Circular Flow in Economics
The Circular-Flow Diagram
Circular Flow in Economics: How households and
businesses interact in the market for resources and in
the market for goods and services, and see how money
keeps the whole process moving.
The circular flow model
highlights the “flows” within
the economy―the flow of
economic resources, goods
and services, and the flow of
money.
The Circular-Flow Diagram…
… is a simple depiction of the macroeconomy.
… illustrates GDP as spending, revenue,
factor payments, and income.
First, some preliminaries:
Factors of production are inputs like labor, land,
capital, and natural resources.
Factor payments are payments to the factors of
production. (e.g., wages, rent)
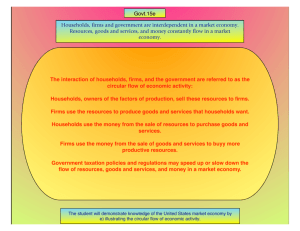
The Circular-Flow Diagram
Households:
own the factors of production,
sell/rent them to firms for income
buy and consume Goods &
Services (g&s)
Firms
Households
The Circular-Flow Diagram
Firms
Firms:
buy/hire factors of production,
use them to produce g&s
sell Goods & Services (g&s)
Households
The Circular-Flow Diagram
Revenue
G&S
sold
Markets for
Goods &
Services
Firms
Factors of
production
Wages, rent,
profit
Spending
G&S
bought
Households
Markets for
Factors of
Production
Labor, land,
capital
Income
What This Diagram Omits…
The government
collects taxes
purchases g&s
The financial system
matches savers’ supply of funds with borrowers’
demand for loans
The foreign sector
trades g&s, financial assets, and currencies with the
country’s residents
Expanded Circular Flow
Households earn income via the
factor markets from wages,
interest on bonds, dividends on
stocks, and rent on land.
Government purchases of
goods and services is paid
Wages, rents,
interest, profits
for by tax receipts as well as
by government
borrowing.
Factor services
Household
Via the financial
markets, private
savings is channeled to
firms for investment
Goods
Government
Firms
(production)
Financial markets
Personal consumption
Other countries
spending.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
© 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
The expanded circular flow diagram shows the
transactions among households, firms, governments, and
the rest of the world.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
These transactions take place in factor markets, goods
markets, and financial markets.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
Firms hire factors of production from households. The blue
flow, Y, shows total income paid by firms to households.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
Households buy consumer goods and services. The red
flow, C, shows consumption expenditures.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
Households save, S, and pay taxes, T. Firms borrow some
of what households save to finance their investment.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
Firms buy capital goods from other firms. The red flow I
represents this investment expenditure by firms.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
Governments buy goods and services, G, and borrow or
repay debt if spending exceeds or is less than taxes.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
The rest of the world buys goods and services from us, X,
and sells us goods and services, M—net exports are X - M
Foreigners can
also buy stocks
and bonds in the
U.S. financial
markets.
Exports (X) generate
an inflow of funds into
the country from the
rest of the world
Imports (M) lead
to an outflow of
funds to the rest
of the world.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
And the rest of the world borrows from us or lends to us
depending on whether net exports are positive or negative.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
The blue and red flows are the circular flow of expenditure
and income. The green flows are borrowing and lending.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
The sum of the red flows equals the blue flow.
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The
Flows of Money Through the Economy
That is: Y = C + I + G + X - M
An Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram: The Flows of Money Through the
Economy
SUMMARY: The Circular Flow… Matching Buyers and Sellers
Income
Households “sell”
resources to
businesses…
Market for
Factors
Factor Payments
…who in turn pay for them with
wages, rent, interest, and profits.
Labor, Land, and
Capital for Sale
Households
Consumption
Labor, Land, and
Capital Purchased
Businesses provide final
goods and services to
households…
Goods and
Services
Purchased
Goods and
Services for Sale
Market for
Goods and
Services
Firms
Firm Revenue
…who in turn pay for them with money.
SUMMARY: The Circular Flow… Matching Borrowers and Lenders
Market for
Factors
Income
Factor Payments
Businesses can borrow from
the bank to obtain capital to
purchase inventory
Private
Savings
Interest
Financial
Markets
Loans
Interest
Households
Public
Savings
Firms
Transfers
Transfers
Government
Individuals and Taxes
governments earn a
rate of return from their
savings
Consumption
Taxes
Government
Spending
Market for
Goods and
Services
Firm Revenue
Circular Flow
Expanded Circular Flow