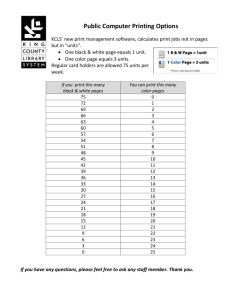
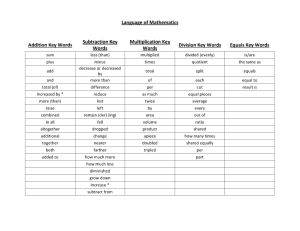
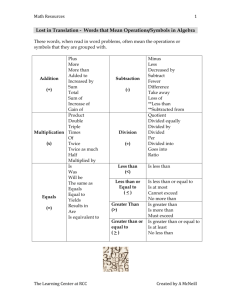
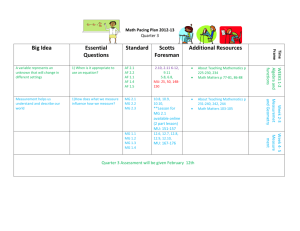
1. - s3.amazonaws.com
advertisement

1-4 Chapter 1 1. 1.-----'s law code is important because it introduced legal concepts like an "eye for an eye" that would influence Western law. Student Response Correct Answer Equals Hammurabi (100%) Equals Hammurabi's (100%) Equals Hammurabis (100%) 1. hammurabi General Feedback: See pages 24-25. Score: 1/1 2. Historians have organized Egyptian history into Student Response A. the Old Kingdom, the Intermediate Period, and the New Kingdom. B. Correct Answer Feedback the Pre-Dynastic period, the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom. C. the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom. D. the Old Kingdom and the New Kingdom. General Feedback: See page 25. Score: 1/1 3. The two main cultures of Neolithic Europe are known as Student Response A. the Villanovans and the Kurgans. B. the Stonehenge people and the Kurgen people. C. the Linear Pottery cultures and the Battle Axe cultures. D. the eastern Neolithic cultures and western Neolithic cultures. General Feedback: See pages 27-28. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Feedback 4. Stonehenge is a famous megalithic structure in 1.-----. (Hint: Name of country.) Student Response Correct Answer Equals England (100%) Equals Great Britain (100%) 1. england General Feedback: See page 28. Score: 1/1 5-9 Chapter 2 5. The international trade in bronze after 1600 BCE Student Response Correct Answer Feedback Correct Answer Feedback A. did not influence the development of western civilization. B. led to the emergence of a common language in Asia and Africa. C. helped create common religious practices among five separate regions. D. helped lay the foundations of western civilization. General Feedback: See pages 33-34. Score: 1/1 6. Women in Egyptian society Student Response enjoyed equality with men in A. matters of property and inheritance. B. were not allowed access to religious services. C. were considered inferior to men in every way. D. had no property rights. General Feedback: See page 37. Score: 1/1 7. The two distinctive civilizations that developed in the eastern Mediterranean during the International Bronze Age were the 1.----- and Mycenaean civilizations. Student Response Correct Answer Equals Minoan (100%) Equals Minoans (100%) 1. minoan General Feedback: See page 44. Score: 1/1 8. 1.-----'s Iliad and the Odyssey tell us more about the social conditions during the International Bronze Age than they do about the Trojan War. (Hint: Name of author). Student Response 1. homer General Feedback: See page 48. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Equals Homer (100%) 9. The Phoenicians' most important cultural contribution was Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. military strategy. B. the alphabet. C. temple architecture. D. the wheel. General Feedback: See page 51. Score: 1/1 10-15 Chapter 3 10. The foundations of Western culture are linked to Student Response A. Roman imperial power and Greek democracy. B. Hebrew religious beliefs and Persian imperial power. C. Hebrew monotheism, Greek philosophy, and Persian imperial power. Correct Answer Feedback D. Greek philosophy and Persian imperial power. General Feedback: See pages 57-58. Score: 1/1 11. The Persian leader who conquered the Medes, Asia Minor, and Babylonia was 1.----- the Great. Student Response 1. cyrus Correct Answer Equals Cyrus (100%) General Feedback: See page 59. Score: 1/1 12. The Hebrew prophets Student Response Correct Answer Feedback Correct Answer Feedback were social critics who urged A. moral reform among the Hebrews. B. suggested that all Hebrews should obey the kings without question. C. argued that the Hebrew commoners should focus exclusively on the afterlife. D. believed observance of religious rituals was critical to political success. General Feedback: See pages 63-64. Score: 1/1 13. What was the status of women in Judaism? Student Response A. They served as the priests of the religion. B. They were considered insignificant. C. Their role was critical because membership in Judaism depended on the mother. D. They alone were allowed knowledge of the Torah. General Feedback: See page 65. Score: 1/1 14. All of the following are true about Greek women except Student Response women could freely divorce A. abusive husbands. Correct Answer Feedback Correct Answer Feedback B. married women were usually confined to their homes. C. some women did work outside the home selling cloth in the market place. D. women were primarily valued as mothers of legitimate sons. General Feedback: See pages 79-80. Score: 1/1 15. Greek science is significant because Student Response Greek scientists rejected the A. role of the gods in nature and instead worked to develop general principles to explain natural phenomena. B. Greek scientists were able to find the fundamental substance of the universe. C. Greek scientists were able to prove the role of the gods in natural phenomena D. Greek scientists demonstrated the inaccuracy of Babylonian scientific data. General Feedback: See pages 83-84. Score: 1/1 CHP 4 1. The period 336-31 B.C.E. is referred to as the Hellenistic age because Student Response Correct Answer Feedback Correct Answer Feedback A. it is named after Helen of Troy. B. the Greeks were known as Hellenes and Greek culture dominated this period. C. it was a period of Persian domination of the Greek or Hellenic world. D. Alexander the Greatʹs nickname was Hellenistes. General Feedback: See pages 93-94. Score: 1/1 2. During the Hellenistic era Student Response A. non-Greek peoples fiercely rejected any encounter with Greek culture. B. the Greeks remained totally uninterested in non-Greek cultures and peoples. C. Greek culture replaced the local cultures across the Hellenistic world. D. Greek culture absorbed many non-Greek elements from non-Greek peoples. General Feedback: See page 94. Score: 1/1 3. Alexander the Great was successful because Student Response A. his soldiers had sworn an oath of loyalty to his father. B. he was a successful soldier and brilliant military leader. C. he was able to buy peace Correct Answer Feedback with the Persian Empire. D. he successfully assassinated his closest rivals. General Feedback: See pages 96-97. Score: 1/1 4. Probably the most famous and most cosmopolitan Hellenistic city was 1.----- in Egypt. Student Response 1. alexandria Correct Answer Equals Alexandria (100%) General Feedback: See page 103. Score: 1/1 5. All of the following are true of women during the Hellenistic era except Student Response A. women were granted full citizenship. Correct Answer Feedback B. women help religious offices. C. women were allowed to compete as athletes in the Olympic games. D. aristocratic women wielded a great deal of political power. General Feedback: See page 103. Score: 1/1 6. The philosophic schools during the Hellenistic era included all of the following except Student Response A. the Sophists. B. the Stoics. C. the Epicureans. D. the Cynics. General Feedback: See pages 104-105. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Feedback 7. Galen Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. was a famous Hellenistic mathematician. B. was a famous Hellenistic astronomer. C. was a famous Hellenistic literary figure. D. was a famous Hellenistic doctor. General Feedback: See page 106. Score: 1/1 8. During the early years after Romeʹs founding, the Roman political system Student Response A. was a democracy. B. Correct Answer Feedback was a monarchy. C. was a republic. D. was an oligarchy. General Feedback: See pages 111-112. Score: 1/1 9. The Roman 1.----- was really just a very powerful advisory body to the consuls. Student Response 1. senate Correct Answer Equals Senate (100%) General Feedback: See age 113. Score: 1/1 10. The 1.----- of the of Orders was a conflict between the patricians and plebians and ultimately led to greater political power for the plebians. Student Response 1. struggle Correct Answer Equals Struggle (100%) Equals Struggle of (100%) Equals Conflict (100%) Equals Conflict of (100%) General Feedback: See page 113. Score: 1/1 11. When Rome defeated its enemies in Italy, it Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. forced the defeated peoples to adopt all Roman religious and cultural practices. B. enslaved all conquered peoples. C. killed off many people in the defeated cities to inspire fear in the defeated peoples. D. allowed the defeated peoples to become citizens. General Feedback: See pages 114-115. Score: 1/1 12. At the Battle of Zama in 202 BCE, Scipio decisively defeated 1.-----. (Hint: Name of person). Student Response 1. hannibal Correct Answer Equals Hannibal (100%) General Feedback: See page 117. Score: 1/1 13. All of the following are true of the Roman family except Student Response A. the family included the husband, wife, children, and anyone dependent on the household, including slaves. B. the male head of household held total power over his wife and children. C. the eldest female was considered the head of the household. D. marriage required the Correct Answer Feedback agreement of both the man and the woman to be considered legal. General Feedback: See pages 122-123. Score: 1/1 14. 1.----- was assassinated by a group of senators in 44 BCE. (Hint: Name of person). Student Response 1. caesar General Feedback: See pages 125-126. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Equals Julius Caesar (100%) Equals Caesar (100%) Equals Ceasar (100%) Equals Julius Ceasar (100%) Equals Cesar (100%) Equals Julius Cesar (100%) 15. At the Battle of Actium in 31 B.C.E., 1.----- defeated Antony and Cleopatra. (Hint: Name of person) Student Response 1. octavian General Feedback: See page 127. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Equals Octavian (100%) Equals Augustus (100%) Equals Octavius (100%) CHP 5 1. The 1.----- refers to a long period of stability and peace in the Roman Empire. (Hint: 2 word Latin phrase) Student Response 1. Pax Romana Correct Answer Equals Pax Romana (100%) General Feedback: See page 132. Score: 1/1 2. Octavian called himself Princeps because Student Response Correct Answer Feedback he wanted to pretend that he A. was not really an emperor. B. he wanted to be considered a prince of Rome. C. he wanted everyone to know he was really an emperor. D. he wanted everyone to consider him the chief priest of all Roman religion. General Feedback: See page 132. Score: 1/1 3. The cult of the emperor was useful to the empire because Student Response A. it provided a target for the anger of the conquered peoples. B. it provided a unifying force for the empire. C. it served as the chief religion of the senate. D. it united the military. General Feedback: See pages 135-137. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Feedback 4. The 1.----- was a large track for chariot races. (Hint: Name of place.) Student Response Correct Answer Equals Circus Maximus (100%) Equals circus (100%) Equals hippodrome (100%) 1. Circus Maximus General Feedback: See page 138. Score: 1/1 5. The emperors of Rome ultimately based their power on Student Response A. Correct Answer Feedback the Roman Senate. B. the non-Roman citizens in the provinces. C. the Roman common people. D. the Roman army. General Feedback: See page 140. Score: 0/1 6. Wealth in the Roman provinces was centered in the Student Response A. the Roman law. B. Correct Answer Feedback provincials in the cities. C. the Roman military. D. farmers in the countryside. General Feedback: See page 141. Score: 1/1 7. The only successful revolt against Roman rule occurred in Student Response A. Jerusalem B. Britain C. Germany Correct Answer Feedback D. Spain General Feedback: See pages 145-147. Score: 1/1 8. 1.----- led a revolt against the Romans in Britain. (Hint: Name of person.) Student Response Correct Answer Equals Boudica (100%) Equals Boudicca (100%) Equals Boudiccea (100%) 1. Boudica General Feedback: See page 147. Score: 1/1 9. The main forces of Romanization in the provinces were Student Response Correct Answer A. the Roman army and Roman religion. B. the Roman army and Roman administrators. C. the Roman army and Roman law. D. the Roman army alone. General Feedback: See pages 149-150. Score: 1/1 10. The 1.----- Decree gave Roman citizenship to all free men and women in the empire. Student Response 1. Antonine Decree General Feedback: See page 149. Score: 1/1 11. Correct Answer Equals Antonine (100%) Equals Antonine Decree (100%) Equals Constitutio Antoniniana (100%) Feedback Roman citizens enjoyed all these legal rights except Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. the right to serve in the legions B. the right to commit suicide. C. the right to vote in assemblies. D. the right not to be made a slave. General Feedback: See page 149. Score: 1/1 12. All of the following are true about slavery during the Roman Empire except Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. it was widespread. B. people became slaves mainly through conquest. C. few Romans opposed or objected to slavery as an institution. D. slaves were always enslaved for life. General Feedback: See pages 154-155. Score: 1/1 13. 1.----- wrote a famous history of Rome consisting of 142 volumes. Student Response Correct Answer Equals Livy (100%) Equals Titus Livius (100%) Equals Titus Livy (100%) 1. Livy General Feedback: See page 156. Score: 1/1 14. The Romans tried Jesus as a Student Response A. religious fanatic. Correct Answer Feedback B. revolutionary. C. traitor to the Roman military. D. blasphemer. General Feedback: See pages 160-164. Score: 1/1 15. The Roman emperors Student Response A. never persecuted the Christians. B. began to persecute Christians as early as the reign of Claudius. C. only persecuted Christians in Jerusalem. D. welcomed Christianity as soon as it emerged. General Feedback: See page 165 Score: 0/1 Correct Answer Feedback Chp 6 1. All of the following contributed to the breakdown of the Roman Empire during the 200s except Student Response A. Correct Answer Feedback rampant deflation. B. unstable leadership. C. invasions in both the east and the west. D. the emergence of Christianity. General Feedback: See pages 170-171 Score: 0/1 2. One of 1.-----ʹs key reforms was his decision to divide the Roman empire into two parts. Student Response 1. Diocletian General Feedback: See pages 172-174. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Equals Diocletian (100%) Equals Emperor Diocletian (100%) Equals Diocletion (100%) Equals Emperor Diocletion (100%) 3. 1.----- defeated Maxentius at the battle of the Milvian Bridge. (Hint: Name of person) Student Response 1. Constantine General Feedback: See page 175. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Equals Constantine (100%) Equals Emperor Constantine (100%) 4. How did Constantine solidify the movement of the Roman Empire to the east? Student Response Correct Answer Feedback He built a new capital city A. called Constantinople in the east. B. He married a Persian princess. C. He gave the western half of the Roman Empire to the Goths. D. He converted to Zoroastrianism. General Feedback: See pages 175-176. Score: 1/1 5. Early Christian leaders modeled their administrative structures on Student Response A. the Bible. Correct Answer Feedback B. Roman pagan religious administration. C. Roman imperial urban administration. D. Persian imperial urban administration. General Feedback: See pages 176-177. Score: 1/1 6. The doctrine of the 1.----- succession was used to justify the preeminent position of the Bishop of Rome over all other Bishops. Student Response Correct Answer Equals Petrine (100%) Equals Petrine Succession (100%) 1. Petrine General Feedback: See page 177. Score: 1/1 7. 1.----- the Apostate tried to restore the old Roman religious beliefs during his reign. Student Response 1. Julian Correct Answer Equals Julian (100%) General Feedback: See page 179. Score: 1/1 8. The disagreement between the Arians and Athanasians concerned Student Response Correct Answer Feedback the nature of Jesus and the A. nature of the Trinity. B. the Petrine succession. C. the relationship between the pope and the emperor. D. the relationship between Christians and nonChristians in the Roman empire. General Feedback: See page 180. Score: 1/1 9. All of the following are true of Asceticism except Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. it was begun by an Egyptian Christian named Antony. B. it allowed a limited number of physical comforts like adequate food and shelter. C. it called for punishment of the body. D. it claimed Christians needed to give up their physical desires if they hoped to have a good spiritual life. General Feedback: See page 182. Score: 1/1 10. As Christianity emerged in the Roman Empire, Jews Student Response A. enjoyed less persecution. B. were allowed to return to Jerusalem and rebuild the Temple. C. suffered greater persecution Correct Answer Feedback and repression. D. continued to enjoy the leadership of the Jewish Patriarch. General Feedback: See pages 185-186. Score: 1/1 11. 1.----- wrote The City of God. Student Response 1. Augustine Score: Correct Answer Equals Augustine (100%) Equals Saint Augustine (100%) Equals St. Augustine (100%) Equals Augustine of Hippo (100%) 1/1 12. The appearance of the 1.----- forced the Visigoths into a violent confrontation with the Roman Empire. (Hint: Group of people). Student Response 1. huns Correct Answer Equals Huns (100%) General Feedback: See pages 191-194. Score: 1/1 13. All of the following are true of Attila the Hun except Student Response his empire survived intact A. after his death. B. he was ultimately stopped by a combined force of Romans, Visigoths, and other German tribes. C. he was nicknamed the "Scourge of God." D. his empire collapsed after his death. General Feedback: See pages 192-195. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Feedback 14. The collapse of the Roman Empire in the West Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. happened in just a few years. B. happened gradually over a number of years. C. happened because of the emergence of Christianity. D. was halted by 476. General Feedback: See pages 195-202. Score: 0/1 15. 1.-----ʹs Corpus of Civil Law (Corpus Juris Civilis) preserved Roman law for future generations. Student Response Correct Answer Equals Justinian (100%) Equals Emperor Justinian (100%) Equals Justinian's (100%) Equals Emperor Justinian's (100%) 1. Justinian General Feedback: See page 197. Score: 1/1 CHP 7 1. 1.----- and Methodius invented an alphabet for the Slavic language. Student Response 1. Cyril Correct Answer Equals Cyril (100%) General Feedback: See page 209. Score: 1/1 2. The religious and political ties between the Rus and Byzantium Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. led to the establishment of Latin Christianity across eastern Europe. B. limited the spread of Latin Christianity in eastern Europe. C. led to the development of a Latin ritual for the eastern Orthodox Church. D. helped consolidate the Bulgars control of Constantinople. General Feedback: See page 209. Score: 1/1 3. The highest point of the Kievan Rus occurred during the reign of 1.----- the Great and Iaroslav the Wise. Student Response 1. Vladimir General Feedback: See page 210. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Equals Vladimir (100%) 4. Heraclius' triumph in Persia Student Response A. led to his victory over the Correct Answer Feedback Islamic armies. B. was widely views as unjust and wrong among the inhabitants of Byzantium. C. did not win back the holy relic of the True Cross for Byzantium. D. overextended Byzantine resources and made Byzantium unable to resist Islamic armies. General Feedback: See pages 211-212. Score: 1/1 5. The three institutions critical to the survival of the Byzantine Empire were Student Response Correct Answer Feedback the emperor, the army, and A. the Christian Church. B. the emperor, the imperial bureaucracy, and the Christian Church. C. the emperor, the army, and slavery. D. the emperor, the imperial bureaucracy, and the army. General Feedback: See page 213. Score: 1/1 6. The Byzantine emperor who first challenged the use of icons was 1.-----. Student Response Correct Answer Equals Leo III (100%) Equals Leo the third (100%) Equals Emperor Leo (100%) Equals Emperor Leo III (100%) 1. Leo III General Feedback: See page 215. Score: 1/1 7. What best describes the outcome of the Iconoclast controversy? Student Response A. Icon veneration was successfully banned across the Christian west. Correct Answer Feedback B. The papacy supported and aided the emperor in the successful end of the use of icons in Christianity. C. Icons were temporarily banned but ultimately restored as an important part of the Orthodox religious practice. D. Icon veneration was successfully ended in the Byzantine empire. General Feedback: See pages 215-216. Score: 1/1 8. The Seljuk Turks defeated the Byzantine armies at the battle of 1.----- in 1071. Student Response 1. Manzikert General Feedback: See page 219. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Equals Manzikert (100%) 9. Before Islam emerged, Arab religious beliefs were Student Response Correct Answer Feedback mainly polytheistic, though A. they did have exposure to monotheism. B. a sect of Christianity. C. a sect of Judaism. D. an early form of Zoroastrianism. General Feedback: See pages 219-220. Score: 1/1 10. Arab communities before the emergence of Islam Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. were matriarchal. B. were generally organized into tribes. C. were organized around a single emperor. D. were formally bound together as a single unified tribe. General Feedback: See pages 219-222. Score: 1/1 11. The 1.----- is the written collection of Muhammad's revelations. Student Response Correct Answer Equals Qu'ran (100%) Equals Quran (100%) Equals Qur'an (100%) 1. Qur'an General Feedback: See page 222. Score: 1/1 12. The word "1.-----" means submission. Student Response 1. Islam Correct Answer Equals Islam (100%) General Feedback: See page 222. Score: 1/1 13. When 1.----- died in 632, most of the Arabian peninsula had converted to Islam. Student Response 1. Muhammad General Feedback: See page 222. Score: 1/1 14. The Shiites emerged after Correct Answer Equals Muhammad (100%) Student Response Correct Answer Feedback A. Muhammadʹs cousin Ali was visited by the angel Gabriel. B. a dispute over who should succeed Muhammad after his death. C. the first jihad. D. the collapse of the Umayyad dynasty. General Feedback: See page 226. Score: 1/1 15. The Umayyads adopted Arabic as the official language of their empire because Student Response they believed a single A. language would serve as a unifying force for the empire. B. it was the language of the Quʹran. C. most of their conquests were in Arabic-speaking areas already. D. Arabic was easier to learn than Greek or Latin. General Feedback: See pages 226-228. Score: 1/1 Correct Answer Feedback