KY Indicator 13 Requirements Feb 2015
advertisement

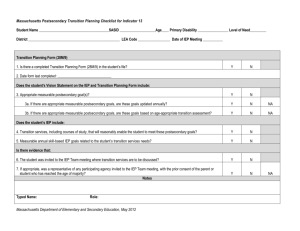
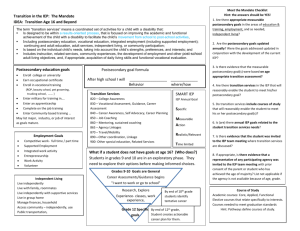
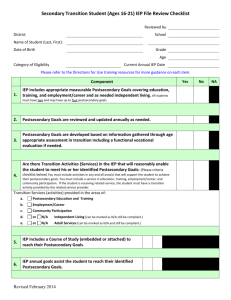
Using Indicator 13 Requirements for Transition Planning to Support College and Career Readiness Rationale Graduation Rate Forty-eight percent (48%) of SWD do not graduate from high school College/Career Readiness Rate Eighty-four percent (84%) of SWD are not ready for College or Careers Evidence for Teacher Evaluation (KFfT) Session Outcomes We are focusing on utilizing transition assessment data to assist students in planning for successful transition. Specifically focused on planning positive outcomes in education/training, employment and (when needed) independent living This will provide evidence of professional growth in KFfT Domains 1 and 4: 1B – Knowledge of Students 1D – Knowledge of Resources 4B – Maintaining Accurate Records 4C – Communicating with Families Taxonomy for Transition Programming Family Involvement Student-Focused Planning Student Developmen t Program Structures Interagency Collaboration Training Objectives To understand and be able to implement the transition planning process for students with disabilities in order to help them: Complete High School Become college and/or career ready To understand appropriate methods of documenting Indicator 13 compliance Indicator 13 Percent of youth with IEPs aged 16 and above with an IEP that includes appropriate measurable postsecondary goals that are annually updated and based upon an age appropriate transition assessment, transition services, including courses of study, that will reasonably enable the student to meet those postsecondary goals, and annual IEP goals related to the student’s transition services needs. There also must be evidence that the student was invited to the IEP Team meeting where transition services are to be discussed and evidence that, if appropriate, a representative of any participating agency was invited to the IEP Team meeting with the prior consent of the parent or student who has reached the age of majority. (20 U.S.C. 1416(a)(3)(B)) Kentucky Indicator 13 “Sub-Indicators” 49A POSTSECONDARY GOALS 49B TRANSITION SERVICES 49C AGENCY INVOLVEMENT 49D CONSENT FOR AGENCY INVITATION 49E MULTI-YEAR COURSE OF STUDY 49F RELATED ANNUAL GOAL(S) 49G TRANSITION ASSESSMENT 49H STUDENT INVOLVEMENT 49I ANNUAL UPDATE Transition Planning Flow Chart Collect Transition Assessments Needs Strengths Preferences Interests Write Measurable Postsecondary Goals Education/Trainin g Employment Independent Living, as appropriate Identify Transition Services Instruction Related Services Community Experiences Employment, Adult & Daily Living Update the Course of Study Write the Annual Goals Coordinate Services with Adult Agencies Postsecondary Goals In order to meet College and Career Readiness guidelines set for all students, the IEP includes appropriate measurable postsecondary goals related to Training or education Employment When appropriate, independent living skills Transition assessments are used to develop post-secondary goals. Education/Training Definition Enrollment in: a) Community/Technical college (2-year program) b) College/University (4-year program) c) College preparatory program d) Other education/training, for example: Job Corps Adult Education Workforce Development Program Community/Technical School Training that is less than 2 years Supported Employment On-the-job Training Military Training Employment Definition Employment includes: Competitive Employment Competitive labor market, full- or part-time Integrated setting at or above minimum wage Supported Employment Competitive employment with intensive supported employment services Other Employment Sample Formula for Developing Education/Training and Employment Goals After high school _______________________, (After high school) (After graduation) (Upon completion of high school _____________ ’s goal is to Allison ___________________________________________________ Attend -year college and take coursework leading to a major in the area of Child Development __________ (education/training behavior where and how ) to be able to become an early childhood education teacher. ____________________________________________. (employment behavior – where and how) Additional Examples: Postsecondary Education/ Training and Employment Goals After high school, Jodi’s goal is to improve job skills through a job training program to be able to work in a retail setting. After graduation, Glenn will complete an associates program in advanced manufacturing to be able to work as an electrical technician in an industrial setting. After high school, Jeremy’s goal is to receive on-the-job training from a job coach to be able to be employed part-time in a local business with supports Non-Examples: Postsecondary Education/Training and Employment Goals After high school, John plans to attend the community college near his home. (Education/Training) John wants to manage the computer labs at the college he attends. (Employment) John hopes to work in the field of information technology when he graduates. (Employment) Independent Living Skills Definition Independent Living Skills are those skills or tasks that contribute to the successful independent functioning of an individual in adulthood (Cronin, 1996) in the following domains: Leisure/recreation Home maintenance personal care Community participation Sample Formula for Developing Independent Living Goal After High School _______________________, Jodi _____________ ’s goal is (After high school) (Student) (After graduation) (Upon completion of high school) assume responsibility for a share of living expenses by saving money earned at work and following a budget set by Jodi and her parents. to__________________________________________________ ___________ (independent living behavior where and how ) Examples: Postsecondary Independent Living Goals Upon completion of high school, Jeremy will independently prepare for work each day, including dressing, making his bed, making his lunch, and accessing transportation. After graduation, Erica will effectively utilize an augmentative communication device at home and in the community that allows familiar and non-familiar individuals to communicate with her regarding needs, wants, and desires. After graduation, Kevin will continue to live with his parents and will participate in his daily care routines to the maximum extent possible. Non-Examples: Postsecondary Independent Living Goals Susan will rely on her family to attend to her daily routines (e.g. feeding, dressing, bathing, activating small appliances / media devices, choice making, etc). Erica wants to attend community dances sponsored by the local YMCA. Stephen will inquire about the obligations and responsibilities of getting an apartment. Employment: Based on a career interest inventory and student survey, Hunter has demonstrated an interest in obtaining a job in the field of landscaping. IEP progress data indicates that he can correctly identify ten common community and vocational vocabulary words with 75% accuracy and also perform familiar tasks with three steps using visual supports with 80% accuracy. Hunter’s cognitive deficits will impact his ability to acquire new skills involving multiple steps in order to independently participate in vocational settings. Hunter will require supervision for attention and safety. Hunter will need supported employment assistance as he explores locations for jobs in landscaping as well as training of work-related skills for those particular locations. Daily Living Skills: Hunter requires assistance with all grooming and hygiene needs. With adapted utensils, he is able to feed himself, but needs assistance with cleaning up his area once he is finished. Parent survey indicates they are most comfortable with Hunter living in a supported living setting with 2-3 roommates. They also indicated that Hunter would like to participate in weekly personal shopping activities after he graduates. Hunter’s deficits in the area of daily living skills will impact his ability to live and perform personal care needs independently after high school. Hunter’s Postsecondary Goals Upon completion of high school, Hunter’s goal is to complete employment skills training and on-the-job training provided through the Office of Vocational Rehabilitation in order to work in a supported employment position as a landscape assistant. Upon completion of high school, Hunter’s goal is to live in a supported living setting with 2-3 roommates and to perform weekly personal shopping activities with assistance. Postsecondary Goals (IEP) Postsecondary Goal(s) (By age 16, or younger if appropriate, and thereafter) (Postsecondary Goal(s) Related to Education/Training, Employment, and if needed, Education/Training and Employment: Upon completion of high school, Hunter’s goal is to complete employment skills training and on-the-job training provided through the Office of Vocational Rehabilitation in order to work in a supported employment position as a landscape assistant. Independent Living: Upon completion of high school, Hunter’s goal is to live in a supported living setting with 2-3 roommates and to perform weekly personal shopping activities with assistance. Postsecondary Goals (Infinite Campus) Postsecondary Goals (Record Review Document) Transition Planning Flow Chart Collect Transition Assessments Needs Strengths Preferences Interests Write Measurable Postsecondary Goals Education/Trainin g Employment Independent Living, as appropriate Identify Transition Services Instruction Related Services Community Experiences Employment, Adult & Daily Living Update the Course of Study Write the Annual Goals Coordinate Services with Adult Agencies Transition Services Definition Transition services are defined as a coordinated set of activities for a student with disabilities that are: Designed to be within a results-oriented process, focused on improving the academic and functional achievement of the student with a disability to facilitate the student’s movement from school to post-school activities Based on the individual student’s needs, taking into account their strengths, preferences and interests What do Transition Services Include? Instruction Related Services Community Experiences Employment Other Post-School Adult Living Objectives When appropriate, acquisition of daily living skills and provision of a functional vocational evaluation Things to Consider: What experiences must the student participate in this academic year that are necessary for achieving the identified postsecondary goals? What services and specific instruction are essential this year for the student to develop skills and knowledge to attain their postsecondary goals? Do we know enough about this student’s vocational skills to identify an appropriate postsecondary employment goal or design activities to support the identified goal? Transition Services – Instruction Definition Instruction activities/strategies can be a formal or informal imparting of knowledge or skills that a student needs to receive in specific areas to: Complete needed courses Succeed in the general curriculum Gain needed skills Transition Services Instruction Examples PROVIDE COURSE OF STUDY LEADING TO A DIPLOMA PROVIDE COURSE OF STUDY LEADING TO AN ALTERNATIVE DIPLOMA MONITOR GRADES/GRADUATION STATUS AND FOLLOW-UP IF ISSUES ARISE MONITOR COLLEGE/CAREER READINESS STATUS TO MAKE ANY CHANGES IN INSTRUCTIONAL PROGRAMMING PROVIDE OPPORTUNITIES TO VISIT COLLEGE CAMPUSES AND MEET WITH STUDENT SUPPORT SERVICES (DISABILITY SERVICES COORDINATOR) Transition Services Related Services Definition ACTIVITIES/STRATEGIES IN THIS AREA SHOULD CONSIDER THE CURRENT AND PROJECTED RELATED SERVICE NEEDS OF THE STUDENT THIS AREA OF THE TRANSITION SERVICES IS NOT FOR SPECIFYING THE NEEDED RELATED SERVICES FOR THE NEXT SCHOOL YEAR. RELATED SERVICES FOR THE COMING SCHOOL YEAR SHOULD BE ADDRESSED IN ANOTHER SECTION OF THE IEP Transition Services Related Services Examples DEVELOP LINKAGES TO ADULT AGENCIES OR PROVIDERS TRANSITION COUNSELING REFERRAL TO DISABILITY SERVICES TO DETERMINE ELIGIBILITY AFTER HIGH SCHOOL REFERRAL TO OVR TO DETERMINE ELIGIBILITY FOR SERVICES Transition Services Community Experiences Definition Community Experiences are activities/strategies that are: Generally provided outside the school building To help prepare the student for participation in community life Transition Services Community Experiences Examples PROVIDE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PRACTICE IN USING RELEVANT COMMUNITY RESOURCES (HEALTH CARE FACILITIES, BANK, LIBRARY, LAUNDRY-MAT, POSTAL SERVICES, CHURCH, RESTAURANTS, HAIR SALON) PRACTICE MAKING AND KEEPING OWN APPOINTMENTS TEACH APPROPRIATE SOCIAL BEHAVIORS IN THE COMMUNITY (TIPPING, ASKING FOR ASSISTANCE, STANDING IN LINE, BEING QUIET IN RELEVANT SITUATIONS) Transition Services Employment Definition Activities/strategies listed in this area focus on development of: work-related behaviors job seeking and keeping skills career exploration skill training apprenticeship training and actual employment Transition Services Employment Examples ASSISTANCE IN PREPARING FOR WORK TOWARDS OBTAINING A LICENSE TO BECOME A __________ ARRANGE FOR MEETING WITH ADULT WORKERS IN THE CAREER FIELD OF __________ ENROLLMENT IN A CAREER AWARENESS PROGRAM PROVIDE A COMMUNITY-BASED CAREER EXPLORATION PROGRAM Transition Services Post-School Adult Living Definition Activities/strategies listed in this area emphasize focus on adult living skills These are generally activities that are done occasionally Transition Services Post-School Adult Living Objectives Examples INSTRUCTION IN HOW TO OPEN A BANK ACCOUNT AND MANAGE FINANCES/BUDGETS/BILLS INSTRUCTION IN HOW TO APPLY FOR CREDIT CARDS AND MANAGE PERSONAL DEBT INSTRUCTION IN HOW TO APPLY FOR HOUSING ASSISTANCE (HUD) INSTRUCTION ABOUT CONSUMER SKILLS, RIGHTS, AND RESPONSIBILITIES Transition Services Daily Living Skills Definition Daily living skills are activities that adults do most every day. These include such things as: Preparing meals Budgeting Maintaining a residence Paying bills Raising a family Caring for clothing Personal grooming Transition Services Daily Living Skills Examples INSTRUCTION IN HOW TO MANAGE DAILY TIME SCHEDULE INSTRUCTION IN HOW TO MANAGE MONEY AND PAY BILLS INSTRUCTION IN HOW TO DEVELOP A PERSONAL FITNESS ROUTINE PROVIDE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PRACTICE PURCHASING FOOD PROVIDE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PRACTICE PREPARING MEALS Transition Services Functional Vocational Evaluation Definition A functional vocational evaluation is an assessment process that provides information about job or career interests, aptitudes, and skills Information is gathered through situational assessments in the setting where the job is performed Information gathered through a functional vocational assessment can be used to refine educational experiences, courses of study, and employment activities/strategies listed in the transition services in the IEP Transition Services Functional Vocational Evaluation Examples CONDUCT A FUNCTIONAL VOCATIONAL EVALUATION MAINTAIN A PORTFOLIO OF OBSERVABLE WORK SAMPLES CONDUCT AN INTEREST/APTITUDE SURVEY Transition Services (IEP) Postsecondary Goal(s) (By age 16, or younger if appropriate, and thereafter) (Postsecondary Goal(s) Related to Education/Training, Employment, and if needed, Independent Living: Education/Training and Employment: Upon completion of high school, Hunter’s goal is to complete employment skills training and on-the-job training provided through the Office of Vocational Rehabilitation in order to work in a supported employment position as a landscape assistant. Independent Living: Upon completion of high school, Hunter’s goal is to live in a supported living setting with 2-3 roommates and to perform weekly personal shopping activities with assistance. Transition Service Agency Responsible Completion of Multi-Year Course of Study leading to an Alternative High School Diploma Community-Based Instruction Special Education Teacher Individual advising on completion of ILP Counselor/Job Coach Community-Based Work Transition Program (in collaboration with Office of Vocational Rehabilitation) Invite Agriculture teacher to transition planning sessions Special Education Teacher/Job Coach Special Education Teacher Provide opportunity for participation in Regional Transition Fair Special Education Teacher Provide information to Hunter’s parents about guardianship, SSI, Michelle P Waiver, and Supported Living Daily Living Skills instruction Special Education Teacher Special Education Teacher Special Education Teacher Transition Services (Infinite Campus) Transition Services (Record Review Document) Transition Planning Flow Chart Collect Transition Assessments Needs Strengths Preferences Interests Write Measurable Postsecondary Goals Education/Trainin g Employment Independent Living, as appropriate Identify Transition Services Instruction Related Services Community Experiences Employment, Adult & Daily Living Update the Course of Study Write the Annual Goals Coordinate Services with Adult Agencies Agency Involvement (Record Review Document) Agency Involvement (Record Review Document) Agency Involvement (IEP) Postsecondary Goal(s) (By age 16, or younger if appropriate, and thereafter) (Postsecondary Goal(s) Related to Education/Training, Employment, and if needed, Independent Living: Upon completion of high school, John’s goal is to attend courses at Community and Technical College to work toward a degree in computer science to be able to work as a network manager for a local medical company. Transition Service Agency Responsible Completion of Multi-Year Course of Study as outlined in John’s Individual Learning Plan High School Instruction related to word processing/keyboarding skills (See annual goal) Self-advocacy training High School Tour of community college campus to familiarize John with surroundings Apply for possible college financial aid High School Vocational rehabilitation referral to determine eligibility for tuition assistance High School and OVR Apply for college and disability support service High School and Disability Support Services Office High School High School Agency Involvement (Notice of ARC) Agency Involvement (Infinite Campus) Agency Involvement (Consent for Invitation) Transition Planning Flow Chart Collect Transition Assessments Needs Strengths Preferences Interests Write Measurable Postsecondary Goals Education/Trainin g Employment Independent Living, as appropriate Identify Transition Services Instruction Related Services Community Experiences Employment, Adult & Daily Living Update the Course of Study Write the Annual Goals Coordinate Services with Adult Agencies Multi-Year Course of Study (Record Review Document) Multi-Year Course of Study (IEP) Example - Course of Study Listings (Alternative Diploma) LANGUAGE ARTS 1 INTEGRATED SOCIAL STUDIES LANGUAGE ARTS 2 WORLD HISTORY LANGUAGE ARTS 3 U.S. HISTORY LANGUAGE ARTS 4 HUMANITIES MATHEMATICS 1 HEALTH EDUCATION MATHEMATICS 2 BASIC MONEY SKILLS MATHEMATICS 3 DEVELOPING CAREERS MATHEMATICS 4 HOME ECONOMICS INTEGRATED SCIENCE LIFE SCIENCE/BIOLOGY EARTH/SPACE SCIENCE INDIVIDUALIZED CAREER WORK EXPERIENCE IN Example - Course of Study Listings (Diploma) ENGLISH 9 ENGLISH 10 ENGLISH 11 ENGLISH 12 ALGEBRA 1 ALGEBRA 2 GEOMETRY PRE CALCULUS CALCULUS INTEGRATED SCIENCE COMPUTER SCIENCE CHEMISTRY BIOLOGY PHYSICS World History US History Integrated Social Studies Humanities Health/PE Art Child Development Nutrition Psychology Preschool Internship Course of Study Document (Career Cruising) Course of Study can be documented: In the online ILP On a district- developed form On the Alternative ILP (Course section) Multi-Year Course of Study (Infinite Campus) Transition Planning Flow Chart Collect Transition Assessments Needs Strengths Preferences Interests Write Measurable Postsecondary Goals Education/Trainin g Employment Independent Living, as appropriate Identify Transition Services Instruction Related Services Community Experiences Employment, Adult & Daily Living Update the Course of Study Write the Annual Goals Coordinate Services with Adult Agencies Related Annual Goal (Record Review Document) Related Annual Goal (IEP) Related Annual Goal (Infinite Campus) Transition Planning Flow Chart Collect Transition Assessments Needs Strengths Preferences Interests Write Measurable Postsecondary Goals Education/Trainin g Employment Independent Living, as appropriate Identify Transition Services Instruction Related Services Community Experiences Employment, Adult & Daily Living Update the Course of Study Write the Annual Goals Coordinate Services with Adult Agencies Transition Assessment Transition assessment is the ongoing process of collecting data on the individual’s needs, preferences, and interests as they relate to the demands of current and future working, educational, living, and personal and social environments. Assessment data serve as the common thread in the transition process and form the basis for defining goals and services to be included in the IEP and is gathered from multiple sources. From: NSTTAC Indicator 13 Training Materials Transition Assessment Sources Sources of assessment information include, but are not limited to, the following: Formal interest surveys, aptitude tests and other surveys Informal interviews with students Student completion of interest inventories Questionnaires to establish student interests and preferences Functional vocational evaluations Quarterly or semester grades throughout high school Current psychological assessment data indicating areas of strengths and weakness College entrance exam scores if applying to 4-year colleges Interviews/surveys with the family Student observations Transition Assessment Examples INDIVIDUAL LEARNING PLAN Career Awareness, Student Interest Inventory, Career Matchmaker, Ability Profiler Academic Records Progress notes, End of grade test scores, Report cards, Curriculum-Based Assessment, State Assessments - EPAS (EXPLORE/PLAN/ACT), CATS MULTI- DISCIPLINARY ASSESSMENT Cognitive, Adaptive, Functional Skills, Communication, Observations SCHOOL OR COMMUNITY - BASED WORK EXPERIENCES INTERVIEW WITH STUDENT & PARENTS http://www.seattleu.edu/ccts/transition-services/ Roger Interpersonal: (teacher/staff) • Lacks understanding of personal space • Lacks control when frustrated or angry • Often speaks for others • Unable to resolve conflicts Academic/functional: (teacher/psych) • Unable to follow 3‐step written directions • Unable to interpret warni ng labels accurately (parents/family) • Unable to operate a calculator accurately Community/Vocational : • Cannot use public transportation successful ly (family/teacher) • Lacks continuous person al hygiene habits (family) • Interrupts coworkers to assist with their work (work supervisor) • Work pace is slow (work supervisor) Interpersonal: (teacher/family) • Friendly smiles and greets all people • Helps others without prompting • Able to communicate needs clearly and appropriately • Able to accept constructive criticism without resentment Academic/functional: (teacher/psych) • Can follow 3‐step verbal directions with up to 2 variables • On Brigance: 25 functional words • Able to add/subtract 2 single digit numbers Community/Work: (Magellan) • Able to recognize multi‐step task procedures • Organizes work in an orderly fashion • Stays on task for extended periods. ASD Prefers: (Casey LifeSkills) • Computer aided interes t inventory: • Interest in working outdoors o with others; o perhaps with plants • Teacher observation: o work in group or with 1 other o clean or unclean wor k environment o leading rather than following • Parent/family observati on o repetition o non‐sedentary o no stress or uncomfortable situations http://www.seattleu.edu/ccts/transition-services/ Expressed: (Roger/family) • Special Olympics • Bowling • Going out with friends • Lifting weights • Animals • Planting flowers • Serving food Observed: • Physical activities • Running track • Talking with older people • Native American weavi ng • Preparing lunches • Karaoke Tested: • video interest survey: Grounds maintenance = high interest • Casey LifeSkills Assessment Inventory‐ areas of concern are personal hygiene, conflict resolution 11/20/2014 School‐based work experiences • 1st semester –assisted in high school kitchen 1 ho ur/day • 2nd semester – continuing in food service experien cein school kitchen to 2 hr/day Community‐based Experiences • Volunteers at senior center at Tuesday Night Bingo • Is equipment manager f orSpecial Olympics tea m AGE-APPROPRIATE TRANSITION ASSESSMENT SUMMARY Roger, age 15 NEEDS: Roger needs to demonstrate the concept of personal space, not to interrupt and answer for others, and learn to resolve conflicts appropriately. (teacher/family observation) Roger needs to demonstrate personal control when he is frustrated or angry. (teacher) STRENGTHS: Roger is friendly, greets everyone with a smile; he helps others without being asked; he is able to communicate his needs clearly and appropriately. (teacher/family) Roger can follow 3step directions with two variables. He knows 25 functional words, is able to add/subtract 2 single digit numbers. Roger recognizes multi-step task procedures, organizes his work in an orderly fashion and stays on task for extended periods. (Brigance) PREFERENCES: Roger prefers physical activities, working and interacting with people and variety in work tasks or personal routine. (teacher/family observation) INTERESTS: Roger is interested in sports, lifting weights, working on lawns, special Olympics and running track. He is interested in tribal arts and crafts, working in food service environments and socializing with friends. (teacher, family, community members) http://www.seattleu.edu/ccts/transition-services/ Transition Assessment: Connection to Present Level Statement Garnet is 15 years old in the 10th grade. Garnet’s Course of Study is outlined through completion of high school. Based on informal interviews with Garnet and completion of her ILP, Garnet’s needs are in the area of interpersonal and intrapersonal skills. Based on an interview with Garnet, teacher and parent observations, and an interest inventory. She excels in sports, especially basketball, and she has a competitive edge. Garnet prefers activities that move at a fast pace and enjoys outside activities. Her preferences are activities that she can do alone, such as computer games, riding her bike. Garnet likes coming up with unique ideas and being in charge. Garnet is a starter on the varsity basketball team. Transition Assessment (IEP) Transition Assessment (Infinite Campus) Transition Assessment (Record Review Document) Transition Planning Flow Chart Collect Transition Assessments Needs Strengths Preferences Interests Write Measurable Postsecondary Goals Education/Trainin g Employment Independent Living, as appropriate Identify Transition Services Instruction Related Services Community Experiences Employment, Adult & Daily Living Update the Course of Study Write the Annual Goals Coordinate Services with Adult Agencies Student Involvement (Record Review Document) Student Involvement (Notice of ARC) Making the IEP Student Centered Students can be involved in their IEP process in four ways: Planning, Drafting, Meeting, and/or Implementing Planning: Starting with the student, gather transition assessment information using multiple strategies from multiple individuals Planning: Involve students in selecting meeting participants (including what outside agencies to invite) Drafting: Write postsecondary goals and annual IEP goals in 1st person Meeting: Involve students in leading the meeting (use PowerPoints, notes, etc.) Implementing: Students set and monitor goals and activities Annual Update (Record Review Document) Annual Update (IEP) Reporting for All Components (Record Review Document) Reporting for All Components (Record Review Document) Additional Resources and Support www.transitiononestop.org www.education.ky.gov Kentucky Educational Cooperatives Special Education Services: • VANESSA GRONECK TRANSITION/CCR PROFESSIONAL LEARNING COACH www.nkces.org