Animal Contributions to Human Needs
advertisement

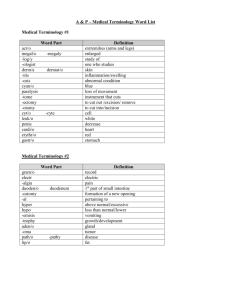
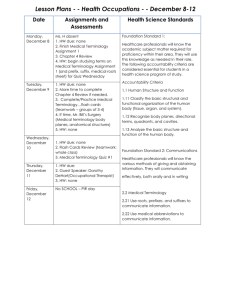
Animal Contributions to Human Needs What animals are used for production purposes? SCIENCE a process through which nature is STUDIED, DISCOVERED, and UNDERSTOOD. Animal Science The PROCESS through which LIVESTOCK ANIMALS are STUDIED and UNDERSTOOD. Animal Science Involves BREEDING, feeding, care and MANAGEMENT of animals; MARKETING and PROCESSING of animals and their PRODUCTS based on knowledge gained through practical EXPERIENCE and RESEARCH. Domestication To adapt an animal for human use Five requirements for domestication 1.The animal is VALUED and there are clear PURPOSES for which it is kept. 2.The animal’s BREEDING is subject to human control. 3.The animal’s SURVIVAL depends upon humans. Five requirements for domestication 4.The animal’s BEHAVIOR (psychology) is changed in domestication. 5.Morphological (STRUCTURAL) characteristics have appeared which occur rarely if at all in the wild. Wild animal not GENETICALLY altered by artificial selection for use by humans Example Tame wild animal a wild animal that, through intervention of man, has adapted BEHAVIORALLY so as to be useful to humans. Example Exotic animal a wild animal belonging to a species whose historic native range lies totally outside NORTH AMERICA Example Domestic animal an animal that has been genetically altered from the original wild species for use by humans through ARTIFICIAL SELECTION Example Feral animal a DOMESTIC animal that lives in the WILD with no human assistance Example Feral population a REPRODUCING group of FERAL animals Example Species a group of closely related animals that can INTERBREED and produce FERTILE offspring Example Breed animals of common ORIGIN with characteristics that distinguish them from other groups within the same SPECIES Example Type animals of the same SPECIES that are grouped together based on the PRODUCTS they produce Example Scientific Names of Domesticated Livestock Animals Genus species European Cattle Bos taurus Indian Cattle Bos indicus Sheep Ovis aries Goats Capra hircus Swine Sus scrofa domesticus Horse Equus caballus Donkey Equus asinus Rabbit Oryctolagus cuniculus Llama Llama glama Alpaca Llama pacos Dog Canis familiaris Cat Felis catus Chicken Gallus domesticus Turkey Meleagris gallopavo Duck Anas platyrhyncha Goose Anser anser Terms of Domesticated Animals Cattle Terminology Species Bovine Cattle Terminology Group Herd Cattle Terminology Adult Male Bull Cattle Terminology Adult Female Cow Cattle Terminology Young Bull Male Calf Cattle Terminology Young Female Heifer Calf Cattle Terminology Newborn Calf Cattle Terminology Castrated Bullock Male or Steer Cattle Terminology Offspring Calf w/Dam at Foot or Suckling Cattle Terminology Birthing Calving Cattle Terminology Mating Serving Sheep Terminology Species Ovine Sheep Terminology Group Flock Sheep Terminology Adult Male Ram, Buck, or Tup Sheep Terminology Adult Female Ewe Sheep Terminology Young Ram Male Lamb or Buck Lamb Sheep Terminology Young Ewe Female Lamb Sheep Terminology Newborn Lamb Sheep Terminology Castrated Wether Male Sheep Terminology Offspring w/Dam Suckling Sheep Terminology Birthing Lambing Sheep Terminology Mating Tupping Goats Terminology Species Caprine Goats Terminology Group Flock or Band Goats Terminology Adult Male Buck or Billy Goats Terminology Adult Female Doe or Nanny Goats Terminology Young Male Buckling Goats Terminology Young Female Goatling Goats Terminology Newborn Kid Goats Terminology Castrated Wether Male Goats Terminology Offspring w/Dam Suckling Goats Terminology Birthing Kidding Goats Terminology Mating Serving Swine Terminology Species Swine or Sus Swine Terminology Group Drove Swine Terminology Adult Male Boar Swine Terminology Adult Female Sow Swine Terminology Young Boar Male Pig or Boarling Swine Terminology Young Gilt Female Swine Terminology Newborn Pig, Piglet, Pigling Swine Terminology Castrated Barrow, Male Stag, Hog Swine Terminology Offspring w/Dam Suckling Swine Terminology Birthing Farrowing Swine Terminology Mating Coupling Poultry Terminology Species Gallus Poultry Terminology Group Flock Poultry Terminology Adult Male Rooster, Cock Poultry Terminology Adult Female Hen Poultry Terminology Young Male Cockerel Poultry Terminology Young Female Pullet Poultry Terminology Newborn Chick Poultry Terminology Castrated Capon Male Poultry Terminology Offspring Clutch, w/Dam Brood Poultry Terminology Birthing Hatching Poultry Terminology Mating ????? Horse Terminology Species Equine Horse Terminology Group Herd, Band, etc. Horse Terminology Adult Male Stallion Horse Terminology Adult Female Mare Horse Terminology Young Colt Male Horse Terminology Young Filly Female Horse Terminology Newborn Foal Horse Terminology Castrated Gelding Male Horse Terminology Offspring w/Dam Suckling or Foal at Side Horse Terminology Birthing Foaling Horse Terminology Mating Serving Functions of Livestock Product- an actual material provided by an animal that can be bought, sold, or used Service- a work provided by an animal Functions of Livestock Food Clothing Power Recreation Food Meat Eggs Milk Honey Clothing Wool Leather Hair/Fur Feathers Power Horses Mules, Donkeys, Burros Llamas, Alpacas Oxen, Water buffalo, reindeer, yak, camels Recreation Pleasure Horses Purebred Herds and Flocks Livestock Exhibitions, Shows, Rodeos Horse Racing Mainstream Domestic Animals Dairy Cattle Beef Cattle Sheep (Wool, Meat, Dairy) Swine Goats (Mohair, Milk, Meat, Cashmere) Horses, Mules, Donkeys, etc Poultry Non-Traditional Domestic Animals Ostrich & Emu Deer and Elk Bison Aquaculture Llamas and Alpacas Alligators Rare Breeds of Domestic Animals Types of Livestock Cattle Beef Type Dairy Type Dual Purpose Multi-Purpose Sheep Wool type Fine Medium Long Colored Meat or Mutton type Dual Purpose Dairy Type Swine Lard Type Bacon Type Meat Type Horses Draft Type Racing Ranch Work/Stock Horse Trotting Pacers Poultry Eggs (Layers) Meat (Broilers) Ornamental Cock Fighting Why Farmers Use Livestock Converts feed to meat; feed generally brings more money when marketed through livestock Utilizes labor the year around Allows for greater production capacity and increases opportunity for making profits Helps maintain fertility of the land Why Farmers Use Livestock May more fully utilize capital, machinery and wasteland (range). Utilizes roughage that can’t readily be sold (poor hay, corn stalks, straw, etc.) Diversifies that farm and/or ranch Personal satisfaction of working with domesticated animals Animal Protein Animal proteins are superior to vegetable proteins for humans Animal proteins have improved amino acid balance over vegetable protein Producing animals for meat, mike, eggs, etc. is not as efficient as compared to cereal grains produced for humans alone Ruminants Have a four compartment stomach Can digest roughages Manufacture essential amino acids and energy Examples include: Cattle Sheep Goats Non-ruminants (Monogastric) Have a single compartment stomach Need supplementary sources of amino acids and vitamins Examples include: Swine Poultry Horses Contributions to Food Needs Vegetarianism -- started in India, due to long-term population pressure and scarcity of feed and forage for animals -- also religious concerns; all life is sacred. Rising Population Pressures -- particularly in developing regions force people to consume foods of plant origin Contributions to food Needs Classification: Developed Countries Developing Countries % Animal Dietary Energy % Animal Protein of Total Protein 25 7 55 21 Contributions to Food Needs Meat -- is important in diet; excellent balance of amino acids, vitamins and especially Vitamin B12 Milk -- approximately 90% of milk for human consumption in the world comes from cattle Over 85% of the world population desires food of animal origin 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Vegan Lacto-Ovo Vegetarian Vegetarian Lacto Vegetarian Ovo Vegetarian Raw Vegan Pescatarian Flexitarian Pollo Vegetarians 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Vegan: No animal products at all Lacto-Ovo Vegetarian: no meat, milk, eggs Vegetarian: no meat Lacto Vegetarian: no meat or milk Ovo Vegetarian: no meat or eggs Raw Vegan: only raw, uncooked vegetables and fruits Pescatarian: Will eat fish, no other meat Flexitarian: Occasionally eats meat Pollo Vegetarians: Eats poultry, no other meat Calories of cultural or Fossil Fuel expended per calorie of food Hunting Game Soybeans Range Lamb Corn Range Beef .1-.2 .2-.5 .3-.4 .4-.5 .5-.6 Coastal Fishing Poultry Hogs Farm Forage Beef Feedlot Beef .9-1.1 1.5-2.0 2.5-3.2 3.0-4.0 10.5-12.0 Feed Conversion Values For each 1lb of gain, each animal eats Sheep Cattle Swine Turkeys Chicken 5-7 lbs 7-8 lbs 3.0-3.5 lbs 3.0-3.5 lbs 2 Livestock Feed Consumption Range/Pasture 34% Processed Feed 7% Feed Grain 26% Hay 32% Wheat 1% Range/Pasture Hay Feed Grains Wheat Processed Feeds US Livestock Producers- 1996 Beef Swine Chickens Dairy Horses Ducks/Geese Goats (milk) Goats (angora) 55.4% 11.9% 10.9% 8.5% 5.4% 2.4% .9% .3% 909,100 182,700 179,200 140,100 88,400 39,600 15,400 5,400 Top States in Beef Production 1. Texas 2. Kansas 3. Nebraska 4. Oklahoma 5. California Utah’s Rank 28th Top States in Dairy Production 1. California 2. Wisconsin 3. New York 4. Pennsylvania 5. Michigan Utah’s Rank 25th Top States in Sheep Production 1. Texas 2. California 3. Wyoming 4. Colorado 5. South Dakota Utah’s Rank 7th Top States in Goat Production 1. Texas 2. New Mexico 3. Arizona 4. Oklahoma 5. California Utah’s Rank ? Top States in Swine Production 1. Iowa 2. North Carolina 3. Michigan 4. Illinois 5. Indiana Utah’s Rank 20th Top States in Layers Production 1. California 2. Ohio 3. Indiana 4. Pennsylvania 5. Iowa Utah’s Rank 33rd Top States in Broiler Production 1. Arkansas 2. Georgia 3. Alabama 4. North Carolina 5. Mississippi Utah’s Rank ?? Top States in Turkey Production 1. North Carolina 2. Minnesota 3. Arkansas 4. Missouri 5. California Utah’s Rank 14th Number of Farms and Ranches 1. Texas 2. Missouri 3. Iowa 4. Kentucky 5. Minnesota Utah’s Rank 36th Land in Farms and Ranches 1. Texas 2. Montana 3. Kansas 4. Nebraska 5. New Mexico Utah’s Rank 28th Utah’s Rank in Other Areas Mink Production 2nd Trout Production 6th Honey Production 24th