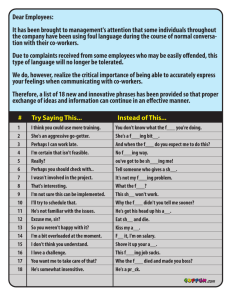
What is international business
advertisement

University Of Finance & Administration INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. Pavla.Breckova@vsfs.cz INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Full-time course = 12 sessions á 90 mins. (summer term 2011) 1-2/ What is international business (IB). IB basic indicators - balance of trade / payment. Territorial / commodity structure of IB. Comparative advantage, free trade / economy. Protectionism x Liberalism. (14.2.2011) 3-4/ Internationalization, drivers. Entry modes and business activities in IB. International market research (PEST/STEEP), and linkage to Competition analysis (Porter) and SWOT. Data collection and their selection in the international environment. (28.2.2011) 5-6/ Guest lecture prof. Eric Severin (Lille University, France) Individual TEAM work on the MARKET STUDY. (14.3.2011) 7-8/ Culture and its role in international business. Cultural elements and multi-culture communication. Social stratification and mobility. Role of religion in IB. Hofstede’s five dimensions of culture differences. TEAM work presentations: foreign market study. (28.3.2011) 9-10/ Globalization – microeconomic and macroeconomic view. Drivers of globalization, pros & cons. International trade barriers. Forms of economic integration. EXPORT microeconomic and macroeconomic view. Export risks and their elimination / securing. TEAM work presentations: foreign market study. (11.4.2011) 11-12/ EASTER (25.4.2011) 2. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / pavla.breckova@vsfs.cz CREDIT conditions B_IB CONDITIONS: PRESENCE at IB lectures: 60% TEAM PRESENTATION – (market study) preparation at home: 15 min. presentation of team work – chosen MARKET STUDY lecture marks based on active PARTICIPATION: communication, reading and discussing topical economic issues / team knowledge COMPETITION If unfulfilled: 1. knowledge test / 2. semester elaborated paper + test 3. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / pavla.breckova@vsfs.cz TRADE BARRIERS Trade barrier = a general term that describes any government policy or regulation that restricts IB AIM: to limit imports to protect domestic producers from foreign competition Anti-dumping Action against dumped imports Anti-dumping measures counter dumping practices occurring when non-EU manufacturers sell their goods in the EU below the normal value (usually the sales price) on their domestic market. Anti-subsidy Action against imports of subsidized 4. products INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz International Business BARRIERS TARIFFs (duties) = is a tax on imported goods NON-TARIFF barriers – including 1. QUOTAs = is a limit on the amount of goods that may be imported 2. Lack of intellectual property protection; 3. Testing, labeling, and certification with an unnecessarily restrictive application of standards; 4. Export subsidies that offer export financing on preferential terms and displace your exports in third-country markets; 5. Investment barriers; 6. REGULATIONS regarding product content or quality Both tariffs and quotas raise the price of and lower the demand for the goods to which they apply 5. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz Effect of IB BARRIERS The EFFECT of tariffs and quotas is the same: to limit imports and protect domestic producers from foreign competition. A tariff raises the price of the foreign good beyond the market equilibrium price, which decreases the demand for and, eventually, the supply of the foreign good. A quota limits the supply to a certain QUANTITY, which raises the price beyond the market equilibrium level and thus decreases demand 6. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz Tariff & Non-tariff measures have important effects on consumption, production & structure of a domestic economy reason for imposing = e.g. protect infant industries TARIFF NON-TARIFF - Fiscal - Protective - Retributive - Prohibitive QUOTA = qty restriction OTHER non-tariff 7. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz ANTI: dumping and subsidy ANTI-DUMPING = action against dumped imports -Anti-dumping measures counter dumping practices occurring when non-EU manufacturers sell their goods in the EU below the normal value (usually the sales price) on their domestic market. ANTI-SUBSIDY = action against imports of subsidized products - Anti-subsidy measures counteract trade distortive subsidies which make subsidised goods artificially competitive (e.g. cheaper) compared to non-subsidised goods 8. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz Summary of basic IB BARRIERS Prohibitive TARIFFS Nationalization Dual use / ‘use conditional’ QUOTAS WEAK IB IMPORT DUTIES Other Sanctions & Embargo PROTECTIONIST measures 9. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz POLITICAL IB barriers Sanctions Embargo Exchange rate manipulation Dual-use Nationalization o expropriation o confiscation Privatization 10. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz Forms of integration Economic (monetary) & Political union Common market Customs union Free trade area 11. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz ECONOMIC INTEGRATION Description I. Free Trade Area: Type of trade bloc, a designated group of countries that have agreed to eliminate tarrifs, quotas and preferences on most (if not all) goods and services traded between them. It can be considered the 1st - 2nd stage of economic integration (Preferential trading area) Customs union Composed of a Free Trade area with a COMMON EXTERNAL TARIFF. The participants set up common external trade policy, but in some cases they use different import quotas. Purposes for establishing a customs union normally include increasing econ. efficiency + establishing closer political and cultural ties between members It is the 3rd stage of economic integration 12. ECONOMIC INTEGRATION Description II. Common / Single market A single market is a type of trade bloc which is composed of a FTA (for goods) with common policies on product regulation, and FREEDOM of MOVEMENTof the FACTORS OF PRODUCTION (capital, labour) and of enterprise and services. The physical (borders), technical (standards) and fiscal (taxes) barriers among the member states are removed to the maximum extent possible. These barriers obstruct the freedom of movement of the four factors of production. To remove these barriers the member states need political will and they have to formulate common economic policies. A common market is a first stage towards a single market, and may be limited initially to a free trade area with relatively free movement of capital and of services, but not so advanced in reduction of the rest of the trade barriers. Economic union 13. Type of trade bloc which is composed of a common market with a customs union. The participant countries have both common policies on product regulation, freedom of movement of goods, services and the factors of production and a common external trade policy. Impact of Economic Integration on firms firms’ viewpoint: integration = two-sided sward ADVANTAGES - opens markets DISADVANTAGES - capturing Economies of Scale (= larger market =>lowering Ø production & distrib. cost) - exposes a firm’s home market to competition 14. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz International unions & agreements EU – European Union • 27 countries, eurozone, free movement of goods, services, capital & labor NAFTA • since 1992, (Mexico, Canada, USA) • Agreement on reduction of duties and further barriers (import licenses and import taxes) FTAA – Free Trade Area of Americas • Other Latin-American countries – free trade area (members: Columbia, Mexico and Venezuela) ASEAN • Trade union of 10 nations South-East Asia (Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, Brunei, Malai, Singapur, Indonesia) • South-East Asia = the most growing economy of the world -> important to create alliance to compete with NAFTA or EU 15. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz TRIAD – NAFTA NAFTA member states • FREE TRADE AREA • From 1994 • Population: 457 million Density: 25.1/km2 • GDP/capita: 35,490 USD • Water 7.4% 16. TRIAD – EUROPEAN UNION EU member states • Economic UNION • GDP / capita: 39.729 USD • Population: - 501 million - density: 115.9/km2 • Water 3.08% 17. TRIAD – ASEAN ASEAN • Free Trade Area • GDP / capita: 5,131 USD • Population: 600 million (8.8% of world population) - density: 135/km2 18. EMERGING MARKETS What is an emerging market? – – – – – Emerging markets are nations with social or business activity in the process of rapid GROW and INDURSTRALIZATION. Currently, there are 28 emerging markets in the world, with the economies of CHINA and INDIA considered to be by far the two largest. The ASEAN–China Free Trade Area, launched on January 1, 2010, is the largest regional emerging market in the world. An emerging market economy (EME) is defined as an economy with low to middle per capita income. • Such countries constitute approximately 80% of the global population, and represent about 20% of the world's economies. The term was coined in 1981 by the World Bank. One key characteristic of the EME is an increase in both local and foreign investment (portfolio and direct). A growth in investment in a country often indicates that the country has been able to build confidence in the local economy EMERGING MARKETS [EM] entering Special problems related to entering EM – Lack of information (problematic data collection) EM’s market-potential analysis: – – – – – – – – Market SIZE Market INTENSITY – estimates wealth, buying power Market GROWTH rate – GDP, energy consumption etc. Market CONSUMPTION CAPACITY – spending capacity (% of middle class, core of buying power) Commercial INFRASTRUCTURE – chanels for com./distrib. Economic FREEDOM – free market principles domination Market RECEPTIVITY – market ‘openness’ Country RISK – of doing business FAIR TRADE Fair Trade: - is an organized SOCIAL MOVEMENT and market-based approach that aims to help producers in developing countries and promote sustainability - The movement advocates the payment of a higher price to producers as well as social and environmental standards. - It focuses in particular on exports FROM DEVELOPING countries to DEVELOPED countries - typically: handicrafts, coffee, cocoa, sugar, tea, bananas, honey, cotton, wine, fresh fruit, chocolate and flowers 21. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz GATT – General Agreement on Tariffs & Trade set up in 1947 to prevent causes leading to Great depression (in 1930’s) AIM: to REDUCE barriers to international trade to PROMOTE a free & competitive trading environment to ensure the int. trade is conducted on a NONDISCRIMINATORY basis by MFN principle (Most Favored Nation) 22. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz WTO – World Trade Organization created by GATT at Uruguay round in 1995 development of IB, more powerful non-tariff barriers WTO granted more power than GATT AIM: to PROMOTE flows by encouraging nations to adopt non-discriminatory & predictable trade policies to REDUCE remaining trade barriers (emphasis on agricultural tariffs & subsidies + relaxing intellectual prop.rights of Pharmaceuticals in less developed countries) establish IMPARTIAL PROCEDURES for resolving trade disputes 23. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz WTO challenges Problem SECTORS • sectors that receive GOV protection in every country: AGRICULTURE & TEXTILES • Distortion by SUBSIDIES, import RESTRICTIONS etc. GATS – General Agreement on Trade in Services • Reduce barriers to trade in services (= diverse & complicated) TRIPS – agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights • Inadequate enforcement of laws prohibiting illegal usage or copying of intellectual property (music, film, SW, pharma) • Efforts to RELAX int.prop.rights in case of LIFE-SAVING DRUGS in under-developed countries TRIMS – Trade-Related Investment Measures Agreement • Control of FDIs 24. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz Individual TEAM work Individual TEAM work on the MARKET STUDY (90 min.) - preparation for the team work results presentation Presentation 28.3.2011: TEAM 1 TEAM 2 Presentation 11.4.2011: TEAM 3 TEAM 4 25. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / pavla.breckova@vsfs.cz MARKET STUDY - elaboration Market study on: PRODUCT PLACEMENT TO A FOREIGN MARKET Elaboration in the mixed teams per UP TO 9 people (e.g. 2 Germans (D) + 2 Polish (PL) + 4 Czechs (CZ)) Ideally if a product from one country (e.g. D) is being placed to the market of the other (i.e. PL) Market study minimum CONTENT: • Characteristics of the PRODUCT + TARGET group • Market ASSESMENT (potential of the market, market analysis – e.g. PEST, STEEP) • Characteristics of the area of specialization (product branch) + possible specifics • RISKS identification - connected with the product’s placement at this particular market • Typical consumers’ BEHAVIOR / target groups’ • MARKETING tools (how you are going to succeed) and DISTRIBUTION channels • Typical BUSINESS PRACTICES at both markets (e.g. business meeting, negotiation, existing business practice, pros & cons, what to put emphasis on, what to pay attention to, etc.) 26. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / pavla.breckova@vsfs.cz MARKET STUDY - presentation Market study on: PRODUCT PLACEMENT TO A FOREIGN MARKET Presentation: PRESENTATION In the mixed (multinational) teams • Power Point live prezentation • Each member of the team will take an active part in the presentation (i.e.presents a part of it) • cca 15 min. + 5 min. discussion and evaluation Presentation essentials: - Slides brief & comprehensive - Never read the slides - Keep eye contact with audience - Gestures make prezentation lively - Be interesting & catch the attention - Speak up INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Presentation essentials 27. Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / pavla.breckova@vsfs.cz KEY terms - Global environment International Business: trade / investment / other GATT WTO Fair trade Economic Integration - forms Economies of scale IB barriers Tariff x Non-tariff measures Duty x Quota State IB policy instruments Emerging markets 28. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / 19063@mail.vsfs.cz Thank you for your attention Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. pavla.breckova@vsfs.cz 29. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS [B_IB] Ing. Pavla Břečková, Ph.D. / pavla.breckova@vsfs.cz