the brain unit packet handout
advertisement

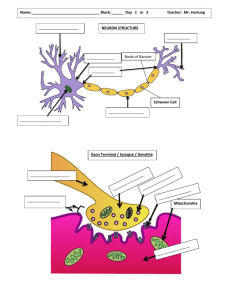
Name:_________________________________ Block:______ Day 1 or 2 Teacher: Hartung STUDY THIS PACKET FOR YOUR BRAIN QUIZ ___________________ NEURON STRUCTURE ___________ Node of Ranvier ___________ Synapse Connection Schwann Cell _________________ ____________________ Axon Terminal / Synapse / Dendrite ___________________ ________________ Mitochondria Mitochondria ________________ Dendrites NEURON STRUCTURE Axon Terminals NodeAxon of Ranvier Synapse Connection Schwann Cell Myelin Sheath Nucleus Axon Terminal / Synapse / Dendrite Axon Mitochondria DRAW A NEURON AND LABEL ITS PARTS: A. B. C. D. E. F. DENDRITE NUCLEUS CELL BODY AXON MYELIN SHEATH AXON TERMINAL DRAW AN AXON TERMINAL / SYNAPSE / DENDRITE AND LABEL ITS PARTS A. B. C. D. E. VESICLE RECEPTOR SITE SYNAPSE DENDRITE AXON TERMINAL MAJOR NEUROTRANSMITTERS: What is their Primary Function? A. DOPAMINE: B. SEROTONIN: C. GLUTAMATE: D. ACETYLCHOLINE E. GABA: TYPES OF NEURONS: What do they do & Where are they primarily Located? 1. SENSORY NEURONS: 2. MOTOR NEURONS: 3. INTERNEURONS: Dopamine (inhibitory & excitatory) - regulates our reward circuitry and pleasure centers Glutamate (excitatory) - required for learning and memory Serotonin A neurotransmitter used by cells in parts of the brain involved in the regulation of sleep, mood and eating – produced in brain and intestines Acetylcholine (excitatory) triggers muscle contraction and stimulates the excretion of certain hormones. GABA (inhibitory) widely distributed in the neurons of the cortex - contributes to motor control, vision, and many other cortical functions o Excitatory is a synapse in which an action potential in a presynaptic neuron increases the probability of an action potential occurring in a postsynaptic cell. o Inhibitory is a synapse in which an action potential in a presynaptic neuron decreases the probability of an action potential occurring in a postsynaptic cell. Sensory neurons: tell the rest of the brain about the external and internal environment Motor neurons: contract muscles and mediate behavior, & stimulate glands and organs. Communication / Computation (Interneurons): Communication neurons transmit signals from one brain area to another & to and from the spinal cord which connects information coming in from the senses & Body. _____________ THE BRAIN structure _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ SPINAL CORD _____________ FUNCTIONS / RESPONSIBILITIES: FRONTAL LOBE: PARIETAL LOBE: OCCIPITAL LOBE: CEREBELLUM: BRAINSTEM: TEMPORAL LOBE: LIMBIC SYSTEM (Thalamus, Amygdala, Hippocampus, Frontal Cortex, others): THE BRAIN structure Parietal Lobe Frontal Lobe Temporal Lobe Occipital Lobe Cerebellum Brainstem Limbic System – emotions & behavior Frontal lobe - reasoning, problem solving, all decisions are made here Occipital lobe – Vision Processor Parietal lobe- stimuli related to touch, pressure, temperature, & pain Temporal lobe - auditory stimuli (hearing) and memory (hippocampus) Cerebellum - coordination, smooth movements of the skeletal system / Muscles Brain Stem – Breathing and blood pressure 1. Draw the Brain 2. Label the Parts 3. List Primary Functions 1. FRONTAL LOBE 2. PARIETAL LOBE 3. OCCIPITAL LOBE 4. CEREBELLUM 5. BRAINSTEM 6. TEMPORAL LOBE 7. SPINAL CORD Cerebellum - is located under the cerebrum. Its function is to coordinate muscle movements, maintain posture, and balance. Brainstem - includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla. It acts as a relay center connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord. It performs many automatic functions such as breathing, heart rate, body temperature, wake and sleep cycles, digestion, sneezing, coughing, vomiting, and swallowing. Ten of the twelve cranial nerves originate in the brainstem. Frontal lobe - Personality, behavior, emotions, Judgment, planning, problem solving, Speech: speaking and writing, Body movement, Intelligence, concentration, selfawareness. Parietal lobe - Interprets language, words, Sense of touch, pain, temperature, Interprets signals from vision, hearing, motor, sensory and memory, Spatial and visual perception Occipital lobe - Interprets vision (color, light, movement) Temporal lobe - Understanding language, Memory, Hearing, Sequencing and organization