AP religions chart
advertisement

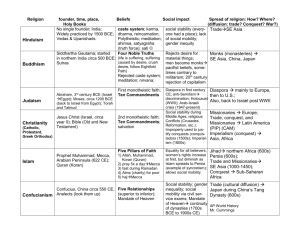
AP WORLD HISTORY Religion Religions: Period 2 Place, Time, Founder, Beliefs about Founder, Major Doctrine, Beliefs, Practices, Holy Books NAME ________________________________ Social Impact Spread, How? —diffusion: trade? Conquest? Diaspora in first century CE; anti-Semitism discrimination; Holocaust (WWII); Arab-Israeli crisis (1947-present) Diaspora mainly to Europe, then to U.S.; Also, back to Israel post WWII Jews themselves spread, but do not convert others Zoroastrianism Persian prophet Zoroaster Judaism First monotheistic faith; Ten Commandments rd One God created universe and he has Abraham, 3 century BCE (Israel Egypt); Moses, circa 1200 BCE (backspecial relationship with humans to Israel from Egypt); Torah Jews are chosen people and Talmud Moses leads them out of Israel All actions good or bad have an effect on this life and the next lives. God (Brahman)social stability (everyis in everything and everything is part of one had a place); lack of social mobility; god Hinduism No single founder; India; Widely practiced by 1500 BCE; Vedas & Upanishads Daoism Founded by Laozi caste system; karma, dharma, reincarnation;gender inequity Polytheistic; meditation; ahimsa, satyagraha (truth force); sati ]Focuses on living in harmony with nature Stresses simple ways of nature and the virture of yielding Views government as unnatural and as a body that should govern the people as Does not spread much outside of India little as possible Religion Place, Time, Founder, Beliefs about Founder, Major Doctrine, Beliefs, Practices, Holy Books Four Noble Truths Buddhism Siddhartha Gautama; started in northern India circa 500 BCE; Sutras Confucianism Confucius, China circa 550 CE, Analects (life is suffering, suffering caused by desire, crush desire, follow Eightfold Path) Rejected caste system; meditation; nirvana; Five Relationships (superior to inferior); Mandate of Heaven Social Impact Rejects desire for material things; Monks (monasteries) men become monks SE Asia, China, Japan pacifist beliefs, sometimes contrary to militarism; 20th century rejection of capitalism Social stability; gender inequality; social mobility via civil service exams; Mandate of Heaven continuity of dynasties (1700s BCE to 1900s CE) One God created universe and humans. Social stability during Christianity Jesus Christ (Israel, circa year 0); Bible (Old and New Testament) Spread, How? —diffusion: trade? Conquest? Trade (cultural diffusion) Japan during China’s Tang Dynasty (600s) Missionaries Europe; Middle Ages; religious 2nd monotheistic faith; Trade, conquest, and Conflicts (Crusades, Ten Commandments; Missionaries Latin Salvation—God sent Jesus to bring humans Reformation, etc.); America Improperly used to jusback to God tify conquests (conquis-tadors(PIP) (CAM) (1500s); ImperialImperialism (conquest) ism (1800s) Asia, Africa Most important missionary Paul. Peter is head of early Roman church M