THE NEWBORN

THE NEWBORN
“I had heard about the negatives---the fatigue, the loneliness, loss of self. But nobody told me about the wonderful parts: holding my baby close to me, seeing his first smile, watching him grow and become more responsive day by day.....For the first time I cared about somebody else more than myself, and I would do anything to nurture and protect him.”
Respiratory Changes
Intrauterine
• Lungs serve no respiratory function
• Oxygen supply secured through the placenta
• Lungs are filled with lung fluid which keeps them partially expanded
Extrauterine
• Within a few minutes after birth the vital capacity is established
• Surfactant reduces surface tension in alveoli and keeps lungs from collapsing
Respiratory Changes
Mechanical
Initiation of
Breathing
Chemical
Sensory
Chemical Events
1. With cutting of the cord, remove oxygen supply
2. Asphyxia occurs
3. CO
2 and O
2 and pH = ACIDOSIS
4. Acidotic state-- stimulates the respiratory center in the medulla and the chemoreceptors in carotid artery to initiate breathing
Mechanical Events
• As the chest passes through the birth canal the lungs are compressed
Fluid expelled
• Subsequent recoil of the chest wall produces passive inspiration of air into the lungs
Air Enters
Mechanical Events
About 60-110 ml. of fluid is squeezed out of the lungs as the chest is compressed
The remaining fluid evaporates or is reabsorbed by the blood vessels and lymphatics surrounding the lungs.
**When a baby is delivered in a presentation other than vertex, it takes longer for the lungs to rid themselves of the fluid
Sensory Events
Thermal-the decrease in environmental temperature after delivery is a major stimulus of breathing
Tactile-nerve endings in the skin are stimulated
Visual-change from a dark world to one of light
Auditory-sound in the extrauterine environment stimulates the infant
Answer this !
Answer
This!
• When a baby is born by cesarean delivery, which of the mechanisms to initiate breathing does it lack?
Cardiovascular
Changes
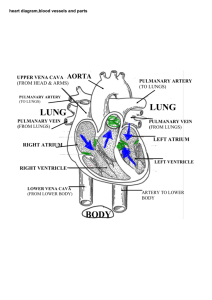
Fetal Circulation
Placenta Umbilical Vein Liver
Ductus venosus Inferior Vena Cava
Right Atrium Foramen Ovale
Left Atrium Left Ventricle Aorta
Fetal Circulation
Enters Rt. Atrium
Foramen Ovale
Lf. Atrium
Lf. Ventricle
Aorta
To the Body
RA
RV
LA
LV
To the body
Fetal Circulation
or
Right Atrium Right Ventricle
Pulmonary Artery Ductus Arteriosus
Aorta Body
(Small amount goes to the lungs)
Fetal Circulation
Aorta
OR
• Right Atrium
Ductus
Arteriosus
• Right Ventricle
• Pulmonary Artery
RA
LA
LV
RV
• Ductus Arteriosus
• Aorta
Cardiovascular Changes
1. Oxygen enters the lungs, and pulmonary alveoli expand
2. Oxygen lowers resistence in the pulmonary vessels allowing blood to flow more freely to and from the lungs
3. Pressure in the right atrium decreases because of flow of blood to the lungs
4. Pressure in the left atrium increases because of flow of blood from the lungs
5. With oxygenation, the ductus arteriosus begins to constrict, becoming functionally closed
6. As pressure in the left side fo the heart begins to exceed that in the right side, the foramen ovale becomes closed.
Cardiovascular Changes
3. Ductus Arteriosus begins to constrict
2. Blood flows to the lungs
1. Pressure in RA decreases
4. Pressure in the
LA increases RT
Flow of blood from the lungs
5. Increase pressure in the LA forces the foramen ovale to close
True / False
• An infant’s first breath results in reduced pulmonary vascular resistance, decreased left atrium pressure, and increased right atrium pressure
• Increase CO
2
, decreased O
2, and increased pH help trigger initial breathing
Renal / Kidney Changes
Intrauterine
Urine if formed in utero and some excreted into the amniotic fluid
Excretion of wastes is the function of the placenta
Extrauterine
• GFR is low --decrease ability to excrete drugs
• Limited ability to reabsorb
Sodium
• Decreased ability to concentrate urine
• Bladder capacity is
6 - 44 ml
• Void within the first 24 hrs. and should void 6 - 10 times per day
Hepatic and Liver Changes
• The newborn’s liver plays a role in:
– Iron storage -for new RBC production. If the mother’s iron intake has been adequate, enough iron will be stored to last 5 months. After about 6 months of age, food containing iron or iron supplements must be given
– Carbohydrate metabolism --Glucose is the main source of energy in the first 4 - 6 hrs. of life. If the fetus experiences hypoxia or stress, the glycogen stores are used ( and may be depleted) to meet metabolic needs.
Hepatic and Liver
• Iron Storage
• Carbohydrate metabolism
– Coagulation --coagulation factors are under the influence of vit. K. The absence of normal flora needed to synthesize vit. K results in low levels of vitamin K and creates a transient blood coagulation alteration between the second and fifth day after birth.
Vitamin K is given prophylactically to combat potential clinical bleeding problems
Conjugation of Bilirubin
Unconjugated bilirubin is a breakdown product derived from hemoglobin that is released from destroyed RBC’s.
Unconjugated bilirubin is not in an excretable form and is a potential toxin, so it must be conjugated, made watersoluble, in order to be excreted from the body.
Conjugation of Bilirubin is a conversion of
Fat Soluble
Unconjugated to
Water Soluble
Conjugated by the enzyme Glucuronyl transferase in the newborn’s liver
Physiological Jaundice
• About 50% of all infants exhibit signs in 2 - 3 days after birth
• Bilirubin levels at birth are about 3 mg./dl and should not exceed 12 mg.
• Nursing Care:
– Keep well hydrated
– Promote elimination
• early feedings tend to keep bilirubin levels down by stimulating intestinal activity thus removing the contents and not allowing reabsorption
Blood Changes
• By the 6th month the bone marrow has become chief site of blood formation
• The infant is born with a large number of RBC’s
Temperature Regulation
A newborn is at a DISADVANTAGE in maintaining a normal temperature because:
Larger body surface in relation to body mass
Small amount of insulating subcutaneous fat
Minimizing Heat
Loss in the Newborn is
IMPERATIVE
Four Avenues of Heat Loss
• Conduction
--Loss of heat to a cooler surface by direct skin contact
• Convection
--Loss of heat to cooler air currents
• Radiation
--loss of heat to cooler surfaces and objects not directly in contact with the skin
• Evaporation
-- loss of heat when water is converted to a vapor.
Heat Production
1. Increase in Muscular activity --shown by crying and restlessness = increases BMR
2. Non-Shivering Thermogenesis - unique to newborns. Uses the infants stores of brown fat.
Brown fat is found in the midscapular area, around the neck, in the axillas, and around the trachea, kidneys, and adrenal glands
Non Shivering Thermogenesis
1. Skin receptors perceive a drop in environmental temperataure
2. Transmit impulses to the central nervous system
3. Which stimulates the sympathetic nervous system
4. Norepinephrine is released at local nerve endings in the brown
5. Metabolism of brown fat
6. Release of fatty acids
7. Release of HEAT!
Heat Maintenance
Peripheral
Vasoconstriction
Subcutaneous
Fat
Curl up in fetal position
Gastrointestinal Changes
• By 36-38 weeks of fetal life, the GI system is fully mature and ready to digest simple carbohydrates, fats, and protein.
• The newborns stomach holds about
50 - 60 cc.
• Pass meconium in 24 - 48 hours after birth. This shows the GI tract is patent.
Immediate Care of the
Newborn
• Ensure a Patent Airway
– Position on side
– Suction mouth then nares
– supply warmed oxygen is necessary
**Always have bulb suction in view !
Clamping of the Cord
• Cord should be clamped off about 1” from base of cord.
• Inspect the cord for 2 arteries and 1 vein.
• Don’t milk the cord
Maintain Body Temperature
• Dry off
• Place in warmer
• Skin to skin contact
Apgar Score
• Scoring system to appraise the newborn
• Done at 1, 5, and 10 minutes after birth
Apgar Score
0 1 2
Heart Rate
Respiratory
Effort
Reflex
Irritability
Muscle
Tone
Color
Absent Slow (less
than 100 )
Over 100
Good Cry Absent
No Response Weak cry or grimace
Flaccid
Slow, weak irregular cry
Some flexion
of
Extremities
Blue / pale Body pink, extremities blue
Heart Rate is the most important !
Vigorous Cry
Active motion
Resists effort to extend
Completely
pink
Apgar Score
• Score of 7 - 10 = Good Condition
• Score of 4 - 6 = Fair Condition
• Score of 0 - 3 = Poor Condition
Score This !
• Baby girl Doe has a heart rate of 102, with slow, irregular respirations. She grimaces when stimulated. She has some flexion in her extremities and her skin color is pale.
• What is her Apgar Score?
Identification of the
Newborn
Mother and infant should have matching “identibands”.
Bands should be placed on infant prior to leaving the delivery room
Footprint of infant and fingerprint of the mother
Eye Care
• Legal requirement that all newborns have treatment to prevent
Ophthalmia neonatorium which can lead to newborn blindness.
• Treated with antibiotic eye medication either ointment or drops
(Tetracycline or Erythromycin )
Hemorrhage Prophylaxis
• Administration of Vitamin K
(AquaMEPHYTON)
• This promotes liver formation of clotting factors
• The newborn does not have bacteria in the GI tract to synthesize vit. K.
• By 5 - 8 days after birth, it is formed.
Transfer to the Nursery
• Identification checks
• Full report must be given to the nursery nurse by the L & D nurse
– Condition of the neonate
– Labor and Birth record
– Antepartal history
– Parent-newborn interaction
Nursing
Assessments of the
Newborn
Physical Assessment
• Temperature
- 97.6 - 98.6
• Heart Rate
- 120 - 160 BPM. Regular rate. PMI on the left side of the chest
• Respirations
- 30 - 60 breaths / min.
Diaphragmatic with a shallow, irregular rate and rhythm. Chest and abdominal movements should synchronize. Periodic Breathing is normal. They are nose breathers. Tachypnea is abnormal
• Blood Pressure
- 80-60 / 45-35.
Measurements and Weights
Length = 18 - 22 inches
Head and Chest Circumference =
Head is 13”; Chest is 12”. Head is larger than the chest by one inch or 2 cm.
Weight 6 - 9 lbs average. Newborns lose 5% - 10% of birth weight the first few days after birth.
Reflexes
• Moro
• Tonic Neck
• Palmar and Plantar grasp
• Babinski
• Feeding--
Rooting, Sucking, Swallowing, Gag
• Protective --
Sneezing, Blinking, Gag
Senses
Touch -most significant in first few weeks
Vision -can see objects 8 - 12 inches from their eyes. They like faces the most, particularily the eyes. Follow objects. Like yellow and red.
Hearing -they will turn toward the sound of a voice. Alert more to a high pitched voice
Taste
-- can discriminate tastes. Sweet / nonsweet.
Smell
-- ability to smell increases over first few days of life. Smell mom’s breast milk.
Skin
• Pink with acrocyanosis
• Desquamation
• Vernix caseosa
• Lanugo
• Erythema toxicum
• Mongolian spots
• Birth marks
Head
• Large. 1/4 size of body
• Fontanels and sutures
– Fontanels should be soft and flat
• bulging = increased intracranial pressure
• depressed = dehydration
• Molding
• Cephalhematomableeding between bone and periosteum that does not cross sutures
• Caput succadenum edema (fluid) under the skin of the scalp that crosses sutures
Face
• Rounded
• Fat pads in the cheeks for sucking
Eyes
• Slate blue
• Spaced 1/3 across face
• Assess for subconjunctival hemorrhage
• Check pupils
• May have strabismus or nystagmus
Ears
• Assess placement
• should align with canthus of eye and where ear attaches to the head
• low set ears = renal or chromosomal problems
• Assess Appearance
• Pinna of ear should have incurving
• No skin tags
• Note Gestation
• Rapid recoil
• Check patency
• Note drainage
Nose
Mouth
• Firm Palate
• Tongue
• short frenulum
• Should not protrude
• Extrusion reflex
• No Teeth
• Epstein pearls
• Nose -- patency
• Mouth
• Neck
• Chest
• Abdomen
• Genitals -- never retract foreskin on male
• Anus -- patency
• Cry -- loud and lusty
Behavorial / Sleep - Awake
States
• Deep sleep
• Light Sleep
• Drowsy
• Quiet alert
• Active alert
• Crying
Daily Nursing Care
Need for warmth and dry
Need for protection from infection
Need for food
Need for attachment and loving
Need for bathing and cord care
Nutritional Needs
• The newborns diet must supply nutrients to meet the rapid rate of physical growth and development
• Daily caloric intake should be 110 -
120 calories / kg. / day
Circumcision
• It is not medically necessary. It is a personal decision of the parents.
• Nursing Care:
• Assess for bleeding and voiding
• Apply vaseline
• Position on side not abdomen