Asthma case study
advertisement

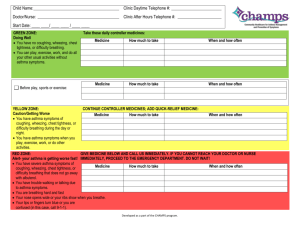
+ Asthma A Case Study Jaymie McAllister NUR3026L: E.B.P. Case Study BMC, UD Summer 2012 + Introduction Purpose: Present and explain a disease to enhance patient care and promote disease awareness. Topic: Asthma Objectives: What is asthma? Presentation and triggers Pathophysiology Statistics Health Promotion + What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Airway narrowing causes increased sensitivity to inhaled agents Airway response to irritants results in even further airway constriction and airway mucus production, making breathing more difficult. + Asthmatic Airway + What Causes Asthma? Atopy The inherited tendency to develop allergies Parents with asthma Respiratory infections during childhood Types of asthma Allergic Exercise-induced Cough-Variant Nocturnal Occasional + Symptoms of Asthma Symptoms: Coughing (especially at night) Wheezing Shortness of breath Chest tightness, pain or pressure Bronchospasm Symptoms vary among different people and depend on the severity of the attack. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VA9C_aCH7F0 (Asthma wheezing) + Triggers of Asthma Triggers can include: Infections Colds, viruses, sinus infections, flu Exercise Varying degrees depending on severity of asthma Weather Sudden changes in temperature and humidity, the presence of cold air Tobacco smoke Allergens Dust, pollen, pets, mold, cockroaches, etc. Irritants Strong odors, perfumes, smoke, air pollution Strong emotions such as laughing or crying Medications + Pathophysiology Triggers provoke airway response The airways under attack display: Hypersensitive inflammatory response Hyperinflation of the lungs Muscle hypertrophy Lamina reticularis thickening Mucosal edema Epithelial sloughing Cilia cell disruption Mucus hypersecretion Allergic airway responses present with immunoglobin E (IgE) response mechanisms Asthma is characterized by the presence of: Increase numbers of eosinophils, neurtrophils, lymphocytes and plasma cells in the bronchial tissues Activated by T-lymphocytes Bronchial secretions Mucus Kaufman, G. (August 18, 2011). Asthma: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Management . In Pubmed.gov. Retrieved July 7, 2012, from http://ehis.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.usf.edu/eds/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?sid=54f5540b-4b13-4875-b9fb13f97362898e%40sessionmgr14&vid=3&hid=4. + Asthma Statistics United States: Morbidity >50% of Americans with asthma had an attack in 2008 185 children and 3,262 adults died from asthma related problems in 2007 alone. Co-Morbidities 1 in 12 people in the U.S. have asthma (8% of population) 1 in 10 children have asthma (10% of children in U.S) Asthma is more prevalent in non-Caucasian groups In 2008, there was a noted 50% increase in the number of African American children with asthma since 2001 Largest increase of all ethnic groups Adults with asthma are 3 times more likely to develop serious depression Adults with asthma are 5 times more likely to develop COPD than adults without asthma. Higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes in adults 45+ than adults without asthma. International Over 300 million people suffer from asthma worldwide and yearly there are nearly 250,000 asthma related deaths http://www.aaaai.org/about-the-aaaai/newsroom/asthma-statistics.aspx. http://www.dhhs.nh.gov/dphs/cdpc/asthma/documents/chapter3.pdf + Diagnostics Asthma is difficult to distinguish between other diseases Diagnostic tests: Family history Past Medical History Auscultation of lung sounds Assess for wheezing HPI Wheezing, shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing Peak Flow Meter Measures rate of air leaving the lungs Also used to monitor response to treatments Spirometry Measure amount and rare of air leaving the lungs Complete Pulmonary Function Test Determines lung volume and diffusion capacity Chest X-Ray Bronchoprovacative Challenge Testing Select irritants are inhaled through a nebulizer to determine asthma triggers Arterial Blood Gas/Pulse Oximetry Determine how well blood is being oxygenated Blood draws Taken to determine the circulation of IgE immunoglobins (indicates allergic response) + Treatments Prognosis: “Asthma cannot be cured. The goal of treatment is to minimize its effects on your life so that most of the time you feel well and are able to do what you enjoy doing.”Harvard Health Publications Group Two main types of drug treatments: Quick Reliever Drugs Taken during an asthma attack Work to quickly relax the muscles surrounding the bronchial tubes- tubes open wider Examples: Albuterol, dispended by an inhaler Controller Drugs Taken regularly to control asthma Reduced need for quick-reliever drugs Examples: Corticosteroids (Nasonex) Long-acting beta agonists (Serevent) Leukotriene modifiers (Singulair) Theophylline (Theo-24) Combination therapies (Advair) Can be inhaled (2-4 puffs PRN), taken PO or injected and are sometimes taken in combination Harvard Health Publications Group. (July 5, 2012). Asthma in Adults. In Krames Signs and Symptoms FastGuides. Retrieved July 7, 2012, from http://go.galegroup.com.ezproxy.lib.usf.edu/ps/ + Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Interventions: Ineffective breathing pattern related to decreased lung expansion. Patient presents with shortness of breath, wheezing and chest pain Collaborative: Administer medications quick reliever drugs, give oxygen, provide nebulizer and increase humidity Encourage Pursed Lip Breathing and Coughing Helps patient concentrate on and potentially control breathing, and coughing may reduce amount of impairing sputum. Adjust patient positioning to promote maximum breathing ability Adjust head of bed upward Expected outcomes: Increase breathing efficiency Increased airway expansion Normalize vital signs + NCLEX Question 1 1. Which assessment finding would help to confirm a diagnosis of asthma for a patient suspected of having the disorder? a) Cyanosis of the upper extremities b) Increased expiratory volume c) Inspiratory and expiratory wheezing d) Normal breath sounds + Question 1 Rationale C; Inspiratory and expiratory wheezing are typical asthma findings. + NCLEX Question 2 A 19-year old male presents to the emergency department with acute asthma. His respiratory rate is 44 breaths per minute, and he appears to be in acute respiratory distress which action should be taken first? 1) A. Take a full medical history B. Give inhaled quick-reliever drugs C. Apply a cardiac monitor D. Provide emotional support to the patient + Question 2 Rationale B; A client having an acute asthma attack needs quickreliever drugs as soon as possible to increase the amount of oxygen being delivered to the body tissues. + Citations Asthma Statistics | AAAAI. (n.d.). The American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology | AAAAI. Retrieved July 19, 2012, from http://www.aaaai.org/about-the-aaaai/newsroom/asthma-statistics.aspxCleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved July 19, 2012, from http://my.clevelandclinic.org/disorders/asthma/hic_asthma_an_overview.aspx Asthma attack - MayoClinic.com. (n.d.). Mayo Clinic. Retrieved July 19, 2012, from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/asthma-attack/DS01068/ Campbell, J. (n.d.). Managed care opportunities for improving ast... [Am J Manag Care. 2011] - PubMed NCBI. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved July 19, 2012, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21761959 Category. (n.d.). Asthma Tests - Diagnostic Tests in Asthma. Asthma- All About Your Asthma. Retrieved July 19, 2012, from http://asthma.about.com/od/adultasthma/tp/asthma_tests.htm Harvard Health Publications Group. (July 5, 2012). Asthma in Adults. In Krames Signs and Symptoms FastGuides. Retrieved July 7, 2012, from http://go.galegroup.com.ezproxy.lib.usf.edu/ps/ Kaufman, G. (August 18, 2011). Asthma: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Management . In Pubmed.gov. Retrieved July 7, 2012,from http://ehis.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.usf.edu/eds/pdfviewer/pdfviewer? sid=54f5540b-4b13-4875-b9fb-13f97362898e%40sessionmgr14&vid=3&hid=4.