AP WORLD HIST E02
advertisement

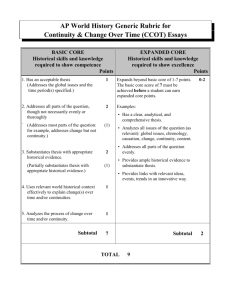
AP WORLD HISTORY (SECONDARY) ESSENTIAL UNIT 2 (E02) (Early Complex Societies: to 600 BCE) (July 2015) Unit Statement: The student will explore the shift in human organization from small bands of foragers to the formation of urban-based societies characterized by settled agriculture and trade. The AP College Board has defined three key concepts that apply to this unit; they include Big Geography and the Peopling of the Earth, Neolithic Revolutions and Early Agricultural Societies, as well as the Development and Interactions of Early Agricultural, Pastoral and Urban Societies. Essential Outcomes: (must be assessed for mastery) 1. The Student Will define key concepts outlined in this unit. 2. TSW outline archaeological evidence of Paleolithic human migration patterns from their origin in East Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas. (AP World History Key Concept 1.1) 3. TSW analyze the development of technological and cultural adaptions as early man inhabited new climate regions. (APWHKC 1.1) 4. TSW describe ways in which the Neolithic Revolution led to the development of new and more complex economic and social systems. (APWHKC 1.2) 5. TSW identify and describe social, political and economic characteristics of early agricultural societies that emerged in Mesopotamia, the Nile River Valley and Sub-Saharan Africa, the Indus River Valley, the Yellow River or Huang He Valley, Papua New Guinea, Mesoamerica, and the Andes. (APWHKC 1.3) 6. TSW outline the growth and expansion of the early state. (APWHKC 1.3) 7. TSW assess the role played by culture in unifying states through laws, language, literature, religion, myths, and monumental art. (APWHKC 1.3) Practiced and Ongoing Skills: (not formally assessed) 1. The Student Will analyze interactions between humans and the environment in different regions around the world in the time period defined by this unit. 2. TSW identify and analyze continuities and changes that occurred in social, political, economic and cultural institutions in different regions around the world in the time period defined by this unit. 3. TSW compare the development and governance of states in different regions around the world in the time period defined by this unit. 4. TSW outline patterns of interaction in trade of commodities, war and diplomacy in different regions around the world in the time period defined by this unit. 11 QSI AP WORLD HISTORY SEC E02 Copyright © 1988-2015 5. TSW describe major transitions in human economic activity including advances in technology, agriculture, labor systems, industry as well as economic systems that developed in different regions around the world in the time period defined by this unit. 6. TSW analyze the process through which social categories, roles and practices were created, maintained and transformed in different regions around the world in the time period defined by this unit. Key Terms and Concepts: The following key terms and concepts should be applied to TSW 1 Paleolithic Homo Erectus Cro Magnon Chinook Epic of Gilgamesh Indo European Migration Akkadians Assyrians Nubia Indra Varna Mandate of Heaven Chavin Popol Vuh Neolithic Homo Sapiens Agricultural Revolution Jomon Lex talionis cuneiform Venus figures Homo Sapien Sapiens Catal Huyuk Australopithecus Neandertal Jericho Natufian Hammurabi Chaldeans Assyrians Hittites Babylon ziggurats Bantu Migrations Osiris Jati Upanishads Oracle bones Lapita Yucatan Phoenicians Hieroglyphics Hyksos Lawbook of Manu Vedas Xia Mohica Maya Sumerians Kush Harappa Moksha Books of the Zhou Shang Olmec Teotihuacan Suggested Materials: Basic Resource: Traditions and Encounters Chapter 1-6 Additional Resource: Documents in World History The Human Record: Volume I Mesopotamian Values: Ideas About the nature of Life and Death: The Epic of Gilgamesh Babylonian Law: How an Early State Regulated its Subjects: Hammurabi’s Code of Law Egypt: Religious Culture and the Afterlife: Book Of the Dead Temple Reliefs: Egypt and Nubia Seals from: Mesopotamia, Harrapan India, and Minoan Crete Book of Documents: Illustration of the Mandate of Heaven Life, Death, and the Gods in Aryan India: The Rig Veda Israelites and their Neighbors: Excerpts from the Books of Genesis and Deuteronomy Other Sources: Princeton AP Review AP Achiever McGraw Hill AP Exam Prep Guide 12 QSI AP WORLD HISTORY SEC E02 Copyright © 1988-2015 Technology Links: http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0073406937/student_view0/index.html This is a website that compliments the textbook for this course. http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu/ This is a resource page for teachers; it includes lesson plans, documents, and articles related to AP World History. http://legacy.fordham.edu/halsall/ancient/asbook.asp This is a digital library of primary source documents in World History. http://apcentral.collegeboard.com/apc/public/courses/teachers_corner/4484.html?excmpid =MTG243-PR-16-cd This is the AP College Board address for the AP World History course; it includes past exams, lesson plans and data related to the exam. http://worldhistoryconnected.press.illinois.edu/AP_WH_Essentials.html This is an AP World History directory with a number of links to other resources helpful in instruction for the AP World History course. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yocja_N5s1I&list=PLBDA2E52FB1EF80C9 The Crash Course World History series by John Green is a comprehensive set of videos, each between ten and fifteen minutes in length, which complement the AP World History course. Unfortunately, schools in certain regions may have difficulty retrieving these sources due to issues related to website accessibility. http://www.pburgsd.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001118/Centricity/Domain/179/blank%20persian %20chart.pdf This is a link to a pneumonic device (PERSIAN chart) used in gathering information in different regions and time periods in AP World History. http://wheretheclassroomends.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/SOAPSTone-QuestionsChart.pdf This is a link to a pneumonic device (SOAPSTONE chart) used in gathering information from primary source documents in AP World History. Suggested Assessment Tools and Strategies: 1. Cornell Notes 2. Chapter Quizzes 3. Document Analysis using SOAPSTONE 4. CCOT ANALYSIS using PERSIAN RUBRIC FOUND ON FOLLOWING PAGE…………………………………… 13 QSI AP WORLD HISTORY SEC E02 Copyright © 1988-2015 Suggested Essential Unit 2 (E02) Rubric Name___________________________________ Class_______ Date____________ All TSW’s must be mastered for a ‘B’. 2 of 2 ‘A’-level blocks should be met for an ‘A’. Teachers may choose to use their own rubrics; however, all TSW’s must be assessed. TSW 1. Define key concepts outlined in this unit. 2. Outline archaeological evidence of Paleolithic human migration patterns from their origin in East Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas, and identify technological and cultural adaptions as early man inhabited new climate regions. 3. Analyze the development of technological and cultural adaptions as early man inhabited new climate regions. 4. Describe ways in which the Neolithic Revolution led to the development of new and more complex economic and social systems. 5. Identify and describe social, political and economic characteristics of early agricultural societies that emerged in Mesopotamia, the Nile River Valley and Sub-Saharan Africa, the Indus River Valley, the Yellow River or Huang He Valley, Papua New Guinea, Mesoamerica, and the Andes. 6. Outline the growth and expansion of the early state. 7. Assess the role played by culture in unifying states through laws, language, literature, religion, myths, and monumental art. ‘A’-Level ‘B’-Level Define key concepts outlined in this unit. Outline archaeological evidence of Paleolithic human migration patterns from their origin in East Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas, and identify technological and cultural adaptions as early man inhabited new climate regions. Analyze the development of technological and cultural adaptions as early man inhabited new climate regions offering original insight and/or a number of specific details. Analyze the development of technological and cultural adaptions as early man inhabited new climate regions offering general ideas from the text. Describe ways in which the Neolithic Revolution led to the development of new and more complex economic and social systems. Identify and describe social, political and economic characteristics of early agricultural societies that emerged in Mesopotamia, the Nile River Valley and SubSaharan Africa, the Indus River Valley, the Yellow River or Huang He Valley, Papua New Guinea, Mesoamerica, and the Andes. Outline the growth and expansion of the early state. Assesses the role played by Assesses the role played by culture in unifying states culture in unifying states through laws, language, through laws, language, literature, religion, myths, and literature, religion, myths, and monumental art offering monumental art offering original insight and/or a general ideas from the text. number of specific details. 14 QSI AP WORLD HISTORY SEC E02 Copyright © 1988-2015 Notes AP World History Rubric for a Document based Question (DBQ) BASIC CORE (competence) 0-7 Points 1. Has acceptable thesis 1 Point 2. Understands the basic meaning of documents. (May misinterpret one document.) 1 Point 3. Supports thesis with appropriate evidence from all documents. 2 Points (Supports thesis with appropriate evidence from all but one document) (1 Point) 4. Analyzes point of view in all or all but one of the documents 1 Point 5. Analyzes documents by grouping them in two or three ways, depending on the question 1 Point 6. Identifies and explains the need for one type of appropriate additional document or source 1 Point Subtotal /7 Points EXPANDED CORE (excellence) (Historical skills and knowledge required to show excellence) Expands beyond basic core of 1-7 points. A student must earn 7 points in the basic core area before earning points in the expanded core area. Examples: Has a clear, analytical, and comprehensive thesis Shows careful and insightful analysis of the documents Uses documents persuasively as evidence Analyzes point of view in most or all documents Analyzes the documents in additional ways - groupings, comparisons, syntheses Brings in relevant "outside" historical content Explains why additional types of document(s) or sources are needed 0-2 Points Subtotal /2 Points TOTAL /9 Points 15 QSI AP WORLD HISTORY SEC E02 Copyright © 1988-2015 AP World History Rubric for a Comparative Historical Essay BASIC CORE (competence) (Historical skills and knowledge required to show competence) 0-7 Points 1. Has acceptable thesis (Addresses comparison of the issues or themes specified) 1 Point 2. Addresses all parts of the question, though not necessarily evenly or thoroughly 2 Points (Addresses most parts of the question: for example, deals with differences but not similarities) (1 Point) 3. Substantiates thesis with appropriate historical evidence 2 Points (Partially substantiates thesis with appropriate historical evidence) (1 Point) 4. Makes at least one or two relevant, direct comparisons between or among societies 1 Point 5. Analyzes at least one reason for a similarity or difference identified in a direct comparison 1 Point Subtotal /7 Points EXPANDED CORE (excellence) (Historical skills and knowledge required to show excellence) Expands beyond basic core of 1-7 points. A student must earn 7 points in the basic core area before earning points in the expanded core area. Examples: Has a clear, analytical, and comprehensive thesis Addresses all parts of the question (as relevant): comparisons, chronology, causation, connections, themes, interactions, content Provides ample historical evidence to substantiate thesis Relates comparisons to larger global context Makes several direct comparisons consistently between or among societies Consistently analyzes the causes and effects of relevant similarities and differences 0-2 Points Subtotal /2 Points TOTAL /9 Points 16 QSI AP WORLD HISTORY SEC E02 Copyright © 1988-2015 AP World History Rubric for a Continuity and Change over Time Essay (CCOT) BASIC CORE (competence) (Historical skills and knowledge required to show competence) 0-7 Points 1. Has acceptable thesis (Addresses global issues and the time period(s) specified) 1 Point 2. Addresses all parts of the question, though not necessarily evenly or thoroughly 2 Points (Addresses most parts of the question: for example, addresses change but not continuity) (1 Point) 3. Substantiates thesis with appropriate historical evidence 2 Points (Partially substantiates thesis with appropriate historical evidence) (1 Point) 4. Uses relevant world historical context effectively to explain change over time and/or continuity 1 Point 5. Analyzes the process of change over time and/or continuity 1 Point Subtotal /7 Points EXPANDED CORE (excellence) (Historical skills and knowledge required to show excellence) Expands beyond basic core of 1-7 points. A student must earn 7 points in the basic core area before earning points in the expanded core area. Examples: Has a clear, analytical, and comprehensive thesis Analyzes all issues of the question (as relevant): global context, chronology, causation, change, continuity, effects, content Addresses all parts of the question evenly Provides ample historical evidence to substantiate thesis Provides links with relevant ideas, events, trends in an innovative way 0-2 Points Subtotal /2 Points TOTAL /9 Points 17 QSI AP WORLD HISTORY SEC E02 Copyright © 1988-2015