Digestion - GLLM Moodle 2
advertisement

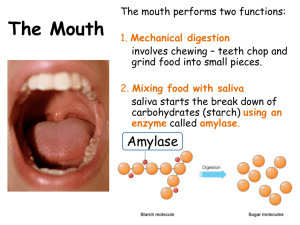
Digestion L3 Definitions Digestion Breakdown of large molecules to small molecules, small enough to pass through the GI tract epithelial cells into the blood Absorption passage of digested food from the GI tract into the blood/lymph 90% takes place in the small intestine/10% in the large intestine 5 basic processes Ingestion Movement (motility – through GI tract) Digestion Absorption Defecation Gastro intestinal tract (GI) mouth throat oesophagus stomach small intestine large intestine MOUTH (Oral cavity) ingestion mastication saliva CHO salivary amylase break down to mono/disaccharides FATS lingual lipase secreted by tongue Oesophagus Swallowing bolus passes into the stomach Constriction of smooth muscle Stomach mixing of food (peristalsis) – CHYME gastric emptying Digestion PROTEINS Pepsin (proteins – peptides) FATS lingual lipase Lining of stomach wall Specialised cells secrete digestive enzymes Acidic environment Folds increase surface area Small intestine absorption (chyme) peristalsis – large intestine Duodenum- 1st 25 cm Jejunum - middle portion Ileum- end portion Digestion in Small Intestine CHO Pancreatic Amylase starch – saccharides FATS bile salts - emulsification – TriG – smaller droplets Pancreatic Lipase -TriG – FA + monoG PROTEINS Trypsin/Peptidases proteins & peptides– Amino acids Large intestine 5 feet long/2.5 inches in diameter absorption of water action of bacteria Digestion in Large intestine CHO bacteria ferment CHO and release Hydrogen,CO2 & Methane PROTEIN bacteria convert remaining proteins to Amino Acids Other organs involved in digestion Liver Gall bladder Pancreas Liver produce bile emulsify lipids Emulsification coating of fat droplets with bile salts prevents droplets from recombining allows more efficient lipase action Micelles - water soluble fat droplets absorbed Gall Bladder store/concentrates bile from the liver secretes the bile in response to body’s need Pancreas secretion of digestive enzymes Pancreatic amylase lipase, trypsin, peptidase Mouth Food is chewed into smaller pieces and mixed with saliva Mouth Food is chewed into smaller pieces and mixed with saliva Oesophagus The tube that connects your mouth to your stomach Oesophagus The tube that connects your mouth to your stomach Stomach Muscular bag that secretes acid Stomach Muscular bag that secretes acid Liver Chemical factory - makes lots of chemcials including bile Liver Chemical factory - makes lots of chemcials including bile Pancreas Produces lots of different enzymes Pancreas Produces lots of different enzymes Ileum Also known as small intestine, place where food is absorbed into the blood Ileum Also known as small intestine, place where food is absorbed into the blood Colon Also known as large intestine, place where water is absorbed from the waste food Colon Also known as large intestine, place where water is absorbed from the waste food Rectum Waste (faeces) is stored here, ready to be got rid of Rectum Waste (faeces) is stored here, ready to be got rid of Anus Ring of muscle that allows the faeces out Anus Ring of muscle that allows the faeces out Task Assign the labels provided to the correct place on the picture of the digestive system