Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
advertisement

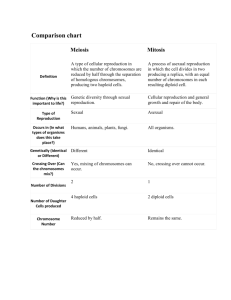
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Fertilization of an egg cell by a sperm cell. In sexual reproduction, haploid gametes fuse to produce a diploid zygote. Some species have two parents, whereas others have just one. Asexual reproduction produces an identical individual Sexual reproduction produces a similar but unique individual In sexual reproduction, a cell division process called meiosis produces eggs and sperm that join during fertilization to produce a new individual. Asexual Reproduction and mitosis Are there male and female bacteria? How would you be able you tell? • Bacteria have just one chromosome; they do not have an X or Y chromosome. They have a very simplified form of reproduction. All prokaryotic and many eukaryotic organisms reproduce asexually. • Cell divides after DNA is replicated. • No gametes are formed, • also occur by fragmentation (a piece of the organism breaking off) Asexual reproduction has advantages and disadvantages. Advantages of asexual reproduction • Simplest and quickest method of reproduction • Produces a clone (an organism that is genetically identical to its parent) • Requires only one parent • Stronger populations in a more favorable environment Disadvantages of asexual reproduction • No genetic variation Without genetic variation, populations can only evolve very slowly because it depends on random mutations for evolution. • Does not allow organisms to adapt to changing environment Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Each gamete is haploid • Each parent contributes ½ of the genetic material for the offspring. • Gametes fertilize to make a diploid offspring. Gametes form through the cell division process called meiosis Sexual reproduction has advantages and disadvantages Advantages of sexual reproduction • Offspring are all different, organisms are able to adapt and evolve to a changing environment • Stronger populations in a less desirable environment • Highly diverse, offspring are a genetic recombination of parents, there is also opportunity for many mutations in meiosis Disadvantages of sexual reproduction • Two parents are required, process is longer the population cannot grow as quickly Similarities and/or Differences Both are methods of reproduction • Asexual one parent is needed and offspring are identical • Sexual two parents are needed and offspring are genetically unique Mutation is a source of variation in both • Asexual offspring are otherwise identical to parent • Sexual offspring are a genetic recombination of parents Start Day 2 Meiosis and Reproduction Do you have ALL your parents' chromosomes? No, you only received half of your mother's chromosomes and half of your father's chromosomes. If you inherited them all, you would have twice the number of chromosomes that you're supposed to have. Humans have 23 pairs. If you received all your parents' chromosomes, you would have 46 pairs! What monomer is DNA is made of? 1. 2. 3. 4. Glucose Amino acid Nucleic acid Phospholipids HAPLOID VS. DIPLOID • A cell with two sets of chromosomes is diploid, referred to as 2n, where n is the number of sets of chromosomes. • Most of the cells in a human body are diploid. • A cell with one set of chromosomes, such as a gamete, is haploid, referred to as n. Gametes are haploid When a haploid sperm (n) and a haploid egg (n) combine, it is called fertilization, and a diploid zygote will be formed (2n). In short, when a diploid zygote is formed, half of the DNA comes from each parent. Which process creates gametes? 1. 2. 3. 4. Meiosis Mitosis Electron transfer chain Gametification During meiosis, four haploid cells are created from one diploid parent cell. MEIOSIS I Meiosis I is where the genetic variation is introduced into the daughter cells. During meiosis I, the pairs of homologous chromosomes are separated from each other. 1. Prophase I: The homologous chromosomes line up together. During this time, a process that only happens in meiosis can occur. This process is called crossing-over, which is the exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes. Crossing-over forms new combinations of alleles on the resulting chromosome, in other words it creates genetic variation. Without crossing-over, the offspring would always inherit all of the alleles on one of the homologous chromosomes. Also during prophase I, the spindle forms, the chromosomes condense as they coil up tightly, and the nuclear envelope disappears. 2. Metaphase I: • The homologous chromosomes line up in their pairs in the middle of the cell. • Chromosomes from the mother or from the father can each attach to either side of the spindle. • Their attachment is random, so all of the chromosomes from the mother or father do not end up in the same gamete. This is called random alignment. 3. Anaphase I: The homologous chromosomes are separated as the spindle shortens, and begin to move to opposite sides of the cell. 4. Telophase I: • The spindle fibers dissolves, but a new nuclear envelope does not need to form. • No DNA replication occurs between meiosis I and meiosis II because the chromosomes are already duplicated. After Meiosis 1 how many copies of DNA are in the dividing cells? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1n 2n 3n 4n During crossing-over, segments of DNA are exchanged between non-sister chromatids. Notice how this can result in an allele (A) on one homologous chromosome being moved onto the other member of the pair. MEIOSIS II During meiosis II, the sister chromatids are separated and the gametes are generated. The steps are outlined below: 1. Prophase II: The chromosomes condense. 2. Metaphase II: The chromosomes line up one on top of each other along the middle of the cell. The spindle is attached to the centromere of each chromosome. 3. Anaphase II: The sister chromatids separate as the spindle shortens and move to opposite ends of the cell. 4. Telophase II: A nuclear envelope forms around the chromosomes in all four cells. This is followed by cytokinesis. An overview of meiosis. Fertilization happens when two gametes join to form a zygote Fertilized egg cells contain all of the genes to make a new organism. Fertilization is an additional way that sexual reproduction increases genetic variation, because it results in the combination of genes from two separate individuals. Review Questions 1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of asexual reproduction? 2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction? 3. How many chromosomes does a diploid human cell have? How many chromosomes does a haploid human gamete cell have? 4. What happens during metaphase I of meiosis? How does this compare to the metaphase of mitosis? 5. What is the product of meiosis? 6. Describe crossing-over.