Models Of North American Citie
advertisement

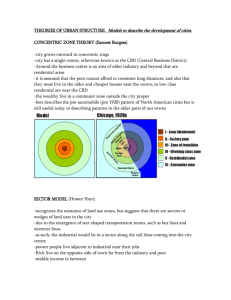
Models Of North American Cities By: Emily Goelz, Dylan Kienitz, and Jake Connelly Concentric Zone Model First model for explaining social group distribution Created 1923 by E. W. Burgess A city grows outward from a central area in series of concentric circles Depending on the city, the size and width of the rings vary Concentric Zone Model Continued Innermost zone: central business district (CBD) Second ring: transition zone Modest older houses with stable working families Fourth ring: working-class homes Industry and poor-quality housing Third ring: working-class homes Concentrated nonresidential activities New and spacious homes Fifth ring: commuter zone Many who work in the center live on the outside Concentric Zone Model Diagram Sector Model Developed in 1939 by Homer Hoyt This model says that a city develops in sectors instead of rings Certain sectors are better for different activities This can be due to the environment of just due to chance Cities grow from the center outward in wedges or sectors The best houses are on the edges of lower class housing sectors causing upper class housing to be from downtown to the edge of the city Industrial areas develop along transportation lines Viewed as a refined version of the concentric zone model Sector Model Continued Upper-class housing tends to stay in the same area When needed upper-class areas will extend away from the CBD (central business district) instead of intruding on the space of other sectors Example of a city: Chicago Upper-class housing extends north along the coast of Lake Michigan Industrial zones follow the major roads and railroads to the South, Southwest, and Northwest of the city Sector Model Diagram Multiple Nuclei Model A city contains more than one area that is the center for the activities Some activities are attracted to particular regions, or pushed away from other regions Such as universities attract scholars and well educated-individuals Business may form “iron triangles” or clusters of related businesses Some activity centers in Atlanta are Centennial Olympic Park and the Atlanta Zoo Businesses that relate to automobiles form very functional and common iron triangles Activities that don’t interact with each other don’t cluster together Food stores and automobile shops do not cluster in the same area of a city Multiple Nuclei Diagram Summary Concentric Zone Model- Cities develop in rings around the central business district Sector model- Cities develop in sectors based on the clustering of similar activities Multiple Nuclei Model- Cities develop with multiple different centers of activities