ST-PP3(Ch9-18)Urbanization
advertisement

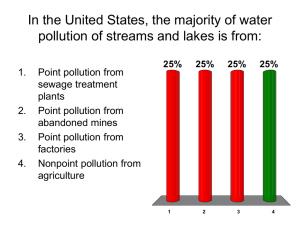
Chapter 9 The Urban World 2 Men and a ? Why are people moving to urban areas? Urban Migration 1800 – 3% Urban 1900 – 14% Urban / 12 cities with 1million people 1950 – 30% Urban / 83 cities with 1million people 2007 – 50% Urban / 400 cities & 19 with over 10million 2050 – 70% Urban Urban = in U.S. any place with more than 2,500 people History of Urban Revolutions First Urban Revolution - 8000 to 2000 BC Population and Urbanization Urbanization Trends in US What is a Megalopolis? Urbanization Pros & Cons? 1. Age Structure 2. Greater Number of Men 3. Poverty & Homeless People 4. Crime Rates 5. Pollution 6. Transportation 7. Infrastructure 8. Immigrants P.O.E.T Elements of an Ecosystem Population Organization Environment Technology = The Ecology of a City Urban Problems 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Land Use Patterns - sprawl or type of development Traditional Land Loss Flooding - location Brownfields - industrial waste Home Waste - disposal Sewage Treatment - 2/3 untreated in developing nations cities 7. Commute Times 8. Urban Heat Islands 9. Pollution - water (sewage), air (ground ozone & Energy Production), noise (traffic & agriculture) 1. Land Use - Georgia 1. Zoning 2. Land Use- Agricultural Loss 3. Flooding 3. Flooding 4. Brownfields Atlanta also has over 950 Brownfield sites within its boundaries. Atlantic Station was built on the site of the old Atlantic Steel Mill. From 1901 through 1997, the Atlantic Steel Mill operated, employing as many as 2000 people. Today, Atlantic Station is known as the largest urban brown field redevelopment in the nation. 5. Sewage in Atlanta A 19-square mile area of Atlanta, with Downtown as its center, is served by a combined sewer system. In a combined system, a single large sewer pipe carries both sewage and stormwater to a water reclamation center for treatment. Neighbors and available land for solid waste? 7. Commute Times 8. Atlanta’s Heat Island & Sprawl Impacts: Hotter = greater energy consumption Runoff = increased 9. Pollution Every unit has something on this topic