Module 7: Cultural Competency
advertisement

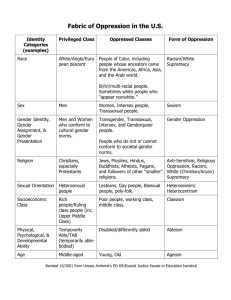
Module 7 Cultural Competency This curriculum is intended to be a tool to assist domestic violence service providers offering victim services (such as those outlined in California Penal Code §13823.15-13823.16) for the purpose of ensuring advocates working with survivors meet the requirements of a “Domestic Violence Counselor” pursuant to Evidence Code §1037.1(a)(1). Objectives • To develop a common language related to issues of oppression and privilege. • To deepen an understanding of intersections between domestic violence intervention, prevention and issues of oppression, privilege and bias. • To develop tools to become allies committed to promoting equity and inclusion within the organizational culture of agencies, programs and services. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 2 Author Unknown “Rather than difference itself, it is the response to difference that is the problem. Rather than culture itself, it is the attitudes about culture that are the problem. Rather than diversity itself, it is the ways in which major institutions of this country have responded to culturally, racially and ethnically diverse people that is the major source of our condition of ...inequality.” Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 3 Communication Agreements Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 4 A Delicate Balance Stance “How we walk in the world” Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 5 Strategies “What we do in the world” Balancing Cognitive and Affective Domains and Application Head: Thinking, Theory Heart: Feeling, Emotion Hand: Action Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 6 Community Building “Community first... then Work.” Dr. James Comer Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 7 Intersectionality (Susanne Knudsen) • Intersectionality is a theory which seeks to examine the ways in which various socially and culturally constructed categories interact on multiple levels to manifest themselves as inequality in society. • Intersectionality holds that various forms of oppression, (e.g. racism, sexism, heterosexism, ageism, ableism, classism, etc.) do not act independently of one another; instead, these forms of oppression interrelate creating a larger, more complex system of oppression that reflects the "intersection" of multiple forms of oppression. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 8 Intersectionality • The theory of intersectionality also suggests that discrete forms, and expressions, of oppression actually shape, and are shaped by, one another. • I.e., in order to fully understand one form of oppression, we need to understand all forms of oppression. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 9 Developing a Common Language: Part I Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 10 Gender and Sexuality: A Visual Map Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 11 Race • A socially constructed concept used to put people in categories based on ancestry and physical characteristics without basis in biological facts. • Biologically speaking, there is no such thing as different human races. • The term has attained socio-political significance as a tool for oppressing groups of people based on common physical characteristics. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 12 People of Color • A term of solidarity used to describe those targeted by racism and denied the status (and the accompanying benefits) of being white. • People of Color include: Peoples of African, Arab/Middle Eastern, Asian and Pacific Islander, Latino/a, Native American, Indigenous, and Biracial/Multiracial/Mixed heritages. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 13 White • A term used to describe people of European ancestry who have historically held positions of dominance and social power in Western society. • Note: Perception only, and the definition has changed over time. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 14 Developing a Common Language: Part II Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 15 Developing a Common Language “You can’t deal with a problem if you don’t name it; once you name it, you can think, talk and write about it. You can make sense of it by seeing how it is connected to other things that explain it and point towards solutions.” - Allan G. Johnson Privilege, Power and Difference Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 16 Common Language Intrapersonal Thoughts STEREOTYPE Feelings / Beliefs PREJUDICE Behaviors / Actions Interpersonal Institutional / Systemic DISCRIMINATION OPPRESSION Policies, Procedures, Practices, Structures, Culture, Laws, Norms, Values Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 17 (i.e. Structural Inequality or the “isms”) Racism • A system of oppression based on race that privileges white people and targets people of color. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 18 Heterosexism • A system of oppression based on sexual orientation that privileges straight people and targets lesbian, gay, bisexual, and queer people. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 19 Sexism • A form of oppression based on gender that privileges men and targets women and transgender/genderqueer people. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 20 Genderism • A system of oppression that grants power and privilege to people whose biological sex is consistent with their gender identity (also called “cisgender” people) and that targets people whose gender identity is different from their biological sex (i.e. transgender or genderqueer people). Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 21 Homophobia • The fear, dislike, or hatred of gay, lesbian, bisexual, and queer people. • This includes: – the fear of being labeled by association with or perceived as gay, lesbian, bisexual, or queer; – the fear of one’s own feelings towards members of the same sex; and – the fear of behavior that is outside the boundaries of traditional gender roles. • Homophobia is used to reinforce both sexism and heterosexism. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 22 Transphobia • The fear, dislike, or hatred of people who are transgender or genderqueer • This includes: – the fear of being labeled by association with or perceived as gender nonconforming; – the fear of behavior that is outside the boundaries of traditional gender roles. • Transphobia is used to reinforce genderism, sexism and heterosexism. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 23 Prejudice vs. Oppression • Homophobia, transphobia, & biphobia are forms of prejudice • Heterosexism & genderism are forms of oppression Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 24 Oppression: How do we get rid of it? Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 25 Table of Oppression Racism Ageism Classism Sexism OPPRESSION Heterosexism Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 26 Anti-Semitism Ableism Table of Oppression Racism Ageism Classism Sexism OPPRESSION Heterosexism Privilege Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 27 Anti-Semitism Ableism Privilege Unearned access to resources that enhance one’s chances of getting what one needs or influencing others in order to lead a safe, productive, fulfilling life. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 28 Table of Oppression Racism Ageism Classism Sexism OPPRESSION Heterosexism Targeting Privilege Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 29 Anti-Semitism Ableism Targeting The denial of access, resources and opportunities that might enhance chances of getting what one wants and influencing others. Systemic injurious treatment directed towards members of target groups (also called systemic discrimination). Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 30 Table of Oppression Racism Ageism Classism Sexism OPPRESSION Heterosexism Ableism Anti-Semitism Collusion Collusion Targeting Privilege Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 31 Collusion Working together to make something happen . . . – Intentionally or unintentionally – Consciously or unconsciously – by action, inaction or silence Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 32 Table of Oppression Racism Ageism Classism Sexism OPPRESSION Heterosexism Anti-Semitism Collusion Privilege Group Collusion Targeting Privilege Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 33 Ableism Privilege Group Collusion The things privilege groups and privilege group members do to perpetuate systems of oppression. Internalized Superiority: When members of privilege groups either consciously or unconsciously learn to look at themselves, each other, and society through a distorted lens such that the structural privileges they enjoy and the cultural practices and values of their group are represented as, seen as, and felt and believed to be normal and universal. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 34 Table of Oppression Racism Ageism Classism Sexism OPPRESSION Privilege Group Collusion Targeting Privilege Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 35 Anti-Semitism Target Group Collusion Heterosexism Ableism Target Group Collusion Things target groups and target group members do to perpetuate their own oppression. Internalized Oppression: Destructive patterns of feelings and behaviors experienced by the targets of oppression, turned inward upon themselves and directed at each other. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 36 Table of Oppression Racism Ageism Classism Sexism OPPRESSION Privilege Group Collusion Targeting Privilege Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 37 Anti-Semitism Target Group Collusion Heterosexism Ableism Audre Lorde… The true focus of revolutionary change is never the oppressive situations which we seek to escape, but that piece of the oppressor which is planted deep within us. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 38 Intersectionality of Oppression Common Tactic Sexism and Sexist Violence/Oppression Emotional abuse Calling a woman a bitch Calling her an angry, black bitch Economic abuse Women paid 76 cents per man’s $1.00 African American women make 53 cents Minimizing Women would get out if it was bad African American women have a matriarchy Blaming Women push men’s buttons + Racism African American women emasculate men Denying When women say no, they mean yes African American women are insatiable animals Privilege of status The Bible says women should submit Real African tradition=patriarchy Women should stay in the home African American women =welfare queens Using children Intersectionality of Oppression Common Tactic Sexism and Sexist Violence/Oppression Emotional abuse Calling a woman a bitch Calling her an angry, black bitch Called an angry, black dyke Economic abuse Women paid 76 cents per man’s $1.00 African American women make 53 cents African American women make 53 cents, with no benefits Minimizing Women would get out if it was bad African American women have a matriarchy It’s just two women in a fight Women push men’s buttons African American women emasculate men Black lesbians try to be men Denying When women say no, they mean yes African American women are insatiable animals Queer blacks are hypersexual Privilege of status The Bible says women should submit Real African tradition=patriarchy “Lifestyle” is against God and community Women should stay in the home African American women =welfare queens Black lesbians are not fit parents Blaming Using children + Racism + Heterosexism Terms about liberation… • Resistance: – Resistance/insurgence: The resistance to or insurgence against oppression and/or internalized oppression by members of a target group. – Also: the resistance to or insurgence against conditioning or unquestioned privilege by members of a privilege group. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 41 Ally • Someone from the non-target group—or a different target group—who will "stand in the way" of oppression when it is aimed at a target person • Someone who will question and resist the institutionalized oppression as best as s/he can. Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 42 Alliance • A close association formed to advance a common interest in anti-oppression philosophies and actions. • Building networks to provide support for transformations. • Inclusion and fostering of diversity are components of an effective anti-oppression alliance. • Multicultural leadership styles can be the catalysts of “alliance.” • Leaders bring people together and inspire them to collective action; ALLIANCE! Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 43 What Can We Do About Oppression as Individuals? Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 44 Top 10 Things Privilege Group Members Do to Avoid Dealing With Oppression… 1. “Yeah, buts” 2. Data Pile On 3. P.L.E.s (Perfectly Logical Explanations) 4. “I’m colorblind. I don’t see color.” 5. “Pull yourself up by your bootstraps.” 6. Reverse Racism 7. “Lighten up, don’t take it so seriously.” 8. “Don’t blame me . . .” 9. Innocent by association or “Some of my best friends are …” 10. BWAME – But What About Me? Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 45 Things Target Group Members Do that Avoid Addressing Oppression… • Generalizing • Only being able to access one emotion as opposed to a full range. • “Our pain is worse than your pain.” • “Don’t air our dirty laundry.” • Numbness • DENIAL – Don’t Even kNow I Am Lying Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 46 Tactics of Oppression • • • • • • • • Emotional Abuse Economic Abuse Isolation Privilege of Status Using Children Minimizing, Denying and Blaming Intimidation and Threats Using Violence Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 47 Tactics of Inclusion • • • • • • • Take action Listen/learn Use your privilege Support the target person’s leadership Go after other non-target group members Take a chance; make mistakes Take care of yourself. Get support, accept support Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 48 Resources Module 7 • Cultural Competency • Published 2012 • Slide 49 This project was supported by Grant Number G-1101CAFVPS from the Administration on Children, Youth and Families, Family and Youth Services Bureau, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) through the California Emergency Management Agency (Cal EMA). The opinions, findings, and conclusions in this publication are those of the author and not necessarily those of HHS nor Cal EMA. Cal EMA reserves a royalty-free, nonexclusive, and irrevocable license to reproduce, publish, and use these materials and to authorize others to do so.