File - Arlington Public Schools
advertisement
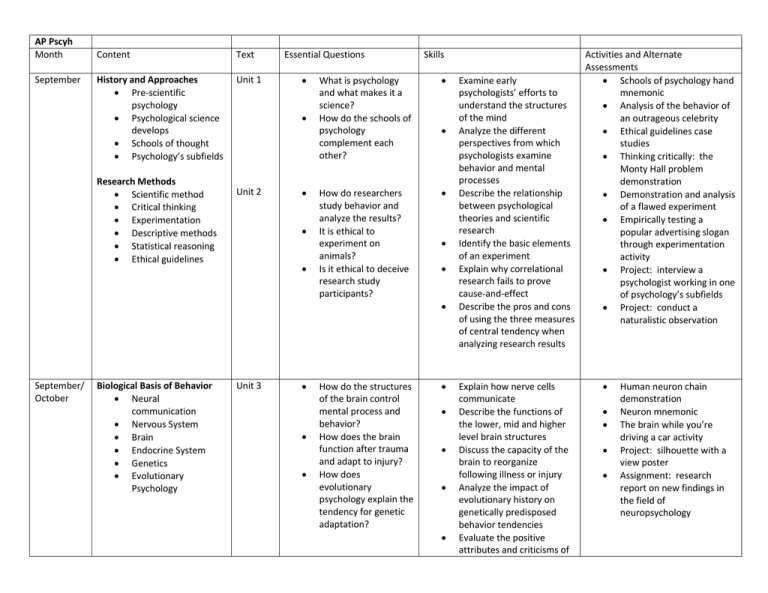
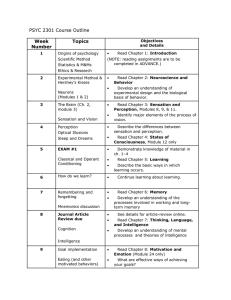
AP Pscyh Month September Content Text History and Approaches Pre-scientific psychology Psychological science develops Schools of thought Psychology’s subfields Unit 1 Research Methods Scientific method Critical thinking Experimentation Descriptive methods Statistical reasoning Ethical guidelines Essential Questions Unit 2 Skills What is psychology and what makes it a science? How do the schools of psychology complement each other? How do researchers study behavior and analyze the results? It is ethical to experiment on animals? Is it ethical to deceive research study participants? September/ October Biological Basis of Behavior Neural communication Nervous System Brain Endocrine System Genetics Evolutionary Psychology Unit 3 How do the structures of the brain control mental process and behavior? How does the brain function after trauma and adapt to injury? How does evolutionary psychology explain the tendency for genetic adaptation? Examine early psychologists’ efforts to understand the structures of the mind Analyze the different perspectives from which psychologists examine behavior and mental processes Describe the relationship between psychological theories and scientific research Identify the basic elements of an experiment Explain why correlational research fails to prove cause-and-effect Describe the pros and cons of using the three measures of central tendency when analyzing research results Explain how nerve cells communicate Describe the functions of the lower, mid and higher level brain structures Discuss the capacity of the brain to reorganize following illness or injury Analyze the impact of evolutionary history on genetically predisposed behavior tendencies Evaluate the positive attributes and criticisms of Activities and Alternate Assessments Schools of psychology hand mnemonic Analysis of the behavior of an outrageous celebrity Ethical guidelines case studies Thinking critically: the Monty Hall problem demonstration Demonstration and analysis of a flawed experiment Empirically testing a popular advertising slogan through experimentation activity Project: interview a psychologist working in one of psychology’s subfields Project: conduct a naturalistic observation Human neuron chain demonstration Neuron mnemonic The brain while you’re driving a car activity Project: silhouette with a view poster Assignment: research report on new findings in the field of neuropsychology evolutionary psychology October Sensation and Perception Five senses Body position and movement Selective attention Illusions Perceptual organization Perceptual interpretation ESP Unit 4 How do we gather information from the environment through our senses? How do the five senses function? How do cues in the environment help perception? How does experience affect perception? Can we always trust our senses and perceptions? November Learning Classical conditioning Operant conditioning Punishments vs. rewards Observational learning Unit 6 November Cognition Memory Information processing Unit 7 What are the key differences between classical and operant conditioning? Is punishment effective in deterring unwanted behavior? Do rewards influence human behavior to the point that they diminish free will? How did early behaviorists attempt to establish psychology as a science? Is memory accurate? How is information stored and retrieved? What is the physiology Contrast the processes of sensation and perception Describe the effects of noise on hearing and behavior Analyze the nature of sensory interaction Describe Gestalt psychology Describe perceptual constancies and their influence on illusions Analyze the role of nature and nurture in perception Explain the importance of context and experience in perception Explain the difference between classical and operant conditioning Identify the different types of reinforcers and schedules of reinforcement Discuss the importance of cognitive processes’ impact on behavior Describe memory in terms of information processing and distinguish among sensory, short-term and Identify the scent lab Video clips on change blindness and inattention blindness Analysis of artwork using perceptual cues ESP demonstrations Project: presentation on one of the five senses Assignment: create an optical illusion based on perceptual constancies and environmental cues Classically conditioning a member of the class Using operant conditioning to lead a member of the class to perform a simple task Lab activity: implicit associations test, conditioning Pavlov’s dog and other learning exercises Project: choose a behavior to modify Short-term memory demonstration The memory chain/game of telephone demonstration Encoding Sensory, short-term, long-term memory Retrieval Forgetting and amnesia Repressed and recovered memories Thinking and Language Thinking Problem solving Making decisions Language structure Language development Animal thinking and language December December States of Consciousness Waking consciousness o Sleep and dreams o Rhythm of sleep o Sleep disorders Dreams Hypnosis Drugs and consciousness o Dependence and addiction o Psychoactive drugs Near-death experiences Motivation, Emotion and Stress Instincts and evolutionary psychology Drives and incentives Hierarchy of needs Unit 5 Unit 8 behind forgetting? Can forgotten memories be recovered? Are repressed memories valid? How are decisions made? How much do emotions interfere with decision-making? Do animals possess language? Why do we dream? Is hypnosis valid and effective? How do drugs affect mental processing and everyday functioning? What is addiction? Do people really “see the light at the end of the tunnel” in near death experiences? What higher and lower level motivations influence our behavior? Do emotions serve a purpose or are they a hindrance? long-term memory Analyze the implications presented when viewing memory as reconstructive Evaluate the positive and negative implications of current neuropsychologicallyfocused memory research Discuss how our beliefs distort logical reasoning Describe the structure of language Analyze the nature/nurture debate in terms of language acquisition Contrast conscious and subconscious information processing Describe the cyclical nature and possible functions of sleep Identify the physiological and psychological effects of drugs Define motivation and identify several theories of motivated behavior Describe Maslow’s hierarchy of needs Discuss physiological and cultural influences on of constructed memory Context and memory demonstrations Information processing: stops on a train demonstration Project: compare recollection of a memory at different points in time Assignment: readings on the research of Elizabeth Loftus and Eric Kandel Dream interpretation activity Video clips on the various uses of hypnosis Psychoactive drugs computer lab activity Project: Sleep and dreams log analysis Assignment: “Ice Kube” addiction simulation Design your own Maslow’s hierarchy of needs Ostracism demonstration “Harry” screen test to express emotion through expression, not words Excerpts from Blink on January Hunger Sex Belonging Theories of emotion Physiology Non-verbal communication Fear Anger Happiness Stress Developmental Psychology Prenatal development Infancy and childhood Gender Social development Moral development Adolescence Adulthood How does society influence the expression of emotions? How can we achieve happiness? What can we do to minimize the negative impact stress can have on our health? Unit 9 Are we products of nature or nurture? Are gender differences a product of genetics or society? How are the elderly viewed and valued? January Personality Psychoanalytic perspective Humanistic perspective Trait perspective Social-Cognitive perspective The Self The unconscious mind Unit 10 Are personalities constant over time or do they change with new experiences? Do personality tests really assess personality? hunger and sex Identify three components of emotion Describe the relationship between physiological states and specific emotions Identify the types of stressors and the stages of the general adaptation syndrome Summarize the impact of stress on health Discuss the impact of physical maturation on children’s memory and motor skills Describe Piaget’s view of how the mind develops Identify Erikson’s stages of social development Explain Kohlberg’s theory of moral development Summarize current views regarding continuity versus stages and stability versus change Describe Freud’s view of personality structure in terms of the Id, Ego and Superego Analyze the contributions of Neo-Freudians Describe the humanistic perspective Discuss research regarding the consistency of behavior over time and across situations reading microexpressions Meditation session Assignment: analysis of motivation in advertising Assignment: biodot biofeedback reflection Project: research a topic presented in the chapter Analyze song lyrics to determine which stage of Erikson’s social development they fit Living will activity and reflection on mortality Assignment: design a Piagetan task to try on a preschooler Assignment: aging simulation and write-up Project: Baby Book assignment Kiersey Temperament sorter, MMPI, TAT, Rorschach and other personality tests Analysis of fictional characters’ personalities from the various perspectives Defense mechanisms skits Project: personality analysis paper February Testing and Individual Differences Assessing intelligence Test construction Cultural bias Group differences Genetic influences Environmental influences Extremes of intelligence Unit 11 Is there one form of intelligence? Can creativity be assessed by a test? Are intelligence tests culturally biased? What accounts for the differences in intelligence scores? Can intelligence be faked? Discuss whether intelligence should be considered a general mental ability or may specific abilities Discuss whether intelligence tests are culturally biased Describe group differences in intelligence tests Discuss the stability of intelligence scores March Abnormal Psychology Defining and classifying DSM-IV Anxiety disorders Mood disorders Dissociation Schizophrenia Personality disorders Prevalence Unit 12 Therapy Psychoanalysis Humanistic Behavioral Cognitive Biomedical therapies o Drugs o Surgery o Electroconvulsive Unit 13 What defines “normal” and “abnormal” behavior? What is the most common disorder? How does society view the mentally ill? Is there one type of treatment that works best for each disorder? Why do therapists use an eclectic approach when treating patients? Identify the criteria for judging whether behavior is psychologically disordered Describe the aims of the DSM-IV Describe the prevalence and symptoms of various disorders and the timing of their onset Evaluate the benefits of and problems related to diagnostic labeling Discuss the rationale and benefits of group therapy Describe the commonalities and differences among the psychotherapies Identify the common forms of drug therapy Divergent thinking/creative intelligence activity: find various uses for common objects Intelligence tests: Australian, AustralianAmerican, Chitling Analysis of the various intelligences in fictional characters and real life figures Assignment: design an intelligence test, avoiding cultural bias and testing for all types of intelligence Project: design a lesson around one of Gardner’s multiple intelligences Case studies of mentally ill patients Reading on the Rosenhan pseudopatient study Therapy skits Project: Fractured Fairytale April April Social Psychology Attitudes and actions Conformity and obedience Social relations o Prejudice o Aggression o Conflict o Attraction o Altruism Unit 14 AP Exam Review All units How do attitudes influence actions? Why is conformity valued so highly in society? Why are people attracted to each other? Do opposites really attract? Identify the conditions under which attitudes have a strong impact on actions Explain the foot-in-the-door phenomenon Discuss the results of experiments on conformity Discuss how group interaction can facilitate group polarization and groupthink May/June Final Project Any unit or multiple units Why study psychology? How does psychology apply to our everyday lives? Analyze an aspect of psychology Apply terminology for multiple units in the final project Evaluation of your teacher’s personality based on situational influences Milgram and Stanford Prison Experiment original footage Demonstrations of a social trap, groupthink and group polarization Assignment: violate a social norm Student-created summary outlines of each unit Review games by unit Choice of projects, with approval and some general requirements