings on the voltmeter V, and ammeter A? Voltmeter, V Ammeter, A A. 3.0 V 1.0 A B. 4.0 V 3.0 A C. 8.0 V 3.0 A D. 12 V 9.0 A 8. In the circuit shown below, what would be the readings on the voltmeter V, and ammeter A? Voltmeter, V Ammeter, A A. 9.0 V 2.0 A B. 9.0 V 5.0 A C. 12 V 5.0 A D. 12 V 12 A 9. What is the current through a 180 W light bulb, if it is connected to 120 V? A. 0.67 A B. 1.5 A C. 120 A D. 21 600 A 23 10. What is the energy consumption of an 1800 W microwave oven used for 30 min? A. 0.90 kWh B. 54 kW h C. 900 kWh D. 54 000 kW h Match the Term on the left with the best Descriptor on the right. Each Descriptor may be used only once. Term _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 11.junction point 12.series circuit 13.parallel circuit 14.joule 15.watt 16.power Descriptor A. B. C. D. E. F. G. more than one path a unit of energy measurement rate of flow of current a unit of power measurement one path for current to travel rate at which energy is transformed location where pathways combine Short Answer Questions 17. A battery is connected to two light bulbs connected in parallel. If the first light bulb “burns out,” what happens to the second light bulb? Explain. ______________________________________________________________________________ 18. A 1400 W hair dryer is used for 15 min. (a) Calculate the electrical energy consumed in the following units: (i)joules___________________________________________________________________ (ii) kilowatthours_____________________________________________________________________ _ (b) If the cost of electricity is 8¢ per kWh, calculate how much it costs to use this hairdryer. 24 19. Use the diagram above to find (a) the current through Lamp 1 ____________________________________________________________ (b) the voltage across Lamp 1 ______________________________________________________________ (c) the power lost in Lamp 1 _______________________________________________________________ 25