Cell Structures and Function Concept 6.4-6.6
advertisement

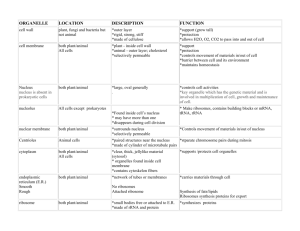
Cell Structures and Function Concept 6.4-6.6 Organelles mini organs with a specific function 6.1 pg 110-114 All living organisms are made of cells. Scientist contributions Robert Hooke- observed cork – dead Anton van Leeuwenhoek- pond water Tiny room-cells Animicules- simple microscopes Schleiden and Schwann Plant and Animals have cells Cell Theory 1. All living things have cells 2. Cell is the basic unit of structure and function. 3. Cells come from other cells. Cell division- mitosis- body cells Reduction division- meiosis- sex cells-egg and sperm. Importance of Microscopes Light microscopes- magnifies up to 1000x. Can see bacteria- diameter of 1-2um. Cannot see smaller cell organelles Electron Microscopes- use electron beams- can magnify 1,000,000 x SEM- Scanning Electron Microscope Surface- 3D detail TEM- Transmission Electron Microscope Internal detail of cell structures Two Main types of Cells Prokaryote- bacteria and archaea no membrane bound nucleus Only ribosomes, lacks most organelles Contains DNA in a center region. Much smaller than eukaryotic cells Earlier in fossil record. Eukaryote- protists,fungi,plants, animals Membrane bound nucleus Membrane bound organelles 100 x larger than prokaryotic cells Appeared later Plant vs Animal Cells Similar: Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane,organelles Differences: Plants- cell wall, definite shape chloroplasts, large central vacuole. Animals- no cells wall, smaller vacuoles. Nuclear Structures Nucleus Control center of the cell Spherical DNA-Deoxyribonucleic Acid Chromatin- DNA attached to proteinsform long fibers. Nuclear envelope (membrane) Surrounds the nucleus Double layer membrane Pores –thousands for substances (RNA) to move into the cytoplasm. Nucleolus Inside the nucleus. Not visible when the cell is dividing. Site of ribosomal RNA production. Cytoplasmic Structures Cytoplasm Between the nucleus and plasma(cell) membrane. Gel-like fluid. Consists of cytosol and organelles. Many organelles are enclosed by membranes. Cytosol is mainly water. Centrioles Found in animal cells Paired cylindrical organelles near the nucleus. Involved in cellular division??? Lie at right angles to each other. Chloroplasts Found in plant cells. Contain green pigment chlorophyll. Site of photosynthesis Disks- thylakoids – solar “power packs” Cytoskeleton Fiber network in the cytoplasm. Changing structural pattern. Composed of: Microtubules Straight, hollow tubes. Shape, rigidity, organization Microfilaments Thinner, solid rods Allows cell to move and change shape. Amoeba- pseudopodia. Ribosomes Made of RNA and proteins. Thousands in every cell. Site of protein manufacture. Bound ribosomes: Bound to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Make proteins for membranes. Make proteins for export Free ribosomes: Suspended in the cytoplasm Make proteins that remain in cytoplasm. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Network of membranes connected to the nuclear membrane Transport system of the cell. Rough ER Bound ribosomes• produce proteins inserted into membranes and exported out thru vesicles. Found in salivary glands. Smooth ER No ribosomes Lipid building Found in ovaries/testes Produce sex hormones Golgi apparatusProcessing and shipping center Flattened stacks One side-receiving dock- vesicles of proteins from ER. Golgi apparatus refines and modifies. Shipping side- sends finished product via vesicles to other parts of the cell. Some vesicles fuse with plasma membrane to release products outside of the cell. Lysosome Digestive plant of animal cell. Digest proteins, lipids, and carbs. Membrane sacs with digestive enzymes. 3 functions Fuse with food vacuoles to digest food Destroy harmful bacteria. Recycle damaged organelles. If a lysosome explodes the cell breaks down. Mitochodria Power house of the cell Site of cellular respiration; results in ATP. ATP= adenosine triphosphate- high energy molecule. Plant and animal cells Structure- envelope with 2 membranes. Cristae- internal folds, provide more sites for cellular respiration. Unique genetic structure; contains DNA Remnant genetic info, from bacteria Humans- mitochondria from Mom. Vacuoles Membrane sacs for storage Undigested nutrients, digestion, waste removal. Contractile vacuoles Pump out excess water in singlecelled organisms. Central vacuole- largest organelle in plants. Stores salts, absorbs water to expand cell. Pigments of flower petals. Poisons in leaf cells. Surface Structures Cell wall Plant cells; also algae, fungi and bacteria. Outside of cell membrane. Protects. Maintains cell shape. Provides support. Cellulose in plant cell wall. cellulose- tough carbohydrate. Wood, paper. Plasma (cell) membraneThin outer boundary of the cell. Regulates chemicals in/out of the cell. Semipermeable. Fluid-like. Proteins surrounded by a phospholipid bi-layer. Movement Structures FlagellaLong, thin whip-like structure Projects from the cell. Propels by “S” shaped motion. CiliaShorter, more numerous than flagella. Composed of microtubules. Moves the cell in “back and forth” motion