Community Health Education Methods Chapter 2

Community Health Education Methods
Chapter 2
PROMOTING HEALTH
EDUCATION IN A
MULTICULTURAL SOCIETY
Cultural Awareness
An understanding of concepts such as cultural awareness, cultural sensitivity, cultural competence, and multiculturalism has become necessary for a health educator to become effective.
Community based efforts have been initiated in response to disease among particular populations.
(i.e. stroke among African Americans.)
Terms to know
Diversity – Divergence among people, rooted in age, culture, health status and condition, ethnicity, experience, gender, sexual orientation, and various combination of these traits.
Cultural Awareness – The consciousness of cultural similarities and differences
Cultural Sensitivity – The knowledge that cultural differences exist
Terms to know
Cultural Competence – A characteristic of those who hold academic and interpersonal skills which allow an increased understanding and appreciation of another group’s difference and similarities.
Multiculturalism – A recognition of racial and cultural diversity, respect for beliefs and culture of others, and a recognition that all members of a society have contributions to make for its betterment.
Terms to know
Multicultural Education – refers to ‘the process of gaining an enhanced knowledge, understanding, and acceptance of the methods of constructive interactions among people of differing backgrounds.’
Diversity Awareness
It is imperative that a health educator become aware of diversity and his of her role in ensuring that diversity issues are addressed.
Being culturally competent results in the health educators going the extra mile to ensure that their workplaces and services they provide are inclusive to all.
Building skills that create an inclusive environment are also important.
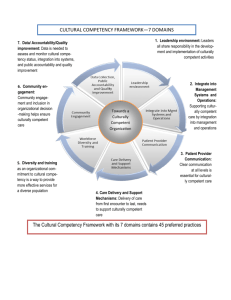
Culturally Competent
The process of becoming culturally competent is not a single-time intervention, but one that needs constant reevaluation and reappraisal both at the individual and organizational levels.
A culturally competent health educator is in a position to determine the extent of the cultural competence of the professional setting, assess and document strengths and weaknesses of the organization, and focus on areas for improvement.
An Inclusive Environment
1)
2)
When creating an inclusive environment, think of these 6 areas of concern
The use of language and verbiage
Understanding the focus population culture
3)
4)
5)
6)
Discussing guidelines
Facilitation skills
Use of materials
Teaching techniques and learning styles
Tips for Incorporating Cultural Competence
Take small steps towards change
Infuse cultural issues into facilitation
Know limits
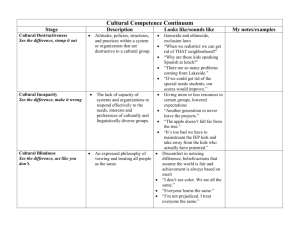
Group Discussion Guidelines
Guidelines for establishing inclusiveness within group discussions
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Respecting the confidentiality of all participants actions and comments
Being sensitive to different levels of expertise among the group
Being sensitive to different personal experiences of group members
Avoiding assumptions about the cultural or ethnic backgrounds of group members
Allowing privacy
Other guidelines the group deems important in order to facilitate tolerance and respect for everyone’s point of view
Your Group
How was inclusiveness established for this course?
How can you ensure inclusiveness within the community group with which you will be working?
Noreen Clark
Noreen Clark, dean of the School of Public Health at the University of Michigan states
“As a society we have to get agreements on what is important, what we value…It’s not a matter of your values being better than mine…It’s a matter of creating a society where both our values coexist.”
What is the key point of her quote?
Professional Barriers
In the health education field, the greatest barriers to multiculturalism confronting health educators are a lack of the following: research, available health education programming specifically targeting diverse populations, and pre-professional training.
Tips for avoiding professional barriers
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Being aware and accepting of cultural differences
Having the ability for cultural self-assessment
Having the required awareness, understanding, and knowledge of focus populations
Developing skills that facilitate diversity
Being sensitive to dynamics inherent with cultural interaction