Rocks - Nebulous Zone
advertisement

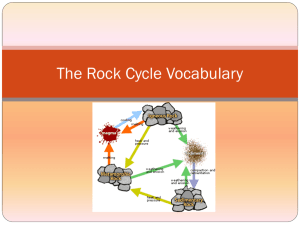
Rocks What Is A Rock? A rock is a hard substance composed of one or more minerals. It may also be made of naturally occurring substances that don’t perfectly fit the definition of mineral. – (ex. Obsidian - volcanic glass) – (ex. Coal – made from once living organisms Types of Rock Igneous – formed of cooled magma. Sedimentary – formed from particles that have been carried along and deposited by wind and water, and then pressed together over time. – Sediments the particles that are carried and deposited. Inorganic sediments- bits of rock. Organic sediments - shells, leaves, bones, stems. Metamorphic – formed when chemical reactions, tremendous heat, and/or great pressure change rock into new rocks. The Rock Cycle the continuous changing of rocks from one kind to another over long periods of time. *note the processes responsible for each stage What is Magma? Slushy mix of molten rock, gases, & mineral crystals Elements in magma – oxygen (O) , silicon (Si), aluminum (Al), iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), potassium (K), sodium (Na) – silica (SiO2) most abundant in magma has greatest effect on magma determines igneous rock composition affects melting temperature of rocks impacts magma flow How Does Rock Melt? Temperatures above 800°C needed Heat to melt rock comes from – leftover heat of formation – radioactive decay of elements the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves. What Factors Can Affect Magma Formation? Temperature – Increases with depth in the earth Pressure – Increases with depth in the earth – As pressure increases, melting point increases Water content – Changes melting point of rock – As water content increases, melting point decreases Mineral composition – Different minerals have different melting points Bowen’s Reaction Series relationship between cooling magma & mineral formation Two main branches of crystallization – Branch 1 Continuous gradual change of mineral composition in the feldspar group – Branch 2 Abrupt change in mineral type in the iron-magnesium groups Magma Types Felsic: – – – – light-colored high silica content viscous, flows slowly Mafic: – dark-colored – low silica content – high iron & magnesium Ultramafic: – low silica – very high iron & magnesium