Chapter 7
advertisement

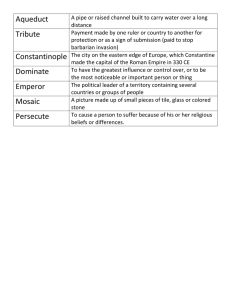
Chapter 9 (I) The Language of Faith: Symbolism and the Arts The Turning Point Emperor Constantine’s conversion in 312 C.E. The Reorganized Empire Diocletian (284-316 C.E.) saved the empire from the third-century crisis. Diocletian’s reform Diocletian Maximian Caesar Caesar Emperor Constantine 313 Edict of Milan Christianity became a legitimate faith. Emperor Constantine 325 Council of Nicaea Purpose: to establish the Christian dogma →the Nicene Creed The Nicene Creed http://www.goarch.org/en/resources/clipart/icondetail.asp?i=55&c =Other&r=Ecumenical_Synod Doctrinal Quarrels (1) (2) (3) Trinity: Christ = Father, Son, Holy Ghost Regionalism: regional hostilities were aggravated. Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches split in 1054. State involvement: Secular interference in Church matters increased, esp. in the East. Hierarchical Organization Patriarchs → bishops in charge of Rome, Jerusalem, Constantinople, Antioch, and Alexandria. Archbishops/metropolitans → provinces Bishops → dioceses Priests → parishes Primacy of the Bishop of Rome (1) a scene of the missionary activities and eventual martyrdom of the Apostles Peter and Paul. (2) the doctrine of the Petrine Succession Primacy of the Bishop of Rome (3) After the capital was moved to Constantinople, the pope replaced the Roman emperor as head of public administration. Spread of Monasticism Fourth century (1) A substitute for martyrdom: a desire to prove one’s religious ardor by self-abasement and suffering. (2) Monasticism satisfied the desires of those who wished to avoid secular temptations. St Simeon Stylite spent thirty-six years living on top of a pillar, in prayer and devotion. East: St. Basil (330-379) Features: fasting, poverty, and celibacy http://www.st-basil.org/ West: St. Benedict (480-547) The Benedictine rule http://www.mycatholictradition.com/ saint-benedict.html The Benedictine Rule Vows: poverty, chastity, obedience A program of “prayer and work” The Benedictine Rule Contributions: (1) Missionary work (2) Emphasize the dignity of Manual labor (3) Learning: Benedictine monasteries became centers for learning and transcribing in the Middle Ages. Women The rise of a negative attitude toward women? (Con) Spiritual egalitarianism: women could be saved as fully as men. (Pro) (1) Excluded from positions of leadership in church (2)Women > flesh; Men > spirit (3) Virginity accepted as the highest standard Marriage Marriage >>> procreation Women >>> limited roles submissive wives mothers Latin Church Fathers Jerome (c. 347-420) Ambrose (340-397) Gregory (c. 540-604) Augustine (354-430) St. Jerome Translated the Bible from Hebrew (OT) and Greek (NT) into Latin: the Vulgate St. Jerome (painted by El Greco) translated the Old and New Testaments into Latin. http://www.tihof.org/images/jerome/greco.jpg St. Jerome Much of the Bible was to be understood allegorically, rather than literally. Classical learning could be valid if subordinated to Christian aims. St. Augustine The Confessions : his autobiography. Established the dualistic model of reality: the “unclean body” and the “purified soul” (by extension, matter and spirit, earth and heaven, Satan and God, state and Church). St. Augustine On the City of God “City of Earth” vs. “City of God” Christianization of Classical Culture (1) A gradual winnowing out of the classical texts that had been produced in Greece and Rome between the 5th century B.C.E. and the 2nd century C.E. Christianization of Classical Culture (2) An understanding of the purposes of classical culture for a Christian audience. Early Christian Art sacophagus catacomb Christ as Good Shepherd Christ as the Good Shepherd, the mausoleum of Galla Placidia, Ravenna, c. 425426. Mosaic. http://mh1.xplana.com/imagevault/upload/c20fadda23a7d46f8003.jpg Christian Symbolism Symbolism and Early Christian Art: (a) Christian monograms; (b) symbols of the four evangelists; and (c) Latin and Greek crosses http://mh1.xplana.com/imagevault/upload/34b4a94ac52f06114f9d.jpg The chi-rho symbol Orans http://www.orderofcenturions.org/IMAGES/orans_catacomb2.jpg Food for Thought Study and identify the iconography of the life of Jesus. http://members.aol.com/nonsto pny/italiano/nativity.jpg The End