the sales comparison approach
advertisement

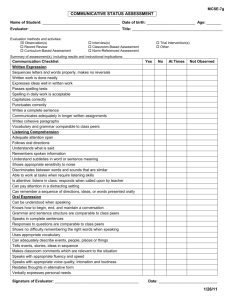
Chapter 8 THE SALES COMPARISON APPROACH CHAPTER TERMS AND CONCEPTS Adjustment techniques Assessment Roll Bracketing Buyer’s motives Central tendency Comparable sale Comparable sale search area Competitive property Concessions Linear and multiple regressions Location Mean Median Mode 2 CHAPTER TERMS AND CONCEPTS Open-market transaction Physical characteristics Public records Range Sales comparison approach Sales history Sample Seller’s motives Standard deviation Submarket Terms of sale Variables Verification 3 LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. List and explain the four steps in the sales comparison approach. 2. Explain the important concepts behind this approach. 3. Explain how comparable. to decide if a sale is 4. Discuss what information about comparable sale should be collected. a 5. Identify the major sources of market data. 6. Outline the statistical techniques appraisers can use to analyze sales. SALES COMPARISON APPROCH Collect Comparable Sales MLS, Public Record, Commercial databases Analyze and Compare them to the Subject Property Adjust for Differences between the Sales and the Subject (market adjustments) Arrive at a Value Opinion for Subject Property Sales Comparison Approach Steps Figure 8-1 Key Concepts of the Sales Comparison Approach • The importance of substitution • The simplicity of market comparisons • The relationship to statistics • The relevance of adjustments • The significance of market data SIGNIFICANCE OF SALES COMPARISON APPROACH • Based upon the Principle of Substitution • Simple, Direct and Reliable • Has Statistical Connections • Includes Methods for Adjusting for Property Differences • Provides Data for Other Approaches Income and cost approaches STATISTICAL CONNECTIONS Samples Market Activity Identifies Market Patterns Brackets the Value Indicates the Most Probable Price SELECTING THE COMPARABLE SALES The Competitive Property Same neighborhood? Define search area Open-Market Transactions Listed in MLS? Date of Sale Close to date of valuation SELECTING THE COMPARABLE SALES How Comparable? Square footage, # bedrooms, # baths Design, age, & amenities Sales History of Subject Three years prior to date of value What Is a Comparable Sale? Figure 8-5 COMPARABLE SALES DATA Transaction Data Date of sale Sales price and terms Legal description Grantor and grantee Personal property included Motivation of Parties Physical Data Land: Size, shape, topography, utilities available Improvements: size & type, quality, condition, special features, any problems COMPARABLE SALES DATA Legal Data Zoning Taxes and assessments Public and private restrictions Location Comparability Detrimental influences Market Conditions General state of the market Availability of financing TESTS OF COMPARABILITY Each Comparable Sale Should Be A competitive property An open market transaction Close in time to the date of value Comparing Locations Figure 8-8 MARKET DATA SOURCES • • • • • • Public Records Multiple Listing Services (MLS) Private/Commercial Data Services Title Insurance Companies Parties to the Transaction Appraisers’ Files SAMPLE GRANT DEED 18 SALES DATA EXAMPLE Figure 8-10 19 DATA RESOURCES ON THE INTERNET Websites of Government Agencies General data on the economy Regulatory information affecting real estate Websites of Industry Service Organizations Industry trends and guidelines Construction cost estimating services Market data banks, appraisal support DATA RESOURCES ON THE INTERNET Websites of Trade Associations Member information services General information for the public APPRAISAL STATISTICAL CONCEPTS Central Tendency Mean = Average value or price Median = Middle value or price Mode = Most common value or price Range = Difference between high and low value Standard Deviation = Description of how values differ from the mean Linear and Multiple Regression Can Calculate relationships between property features and property price Can Suggest value of the subject property SUMMARY The sales comparison approach is one of the three approaches used to estimate value. The main feature of the sales comparison approach is the process of analyzing sales and comparing them to the subject property, based on the principle of substitution. The sales comparison approach consists of four steps. 1. Research the sales. 2. Analyze the sales. 3. Adjust the sales for differences between the sales and the subject property. 4. Arrive at a value estimate.