File
advertisement

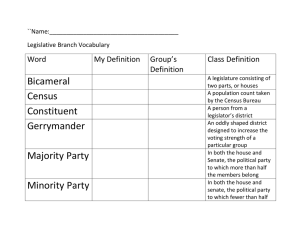
STRUCTURE & FUNCTION of FEDERALISM • Federalism, Separation of Power, Checks & Balances • Legislative Branch - Congress • Executive Branch – President • Judicial Branch – Supreme Court • NC State Government • NC Local Government FEDERALISM, SEPARATION OF POWER, CHECKS & BALANCES • Federalism – System of Government in which the Federal (National, Central) Government shares power with the states. Powers… Enumerated (Federal) Reserved (States) Concurrent (Shared by both) • Separation of Power – Dividing powers between 3 Branches of Government. Branches… Legislative – Makes Laws Executive – Enforces Laws Judicial – Interprets Laws • Checks & Balances – Powers given to each branch over the other 2 branches (checks) to balance the power & protect citizen’s rights. CHECKS & BALANCES LEGISLATIVE BRANCH - CONGRESS CONGRESSIONAL TERMS • 2 Years in Length • Currently the 113th Term of Congress CONGRESSIONAL SESSIONS • Regular Session – Must Meet once a Year (January 3 – December) • Special Session – President Calls – Times of Crisis • Joint Session – State of the Union Address HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES BASIC INFORMATION • Term Length – 2 Years • Requirements for Members 25 years old 7 year US Citizen Resident of the State • 435 Members • Based on State Population • Changes w/ Census (10 yrs) VOCABULARY • Census – Population Count • Constituents – people who vote in an election • Gerrymandering – dividing a state into odd-shaped districts for political reasons SENATE BASIC INFORMATION • Term Length – 6 years (1/3 every 2 years) • Requirements for Members 30 years old 9 year US citizen Resident of the State • 100 members • 2 per state CONGRESSIONAL LEADERS HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES • • • • • Speaker of the House – Chosen by the majority party Majority Leader – Leader of political party with most seats Minority Leader – Leader of party with fewer seats Majority Whip – From majority party – job is to get majority members to support party legislation. Minority Whip – From minority party – job is to get minority members to support party legislation. • • • • • • SENATE President – VP of the US President Pro Tempore – Usually the most senior member of the majority party Majority Leader – Leader of political party with most seats Minority Leader – Leader of party with fewer seats Majority Whip – From majority party – job is to get majority members to support party legislation. Minority Whip – From minority party – job is to get minority members to support party legislation. Powers of Congress (Money, Trade, & Foreign Policy) • • • • • Taxes Tax Bills – Begin in the House (Why?) Authorization Bill – Creates a Project. Appropriations Bill – Provides $ for a Project. Trade Commerce Clause – gives Congress power to regulate foreign & interstate trade. (air traffic, railroads, trucking, radio, television, air pollution, stock market) Foreign Policy Powers dealing with other countries. (declare war, oversee army & navy, approve treaties, regulate trade) Powers of Congress (Non-Legislative Powers) • • • • • Amending the Constitution – propose 2/3 of Congress Counting Electoral Votes – If no 270 – House votes Impeachment Process – House Impeach; Senate holds trial (removal/punishment) Oversight – Review presidential actions, and how well laws are enforced. Investigation – Investigate executive/judicial actions. Powers Denied to Congress 1. Suspend the Writ of Habeas Corpus 2. Pass a Bill of Attainder 3. Pass an Ex Post Facto Law 4. Tax Exports HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW EXECUTIVE BRANCH BASIC INFORMATION CONSTITUTIONAL REQUIREMENTS • • • 35 years old Natural Born Citizen Live in US 14 Years GENERAL • • • 4 year term 2 term limit (10 year maximum) (except FDR) $400,000 yearly – life • TRADITIONAL REQUIREMENTS • • • White Males (Except Obama) Protestant (Except JFK) College Educated (Many) PRESIDENTIAL SUCCESSION • • • • Vice-President Speaker of the House President Pro Tempore Cabinet Members ELECTORAL COLLEGE • Purpose – Officially Elects the President & Vice-President NUMBERS • 538 Total • 270 to win • Each State – Equal to total members in Congress • Winner Take All – Majority of Votes in a State – Takes all Electoral Votes. (Except 2 States) ROLES & POWERS OF THE PRESIDENT Chief Executive • • • Enforce laws passed by Congress Issue Executive Orders Create Budget Commander-in-Chief • • • Chief Diplomat • • • Enter into Treaties Make Executive Agreements Appoint Ambassadors Legislative Leader • Introduce legislation • State of the Union Address Economic Leader • Prepare the Federal Budget Head of Armed Forces Call out troops War Powers Act – report to Congress within 60 days Chief of State • • • • Meet with foreign dignitaries Throw out first baseball Easter Egg Hunt Symbolic Leader Party Leader • Lead political party • Support members running for office Foreign Policy Nation’s overall plan for dealing with other countries Goals of Foreign Policy • National Security – ability to keep nation safe from attack • International Trade - provide markets to sell goods • Promote World Peace • Promote Democracy Foreign Policy Nation’s overall plan for dealing with other countries Executive Agencies & Departments • • • • Department of State Department of Defense CIA National Security Council Foreign Policy Vocabulary • Treaty – formal agreement between two or more nations. President enters into treaties, must be approved by Senate. • Executive Agreement – agreement between President and the leader of another country. • Ambassador – appointed by President to represent US in another country. • Foreign Aid – money, food, or military assistance given to another country. • Limitations – Trade Sanctions & Embargoes IMPEACHMENT PROCESS • 1. 2. 1. 2. 3. Impeachment – The process of bringing formal charges against a public official. According to the Constitution, any public official, including the president, can be impeached and removed from office for treason, bribery, or serious misconduct. 2 Steps of the Impeachment Process House of Representatives – must pass by a majority vote the “Articles of Impeachment”. Senate – Chief Justice of the Supreme Court presides over the Senate acting as a court. A 2/3 vote of Senators is required to remove an official from public office. 3 Historical Examples Andrew Johnson (Tenure of Office Act) Impeached, not removed Richard Nixon (Watergate Scandal) Resigned before Impeachment Bill Clinton (Perjury) Impeached, not removed JUDICIAL BRANCH BASIC INFORMATION Types of Cases • • • • • Civil – involves a lawsuit filed (plaintiff), and (defendant) court decides responsibility Criminal – involves a crime committed. (Plaintiff = government) v. (defendant = accused) Judges Appointed by the President Approved by 2/3 of the Senate Serve Life Terms JURISDICTION • Jurisdiction – a court’s authority to hear a case 4 Types of Jurisdiction 1. Original Jurisdiction – a court’s authority to hear a case first. Appellate Jurisdiction – a court’s authority to hear appeals. Exclusive Jurisdiction – federal courts have authority to hear cases. Concurrent Jurisdiction – both state and federal courts can hear cases. 2. 3. 4. US DISTRICT COURTS Jurisdiction • • • • • • 94 Courts in the US – At least One in every State Original Jurisdiction – Hear Cases first Types of Cases – Civil, Criminal People Involved – Judge, 12 Jurors, Plaintiff, Defendant Decisions – Responsible, Not Responsible, Innocent, Guilty Responsible or Guilty – Have Right to Appeal US CIRCUIT COURTS • • • • • • 12 Courts Nationwide + 1 Federal Circuit Appellate Jurisdiction – Hear appeals from District Court Types of Cases – Criminal & Civil People Involved – 3 Judges, Plaintiff, Defendant Decisions – Uphold, Overturn, Remand Uphold – May appeal to the Supreme Court US SUPREME COURT • 1 Supreme Court • Jurisdiction – Original, Appellate • Types of Cases – Disputes between states, involving ambassadors, admiralty/maritime law, appeals dealing with Constitutional Issues • People Involved – 9 Supreme Court Justices, Plaintiff, Defendant • Decisions – Uphold, Overturn, Remand • Written Opinions – Majority, Concurring, Dissenting NC State Constitution State & Federal Government Similarities - Preamble - Bill of Rights - Framework of Gov - 3 Branches of Gov - State Powers - Gov Responsibilities - Provision for Local Gov - Amendment Process Constitutional Principles - Popular Sovereignty - Checks & Balances • • • - Separation of Power - Amendment (flexibility) NC Constitution Constitution of 1776 – created a bicameral legislature, executive headed by governor and a Council of State, and a court system. Constitution of 1868 – US Congress required all former Confederate States to rewrite Constitution. All men 21 years or older could vote, regardless of race. Constitution of 1971 – Freedom of Speech and equal protection added. NC General Assembly (Legislative Branch) LEGISLATIVE BRANCH – General Assembly – Make the Law Statute – a law passed by the state government. House of Representatives Members 120 Term Length 2 years Qualifications 21 years old district 1 year Senate 50 2 years 25 years old 2 years in NC district 1 year Legislative Sessions – odd # years = long session – January to June. even # years = short session – begins in May and lasts 6 weeks. Governor may also call special sessions. Law Making Process – very similar to US Congress. Override veto only requires 60% of both houses. NC Executive Branch EXECUTIVE BRANCH Governor – Enforce the Law Term Length – 4 Years – 2 consecutive term limit Qualifications – 30 years old, live in US 5 years, live in NC 2 years Lieutenant Governor Term Length – 4 Years Qualifications – 30 years old, live in US 5 years, live in NC 2 years Duties - President of the Senate, serves on various boards & commissions. Executive Departments Cabinet – 10 members appointed by the governor Council of State – 8 members elected by the people of NC. Operate independently of the Governor. NC Judicial Branch JUDICIAL BRANCH Interpret the Law District Court – civil cases < $10,000; misdemeanors, domestic, juveniles – judges elected 4 year terms Superior Court – civil cases> $10,000; felonies, appeals of misdemeanors – judges elected 8 year terms Court of Appeals – 3 judges per case; appeals except the death penalty – judges elected 8 year terms Supreme Court – 7 justices; appeals – first appeal of death penalty – judges elected 8 year terms Landmark Court Decisions Bayard v. Singleton (1787) – family property seized by state law for being a loyalist. Appeals court ruled law unconstitutional (judicial review – state gov) Leandro Case (1997) – ruled that the state constitution does not require equal funding of education. GOVERNMENT FINANCES State Budget Process Fiscal Year – (July 1 – June 30) Budget – Begins July 1 of odd-numbered year – June 30 of next odd-numbered year. Revenue - $ the state government has to operate. (Taxes, fees, etc…) Expenditures - $ the state government will spend on programs. Balanced Budget – Expenditures = Revenue Governor – prepares budget for two fiscal years. General Assembly – must pass the budget. Propose ways to raise revenue & cut expenditures. Often they do not pass budget by July 1. LOCAL GOVERNMENT • Types of Local Government – County & Municipality • Municipality – a city, town, or village with an organized government and the authority to make and enforce laws. (State General Assembly grants charter) • Ordinance – a law passed by a local government. • Zoning – designating different areas of land for different uses. 1. 2. 3. • residential – housing commercial – business (retail, etc…) industrial – factories Annexation – incorporating land into a municipality. COUNTY GOVERNMENT County Government County Commissioners – voters elect commissioners (3-11). Chairperson – may be elected or chosen by commissioners. County Commissioners are responsible for the following… • Hire administrators for education, elections, mental health, public health, social services, alcoholic beverage control, and soil and water conservation. County Manager – Hired by the County Commissioners. Responsible for budget. • LEA – Local Education Authority Voters elect a school board to carry out state education policy. MUNICIPAL GOVERNMENT • • • • • Municipality Government Each municipality elects a governing board. (City Council, Town Council, Board of Commissioners, Board of Alderman) Elections (At Large, by Ward, or Mixture) Pass Ordinances – municipal policies, approve budgets, set municipal tax rates, regulate what people can do in the municipality. Mayor-Council Plan Usually elected, not always. In this system the mayor serves as the executive. Carries out policies, budget, etc… Council-Manager Plan Governing board hires a professional called a “manager”, to carry out policies. This is how Kernersville, W-S, etc… operate. GOVERNMENT FINANCES Local Government Budget • Expenditures utilities (water, sewage) public safety public schools public health mental health social services • Revenues user Fees (water, sewage) property tax intergovernmental revenue • C&G.2 • 2.1 Distinguish between the structures of the branches of government and the levels of government in the United States. In your response indicate three differences between them. • 2.2 Compare and contrast two roles of North Carolina state and local government in the lives of citizens. 2.3 "The object of the [Fourteenth] Amendment was undoubtedly to enforce the absolute equality of the two races before the law, but in the nature of things it could not have been intended to abolish distinctions based upon color, or to enforce social, as distinguished from political, equality, or a commingling of the two races upon terms unsatisfactory to either." —Justice Henry Billings Brown, speaking for the majority in Plessy v Ferguson We conclude that, in the field of public education, the doctrine of "separate but equal" has no place. Separate educational facilities are inherently unequal. Majority Opinion Brown v Board of Education of Topeka Kansas 1954 Critique how Plessy vs Ferguson and Brown vs Board of Education demonstrate the concept of a “living constitution”, utilize the excerpts from the court documents provided. In your response, discuss two differences.