Population Density and Distribution KEY CONCEPTàEach
advertisement

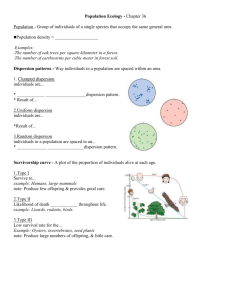
Population Density and Distribution KEY CONCEPTEach population has a density, a dispersion, and a reproductive strategy. HIGHLIGHT/UNDERLINE the important information in the text box below. Recall that a population is a group of the same species living in the same area. A population can be measured in many ways. One way is by its density. Population density is a measure of the number of individuals living in a defined area. Population density is measured by creating a ratio of individuals that live in a particular area to the size of that particular area. The formula for population density is: # of individuals / area (units²) = population density For example, if there are 50 deer living in an area of 10 km², the population density would be 5 deer per km². A population can also have a dispersion pattern. Population dispersion is how the individuals of a population are spread out in a specific area. There are three types of population dispersion patterns: Clumped dispersion shows that individuals live close together in groups or packs. This type of dispersion may help with hunting and feeding, as well as protection from predators. Uniform dispersion may indicate that individuals are territorial and compete for limited resources by living at specific distances from one another. Random dispersion shows no distinct pattern within a specific area. The reproductive strategies for a population are illustrated through survivorship curves. Survivorship curves illustrate the number of individuals in a population surviving over time. 1. What is a population density? 2. Calculate the population density for a group of 30 birds that live in an area of 3 km 2 3. What are the three types of population dispersion patterns and what are the characteristics of each population? Practice Questions: 1. Which of the following describes the density of a population? a. 5 sloths dispersed randomly. C. 100 wolves per square mile b. 100 people in the area d. 1 acre per family 2. The way in which individuals of a population are spread out is called a. population density. C. survivorship b. population dispersion. D. predation 3. Zebra herds that live and move together are an example of what type of dispersion? a. lumped dispersion c. random dispersion b. uniform dispersion d. territorial dispersion 4. What does a survivorship curve show? a. the number of births and deaths each year c. the number of offspring born in a particular year b. the number of predators that fed on a species’ eggs d. the number of offspring still alive over time 5. Most large mammals have type 1 survivorship curves, which means they have a. low infant mortality and high rates C. high numbers of offspring so that a few will survive of survival into old age. b. roughly equal survivorship rates at all ages. D. very high levels of predation and uniform dispersion Power Notes: