Business Law
advertisement

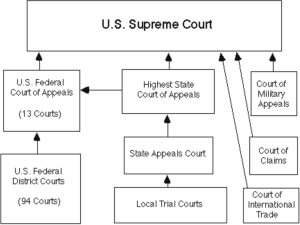
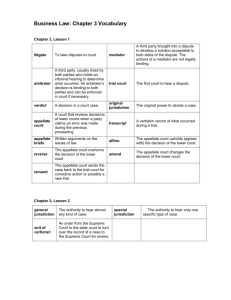
Business Law Chapter 3 – The Court System Section 3.01 – Dispute Resolution Private Resolution Mediation • Mediator tries to develop a solution acceptable to both sides • The actions of a mediator are advisory—not binding of the dispute. Arbitration • An arbitrator usually holds an informal hearing to determine what happened. • The arbitrator’s decision is binding on both parties. • The decision can be enforced by court order if necessary. Different Levels of Courts Trial Courts • A trial court is the first court • A trial court has original jurisdiction to hear a dispute. over a case. Appellate Courts • An appellate court reviews decisions of lower courts when a party claims an error was made during the previous proceeding. • Appellate courts are concerned with errors of law rather than questions of fact • Do not hear witnesses • Examine transcripts of trial • Review appellate briefs • Appellate court decisions: • Affirm (uphold) the decision of the lower court • Reverse (overturn) the decision of the lower court • Amend (change) the decision of the lower court • Remand the case—send it back to the trial court for corrective action or possibly a new trial. Section 3.02 – Federal Court System 3 Levels of Federal Courts 1. Federal District Courts • Lowest level of federal court with general jurisdiction (1st court to hear a dispute) • Trial court of the federal system • Jurisdiction over: • Federal questions or cases that arise under the Constitution , US laws or treaties • Lawsuits b/w citizens of different states or US citizen and a foreign nation • $75,000 in dispute 2. Federal Court of Appeals • Appellate court for Federal District Courts • No new evidence or witnesses • Review transcripts & oral arguments • 13 Federal Courts of Appeal • 12 assigned to a geographic area • 1 Federal Circuit • Patent cases • Special jurisdiction (Int’l Trade Commission) 3. U.S. Supreme Court • Some original jurisdiction; cases affecting ambassadors • Mostly appellate jurisdiction • Decisions of USSC re: Constitution are final Federal Court System United States Supreme Court 13 United States Courts of Appeals State Supreme Court U.S. District Courts Specialized Federal Courts Many Federal Agencies Section 3.03 – State Court System Structure of State Court Systems Courts of Limited Jurisdiction • Lessens burden on Trial Court • Specialized or relatively minor jurisdiction • Can be appealed to the circuit court • Juvenile Courts • Emphasis on rehabilitation , not punishment • Records do not become public knowledge • Rehabilitation fails, can be tried as an adult • Municipal Courts • Courts that administer ordinances • Traffic division • Criminal division • Probate Court • Wills and deeds • Small Claims Courts • Attorneys generally are not • < $5,000 required Typical State Court System State Supreme Court Intermediate Appeals Court (in populous states) Trial Court (of original general jurisdiction) Family Court Juvenile Court Justice of the Peace Municipal Court Probate Court Criminal Court Small Claims Court Analyzing Cases Lesson 3.01 1. Nick at Ward Electronics is getting ready to enter into a series of contracts with a new group of suppliers. He is concerned with avoiding the delays and high costs of any litigation that might result from the new agreements. He asks you for your recommendation. Any ideas? 2. Melissa is convicted of second-degree murder for killing Chris, a guy she had been seeing over the last few months. The court sentenced her to 30 years in jail. One year after her trial, Melissa admits that she withheld evidence that would have cleared her. She stated she did so to protect her twin sister Emma, who actually committed the crime, but who was dying of cancer at the time. She further states that she did not want her sister to spend the last years of her life behind bars. Her sister has since died. The evidence is conclusive as to her innocence. Should the court set aside her conviction due to the new evidence? What policies would support the court in not doing so? Lesson 3.02 1. Jason Moore, a citizen of Oregon sued Mark Fendyk, citizen of Oregon as well, for spilling his hot coffee on him as he bumped into him at the train station. Moore asked for $55,000 in damages, but his case was thrown out of federal district court. He wanted to appeal to the USSC. Where should his case be heard? 2. Katie Wells, a citizen of Iowa, is being sued by citizen of Kansas, Jackie Cohen, after she tripped over some warped floorboards of the stairs to Wells’ business property. Jackie sustained injuries and is asking for $40,000 in damages. Where should this case be litigated? 3. In a case involving an appeal, Natasha believed that Jake Soth had previously lied in court. She thought that with an appeal she would most likely win because she now had the evidence to prove it through a new witness. Is her thinking correct? 4. Michael of Chicago claims that he was injured when Steven, also of Chicago, hit him while rollerblading. He is suing for $25,000 in damages. After Michael filed his suit in federal district court, Steven’s lawyer objected on two grounds. What were they? Lesson 3.03 1. Darrin is walking on Chris’s porch, when he fell through and broke his leg. Darrin is now suing Chris for a sum of money no greater than $15,000. What court would this case be tried in? 2. Seventeen year old Nick is caught stealing from a department store. He is sent to juvenile court, could he be tried as an adult? 3. Brian was driving while under the influence, was pulled over and arrested. He was sentenced to pay thousands of dollars in fines and his license was suspended for no less than 1 year. Brian’s lawyer makes an appeal to the State Courts of Appeals. In his argument, he states that Brian was not speeding; he obeyed all traffic laws and was not driving recklessly. Should this new evidence presented by his lawyer be allowed? 4. Bob lives in Virginia and Bill lives in Florida. Bob owes Bill $2000, if the debt isn’t paid can Bill takes Bob to Federal court? 5. Emma is being tried for felony vandalism. She was seventeen when the crime was committed but is 18 when the trail is occurring. Should she be tried as a juvenile or as an adult? How will the punishments differ?