File
advertisement

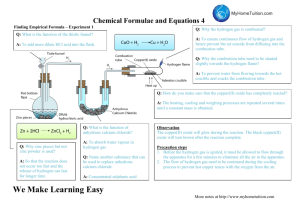
Using the idea of moles to find formulae The empirical formula of a chemical compound is the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound • 3.2g of copper reacted with 0.8g of oxygen. What is the formula of the oxide of copper that was formed? (At. Mass Cu=64: O=16) Substance Copper oxide 1. Elements Cu 2. Mass of each element (g) 3.2 3. Mass / Atomic Mass 4. Ratio (divide by lowest) 5. Formula O 0.8 0.8/16 =0.05 3.2/64 =0.05 1:1 CuO • We found 0.50g of magnesium reacted with 0.28g of oxygen. What is the formula of the magnesium oxide that was formed? (At. Mass Mg=24: O=16) Substance Magnesium oxide 1. Elements Mg 2. Mass of each element (g) 3. Mass / Atomic Mass 4. Ratio (divide by lowest) 0.50 5. Formula O 0.28 0.50/24 = 0.02 1:1 MgO 0.28/16 =0.02 An oxide of hydrogen Calculate the empirical formula of a compound with the percentage composition: C 39.13%; O 52.17%; H 8.700%. It is clear at this stage that dividing by the smallest has not resulted in a simple ratio. You must not round up or down at this stage. You must look at the numbers and see if there is some factor that you could multiply each by to get each one to a whole number. If you multiply each by 3 you will get: C O H 3 3 8 So C3H8O3 is the empirical formulae You need to be careful about this; the factors will generally be clear and will be 2 or 3. You must not round 1.33 to 1 or 1.5 to 2. Exercise 5: Calculation of formulae from experimental data pp52-