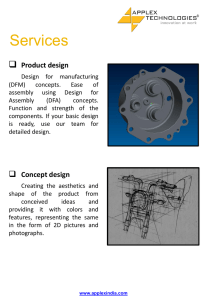
Reverse Engineering
advertisement
Reverse Engineering When is it the most cost effective? Raymond Utz The Problem • When is Reverse Engineering the correct choice over Forward Engineering? Terminology • Reverse Engineering - the process of recovering the design conditions of a legacy system that is currently being used and that is not fully documented. • Forward Engineering - is the process of moving from high-level abstractions and models to the physical implementation of a system. Benefits and Drawbacks of Reverse Engineering • There is already a working system in place • If tools are available then process can be automated to an extent • The legacy system could be very hard to follow • The lead software engineers for the legacy system are usually not around What and How to measure • Looked at the Algorithmic Model: – Effort = A x SizeB x M – “A” is a constant factor for all local projects of the same type – “Size” is the number of lines of code or function points – “B” is usually assigned the values between 1 and 1.5 – “M” is a multiplier that consists of the sum of process, product, and development attributes Effort = A x SizeB x M • The main difference between Reverse and Forward Engineering in this model would be the “Size” • “M” would also vary because of the many factors it is based on Ethics • Therac 25 system – They Reverse Engineered code for different hardware due to the cheaper cost – A lot of the problems could have been stopped by just Forward Engineering a new system Conclusion • To improve a system’s maintainability no matter the size Reverse Engineering would be the best choice • To try and migrate a small system to new hardware it would be beneficial to Reverse Engineer the design as a means to Reengineer the system. – For a larger system Forward Engineering would be beneficial








![[MER93] Merlo, E., Girard, J.F., Kontogiannis, K., Engineering of User Interfaces”,](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/014835691_1-505b4dabdedd77635360f0aefe13440a-300x300.png)