Glossary of Key Fundraising
advertisement
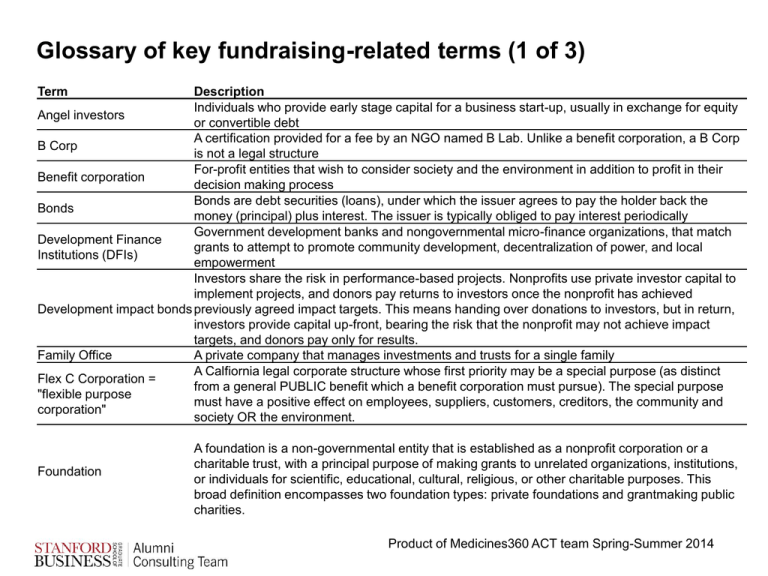
Glossary of key fundraising-related terms (1 of 3) Term Description Individuals who provide early stage capital for a business start-up, usually in exchange for equity Angel investors or convertible debt A certification provided for a fee by an NGO named B Lab. Unlike a benefit corporation, a B Corp B Corp is not a legal structure For-profit entities that wish to consider society and the environment in addition to profit in their Benefit corporation decision making process Bonds are debt securities (loans), under which the issuer agrees to pay the holder back the Bonds money (principal) plus interest. The issuer is typically obliged to pay interest periodically Government development banks and nongovernmental micro-finance organizations, that match Development Finance grants to attempt to promote community development, decentralization of power, and local Institutions (DFIs) empowerment Investors share the risk in performance-based projects. Nonprofits use private investor capital to implement projects, and donors pay returns to investors once the nonprofit has achieved Development impact bonds previously agreed impact targets. This means handing over donations to investors, but in return, investors provide capital up-front, bearing the risk that the nonprofit may not achieve impact targets, and donors pay only for results. Family Office A private company that manages investments and trusts for a single family A Calfiornia legal corporate structure whose first priority may be a special purpose (as distinct Flex C Corporation = from a general PUBLIC benefit which a benefit corporation must pursue). The special purpose "flexible purpose must have a positive effect on employees, suppliers, customers, creditors, the community and corporation" society OR the environment. Foundation A foundation is a non-governmental entity that is established as a nonprofit corporation or a charitable trust, with a principal purpose of making grants to unrelated organizations, institutions, or individuals for scientific, educational, cultural, religious, or other charitable purposes. This broad definition encompasses two foundation types: private foundations and grantmaking public charities. Product of Medicines360 ACT team Spring-Summer 2014 Glossary of key fundraising-related terms (2 of 3) Term Gender-lens investing Grants High impact philanthropy Description Investors use gender as a category of analysis in company diligence, prioritizing bets on value opportunities in three types of firms: companies led by women, companies that promote gender equity, and companies that benefit women through products and services Funds given to charitable organizations, that do not have to be repaid and are usually one of two types: 1. General Purpose or Operating Support Grants and 2. Program Development or Project Support Grants High impact philanthropy begins with a philanthropist’s personal commitment to making a change in the world and caring enough about a particular issue to remain engaged in the long-term and focused on best practices that make a difference Investment in for-profit companies that have social impact potential Impact Investment Investment thesis Not-for-profit (also called nonprofit) NFP Private equity funds Profit-status Investments intended to create positive impact beyond financial returns The goal of an investor with respect to how they weight financial return and social and/or environmental impact in their investment goals, e.g., balancing both financial returns and impact or optimizing one while maintaining a minimum target (or “floor”) for the other. A not for profit organization is one where money donated to it, or that it earns, is used in pursuing the organization's objectives. Not-for-profit organizations can apply for a tax exempt status and donations made to a tax exempt not for profit organization may also be tax-deductible for the donor. A not-for-profit organization has no equity - automatically excluded from equity funding sources Pools of capital managed professionally by a regulated financial institution (e.g. asset management company) The status of a company or fund as forprofit or non-profit. Product of Medicines360 ACT team Spring-Summer 2014 Glossary of key fundraising-related terms (3 of 3) Term Program Related Investment (PRI) Search funds Social impact bonds Social Enterprise (also called Impact business) Social Venture Capital Venture Capital Funds Venture Philanthropy Description A PRI is a low-cost loan (or sometimes an equity investment or a guarantee), provided at belowmarket rates, to strengthen the recipient’s mission-focused work. The lending foundation is reasonably confident of repayment of its full principal amount with some limited returns. The goal of the PRI is full return of its investment, with limited return on its investment, so that the pool of PRI capital remains intact for re-lending to support the foundation’s charitable and programmatic goals into the future. Investment vehicle in which investors financially support an entrepreneur's efforts to locate, acquire, manage and grow a privately held company. The model offers relatively inexperienced professionals with limited capital resources a quick path to managing a company in which they have a meaningful ownership position. Government has the obligation to repay investors only if the program succeeds – otherwise investors lose their monies. This means that investors take full execution risk. As a compensation for assuming this risk, investors receive a small interest payment and a share of the non-financial benefits linked to promoting social goods. Therefore investors require transparency and a strong say in the process to mitigate this risk (e.g. the ability to replace the program manager). A financially-sustainable enterprise that operates with a social and/or environmental mission Social venture capital is a form of venture capital investing that provides capital to businesses deemed socially and environmentally responsible. These investments are intended to both provide attractive returns to investors and to provide market-based solutions to social and environmental issues. Pools of capital managed professionally by a regulated financial institution (e.g. asset management company) Typically used to describe venture capital organization investments in non-profits, deploying a VC strategy such as taking a seat on the board of directors and offering hands-on guidance. In a second model, the funds come from a NFP (e.g. MS Society's Fast Forward Fund) to fund novel science at for-profit startups. Product of Medicines360 ACT team Spring-Summer 2014







