WATER
advertisement

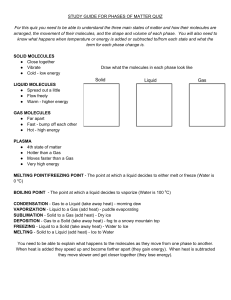
WATER UNDERGROUND WATER Porosity: measure of how much of a rock is open space. This space can be between grains or within cracks of a rock Permeability: measure of the ease with which a fluid can move through a porous rock. POROSITY AND PERMEABILITY LAB Question: What is the porosity and permeability of different soils and rocks? Hypothesis: If soil, sand, and pebbles are used, then _________ will have the greatest porosity. Hypothesis: If soil, sand, and pebbles are used, then _________ will have the greatest permeability. Observations: Conclusion: MINI POROSITY LAB Sandstone Limestone Basalt Find dry mass, soak overnight, find wet mass. Which stone would serve as a better aquifer? WATER Water: H2O molecule Hyrdogen Bond: weak attraction between H (+ charge) and O (-charge) Water molecules have one negative charge and two positive charges (opposite charges attract) STATES OF WATER Molecules are always moving, Changing from one state to another, heat is either lost or gained Gas: molecules are separate, lots of heat so moving fast Liquid: molecules form weak attraction (hydrogen bond), move more slowly Solid: hydrogen bonding holds together in 6 sided lattice pattern, least heat energy, move slowly Heat travels from areas of high temp to low temp ex: you are holding ice, heat travels form hand to ice Evaporation: molecules if liquid water move quickly breaking bonds becoming water vapor. Heat is ABSORBED. EX: Water in pan on stove. Heat from pan goes to water, water molecules heat up and become gas molecules. Condensation: air molecules slow down, weak bonds are made. Heat is RELEASED. EX: Water Vapor near mirror, heat leaves water and goes to mirror. Air molecules cool down and become liquid water. Freezing: Melting: DURING FREEZING TEMPERATURES, WHY WOULD THEY SPRAY DOWN ORANGE TREES WITH WATER? PROPERTIES OF WATER 1. More things dissolve (become incorporated into a liquid) in water than in any other substance. Compounds that also have positive or negative charges form hydrogen bonds with water. Nutrients in soil dissolve in water and are taken up through plants roots. 2. When water freezes, the molecules form a lattice pattern Cold water molecules move close together. During freezing, instead of moving very close together, a lattice structure (ice) forms. Solid water molecules are farther away then liquid water molecules. Therefore, ice is less dense than liquid causing ice to float. If ice were denser, then ponds and lake would freeze from the bottom up and plant life would be affected. DENSITY Density: heating and cooling affects the density of water. Heating water speeds up the movement causing the molecules to move farther apart. This is why warmer water is less dense than colder water. As water cools, molecules lose heat and move more slowly moving closer together making cold water denser. Ice is less dense due to its lattice structure, so it floats. ADHESION AND COHESION Cohesion: attraction between water molecules between each other Surface Tension: result of cohesions, water molecules attracted to each other but not the gas molecules above the water surface water. Water surface to behave like a stretched membrane Adhesion: attraction of water molecules to other substances, like soil or glass Capillary action: water adheres to other substances, water molecules can travel this way. EX: Water moving up a paper towel WATER CYCLE Evaporation: liquid to a vapor, may evaporate from the ocean, river, lake or glacier Condensation: when water vapor cools, clouds form when water vapor condenses into water droplets or ice crystals Precipitation: water falls from the sky as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. High up in the atmosphere, precipitation usually stars as snow and melts into rain. Runoff: precipitation that reaches the ground and flows on the surface Infiltration: percolates into the soil becoming groundwater Transpiration: evaporation of water from pores (stomata) on the surface of plants’ leaves. Helps plants transport water upward from their roots through their tissues. Cohesive and adhesive properties of water all contribute to water circulation through a plant. Evapotranspiration: combined effects of evaporation and transpiration WATERSHED Watershed: Area that drains water to a low point: river stream, arroyo, lake, etc. Majority of Arizona’s land is contained within the Colorado River Watershed, which mean that water that falls on most of the water as rain or snow as the potential to find its way through tributaries and groundwater movement to the Colorado River. GROUNDWATER: READING 1 WHAT, WHERE, HOW AND WHY Unsaturated Zone Saturated Zone Aquifer Discharge Direction Water Flows Artesian Well/Aquifer Spring Water Table Recharge