Problems for chapter 18 1307
advertisement

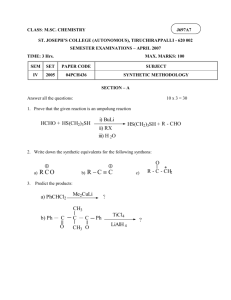
PROBLEMS CH 18 Learning Check Give the common and IUPAC names, and classify each as primary, secondary, or tertiary. 2 Solution A. STEP 1 Name the longest carbon chain bonded to the N STEP 1 atoms as alkanamines by replacing e of the STEP 1 alkane name with amine. Propanamine STEP 2 Number the carbon chain to show the position of STEP 2 the amine group and any substituents. CH3—CH2 —CH2—NH2 3 2 1 Propylamine (common), 1° 1-Propanamine (IUPAC) 3 Solution (continued) B. STEP 1 Name the longest carbon chain bonded to the N STEP 1 atoms as alkanamines by replacing e of the STEP 1 alkane name with amine. ethanamine STEP 2 Number the carbon chain to show the position of STEP 2 the amine group and any substituents. 4 Solution (continued) B. STEP 3 In a secondary or tertiary amine, use the prefix STEP 3 N- to name groups attached to the N atom. Ethyldimethylamine (common), N,N-Dimethylethanamine (IUPAC), 3° 5 Learning Check Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following: A. 2-pentanamine B. N-methyl-1-butanamine 6 Solution Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following: A. 2-pentanamine B. N-methyl-1-butanamine CH3—CH2—CH2—CH2—NH—CH3 7 Learning Check Give the common and IUPAC names for each of the following: A. B. NH2 C. 8 Solution Ethylmethylamine(common); N-methylethanamine A. B. Butylethylmethylamine (common); N-ethyl-N-methyl-1-butanamine NH2 C. Aniline 9 Classification of Amines Amines are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary. In a primary (1) amine, one carbon group is bonded to the nitrogen atom. A secondary (2) amine has two carbon groups. A tertiary (3) amine has three carbon groups. 10 Learning Check Consider the following compounds: 1) CH3—CH2—CH2—NH2 2) CH3—CH2—NH—CH3 3) CH3—CH2—CH2—CH3 A. Which compound has the highest boiling point? B. Which compound(s) is/are soluble in water? 11 Solution Consider the following compounds: 1) CH3—CH2—CH2—NH2 2) CH3—CH2—NH—CH3 3) CH3—CH2—CH2—CH3 A. Which compound has the highest boiling point? 1) CH3—CH2—CH2—NH2 B. Which compound(s) is/are soluble in water? 1) CH3—CH2—CH2—NH2 2) CH3—CH2—NH—CH3 12 Learning Check Identify the following heterocyclic amines: A. B. C. N N N H H H 13 Solution Identify the following heterocyclic amines: A. B. C. N N N H H H Piperidine Pyrrolidine Pyrrole 14 Learning Check Identify the heterocyclic amine in serotonin. 15 Solution The heterocyclic amine in serotonin is pyrrole. 16 IUPAC Names of Amides Write the IUPAC name for STEP 1 Determine the alkane name of the carbon chain in the carboxyl portion and replace e with amide. butanamide STEP 2 Name each substituent on the N atom using the prefix N- and the alkyl name. N-ethylbutanamide 17 Examples of IUPAC and Common Names N-Methylethanamide (IUPAC) N-Methylacetamide (common) — O H ║ CH3—C H2—C—N—CH2—CH3 N-Ethylpropanamide (IUPAC) N-Ethylpropionamide (common) 18 Learning Check Write the IUPAC name for the following: O CH2—CH3 ║ │ CH3—CH2—CH2—CH2—C—N—CH2—CH3 19 Solution STEP 1 Determine the alkane name of the carbon chain in the carboxyl portion and replace e with amide. pentanamide STEP 2 Name each substituent on the N atom using the prefix N- and the alkyl name. N,N-diethylpentanamide 20 Learning Check Draw the condensed structural formulas of the following amides. A. pentanamide B. N-methylbutyramide 21 Solution Draw the condensed structural formulas of the following amides. A. pentanamide B. N-methylbutyramide 22 Learning Check Give the common and IUPAC names for the following amides, and classify them as primary, secondary, or tertiary. A. B. 23 Solution Give the common and IUPAC names for the following amides, and classify them as primary, secondary, or tertiary. A. Butryamide (common) butanamide (IUPAC) primary (1) B. N-Ethyl-N-methylacetamide (common) (3) N-ethyl-N-methylethanamide (IUPAC), tertiary 24