EDUC220_Apr2013 - Heartland Community College
advertisement

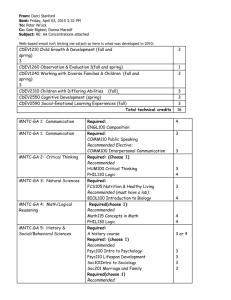
Heartland Community College Master Course Syllabus Social and Business Sciences Division Course Prefix and Number: EDUC 220 Course Title: Educational Psychology DATE PREPARED: 2/15/95 DATE REVIEWED: DATE REVISED: 12/3/04, 2/10/06, 10/7/11, 4/12/13 PCS/CIP/ID NO.: 11-421801 IAI NO. (if available): EFFECTIVE DATE OF FIRST CLASS: 8/15/95 CREDIT HOURS: 3.0 CONTACT HOURS: 3.0 LECTURE HOURS: 3.0 LABORATORY HOURS: 0.0 Catalog Description: Prerequisite: PSY 101 and EDUC 101 or CHLD 101 or equivalent education course with grade of C or better, or permission of division dean. This course provides an introduction to psychological principles underlying educational practice. Theories concerning cognitive and psychological development, human learning, and motivation are studied with emphasis on application for instruction, including assessment. Emphasis will also be placed on learner-centered instruction and diversity. Required Textbook: Bohlin, L., Cisero Durwin, C. & Reese-Weber, M. (2013). EdPsych Modules (2nd ed.). New York, NY: McGrawHill Higher Education. Relationship to Academic Development Programs and Transferability: EDUC 220 fulfills 3.0 semester hours of elective credit for the A.A. and A.S. degrees. It should transfer to most colleges and universities as an elective course. However, since this course is not part of either the General Education Core Curriculum or a baccalaureate major program described in the Illinois Articulation Initiative, students should check with an academic advisor for information about its transferability to other institutions. Learning Outcomes/Course Objectives/Standards Based on the Illinois Professional Teaching Standards (IPTS) There are three levels that correspond to the standards/indicators identified below: Partially Introduced: Concepts/materials are partially covered at a beginning level of knowledge and/or skill. Introduced: Concepts/materials are covered at a beginning level of knowledge and/or skill. Met: Concepts/materials are covered at a proficient level of knowledge and/or skill. Outcomes/Objectives/Standards *GE Code DI 1 Understands the spectrum of student diversity (e.g., race and ethnicity, socioeconomic status, special education, gifted, English language learners (ELL), sexual orientation, gender, gender identity) and the assets that each student brings to learning across the curriculum Understands how each student constructs knowledge, acquires skills, and develops effective and efficient critical thinking and problem-solving capabilities Understands how teaching and student learning are influenced by development (physical, social and emotional, cognitive, linguistic), past experiences, talents, prior knowledge, economic circumstances, and diversity within the community Understands the impact of cognitive, emotional, physical, and sensory disabilities on learning and communication pursuant to the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (also referred to as “IDEA”) (20 USC 1400 et seq.), its implementing regulations (34 CFR 300; 2006), Article 14 of the School Code [105 ILSC 5/Art. 14] and 23 Ill. Adm. Code 226 (Special Education) Understands the impact of linguistic and cultural diversity on learning and communication Understands his or her own personal DI 3 perspectives and biases and their effects on one’s teaching Method of Assessment **IPTS Assignments (e.g. educational autobiography, article analysis, blog entries, current events, philosophy of education paper, dispositions, lesson plans, written papers); case studies; discussions (e.g. classroom, online, etc.); exams (e.g. quizzes, tests, etc.); guest speakers; observations (and reporting of this information); portfolio submissions; presentations (e.g. individual, group, etc.); projects; and/or reflective journals / selfassessments (via face-toface and/or in online platform or a combination of the two) Part. Intro. – 1A Intro. – 1B Intro. – 1C Part. Intro. – 1D Intro. – 1E Part. Intro. – 1F Understands how to identify individual needs and how to locate and access technology, services, and resources to address those needs Facilitates a learning community in which individual differences are respected Intro. – 1G DI 5 Uses information about students’ individual experiences, families, cultures, and communities to create meaningful learning opportunities and enrich instruction for all students Understands the theories and philosophies of CT 1 learning and human development as they relate to the range of students in the classroom Understands the Illinois Learning Standards (23 Ill. Adm. Code 1, Appendix D), curriculum development process, content, learning theory, assessment, and student development and knows how to incorporate this knowledge in planning differentiated instruction Understands how to develop short- and longrange plans, including transition plans, consistent with curriculum goals, student diversity, and learning theory Understands the principles of and strategies CT 1 for effective classroom and behavior management Understands how individual influence groups and how groups function in society Understands how to help students work cooperatively and productively in groups Understands factors (e.g., self-efficacy, positive social interaction) that influence motivation and engagement Understands the cognitive processes associated with various kinds of learning Understands principles and techniques, along with advantages and limitations, associated with a wide range of evidence-based instructional practices Understands appropriate and varied CT 1 instructional approaches used before, during, and after reading, including those that develop Part. Intro. – 1K Intro. – 1L Intro. – 2A Intro. – 3A Part. Intro. – 3B Intro. – 4A Intro. – 4B Intro. – 4C Intro. – 4D Intro. – 5A Intro. – 5B Intro. – 6A word knowledge, vocabulary, comprehension, fluency, and strategy use in the content areas Understands writing processes and their importance to content learning Understands the purposes, characteristics, and limitations of different types of assessments, including standardized assessments, universal screening, curriculum-based assessments, and progress monitoring tools Understands measurement theory and assessment-related issues, such as validity, reliability, bias, and appropriate and accurate scoring Understands current terminology and procedures necessary for the appropriate analysis and interpretation of assessment data Understands how to select, construct, and use assessment strategies and instruments for diagnosis and evaluation of learning and instruction Understands the collaborative process and the skills necessary to initiate and carry out that process Understands the benefits, barriers, and techniques involved in parent and family collaborations Understands school- and work-based learning environments and the need for collaboration with all organizations (e.g., business, community agencies, nonprofit organizations) to enhance student learning Evaluates best practices and research-based materials against benchmarks within the disciplines Identifies paths for continuous professional growth and improvement, including the design of a professional growth plan Reflects on professional practice and resulting outcomes; engages in self-assessment; and adjusts practices to improve student performance, school goals, and professional growth Intro. – 6D Intro. – 7A Intro. – 7C Intro. – 7D CT 2 Intro. – 7E Part. Intro. – 8B Part. Intro. – 8D Part. Intro. – 8E Intro. – 9A CT 3 *Heartland Community College General Learning Outcomes Intro. – 9D Intro. – 9K **Illinois Professional Teaching Standards Course Content/Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Role of Educational Research Personal Development (Context, Social, Emotional, Moral) Development Learner Development (Brain, Cognitive, Language) Learner Theories (Behavioral, Social Cognitive, Information Processing) Motivation Classroom Management and the Ecology of the Classroom Classroom Instruction and Instructional Strategies Learner Differences (Diversity, Intelligence, Gifted/Creative, Emotional/Social/Behavioral Disorders) 9. Assessment (Construction, Use, Performance, Standardized Tests and Scores) Assessment/Artifacts Used in EDUC 220: These assessments / artifacts used in EDUC 220 may be presented via a face-to-face environment, in an online platform or a combination of the two formats. Assignments (e.g. educational autobiography, article analysis, blog entries, current events, philosophy of education paper, dispositions, lesson plans, written papers) Case studies Discussions (e.g. classroom, online, etc.) Exams (e.g. quizzes, tests, etc.) Guest speakers Observations (and reporting of this information) Portfolio submissions Presentations (e.g. individual, group, etc.) Projects Reflective journals / self-assessments Methods of Evaluation: Multiple means of assessing and evaluating student learning will be utilized throughout the semester. These include, but are not limited to: attendance, participation, preparation, reflections, individual and group projects, papers and written assignments, case studies, current events, article analysis, quizzes, tests, self-assessment activities, journals, and a philosophy of education. Each assignment will count toward one of the several components of the final grade, each of which carries a different weight toward the point total in EDUC 220. Letter grades will be assigned according to the following scale: 100% – 90% = A 89% - 80% = B 79% – 70% = C 69% – 60% = D 59% or below = F Required Writing and Reading: This course requires approximately 20-30 pages of reading per week. The majority of the reading will come from the textbook but some additional materials (articles, journals, websites, etc.) may be assigned. A minimum of 10 pages of college level writing is also required in this course. Writing assignments may include papers of various lengths, some essay exams, several reflection papers, summaries of articles and current events pertaining to education, a written philosophy of education and various projects as deemed appropriate by the instructor. Estimates are based on a 16 week course schedule. Please note if your class is not a 16 week class your weekly reading assignment will be increased. Throughout this course students will be required to collect and post artifacts and assessments into a PowerPoint presentation that serves as the beginning of the student’s educational portfolio.