Kinetic Energy
advertisement

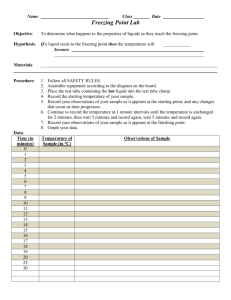
Thermodynamics: the study of thermal energy Heat (energy) Transfer Potential Energy - Stored in the vibrations of the molecules - Limited by the “degrees of freedom” available to the molecule Kinetic Energy - Motion of atoms and molecules - Reflected in the TEMPERATURE of the substance Faster = higher temperature Potential If the molecules have many “degrees of freedom”, Energy they can store more potential energy, with less change in the kinetic energy of the molecules. Therefore, the temperature will change slowly. Kinetic Energy If the molecules have few “degrees of freedom”, they can store little potential energy, with more change in the kinetic energy of the molecules. Therefore, the temperature will change more rapidly. Kinetic-Molecular Theory As a substance gets hotter, its molecules move faster! Faster molecules have higher kinetic energy. A higher kinetic energy is reflected by a higher temperature! You may not be able to SEE molecules moving fast without a microscope, but you can see an increase in temperature on a thermometer. Microscopic: Cannot be seen by eyes aloneusually you can’t “measure” the kinetic energy of the molecules Macroscopic: Can be seen with eyes aloneyou can measure the temperature! Kinetic-Molecular Theory As a substance gets hotter, its molecules move faster! Faster molecules have higher kinetic energy. A solid: the molecules are tightly packed together and move more slowly. When you add heat… A liquid: the molecules are not packed as tightly together and move around. When you add more heat… A gas: the molecules are not bound together and move very fast. When you add more heat….. A plasma: the atoms themselves are ripped apart to become ions. Heat Transfer Since the atoms in aluminum can store more potential energy than the atoms in gold, as heat flows, the gold atoms will gain more kinetic energy so that the temperature of gold rises much faster than the temperature of the same mass of aluminum. In one episode of the original TV series, “Mission Impossible”, the team utilized that fact that gold heats up so quickly compared to other materials. They drilled a hole in the bottom of a vault and inserted an electric heat rod. The gold in the vault heated up, melted and flowed through the hole in the bottom of the vault before any of the paper money or other coins got too hot. Would that really work?? Hmmm, maybe- but don’t try it! Specific Heat Capacity, “c” • The specific heat capacity, “c”, of a substance is the amount of heat required per kilogram to raise the temperature by one degree. • Different substances have different specific heat capacities. Aluminum has a higher specific heat than gold! More heat must be transferred into aluminum than into gold for the same change in temperature • The higher the heat capacity, the more heat the substance can “hold” or “give off” with minimal temperature change. Unit: J/kg·K (or J/kg·°C) Specific Heat Capacity of Water For example, you put 1 kg piece of metal on a hot plate for two minutes. You also put a container of 1 kg water in on an identical hot plate. Would you rather place your finger on the metal or in the water? The metal will be at a much higher temperature! Both received the same amount of heat energy. But water has a higher specific heat capacity- it can absorb or release more heat energy with little temperature change. – – – – Water has one of the highest specific heats of all substances. It can absorb and give off great amounts of heat energy with little temperature change. It takes a long time to heat water and it takes a long time for water to cool down! Another example: The filling on a hot apple pie burns our tongues and not the crust even though they are the same temperature because of the water content in the filling. The filling can give off a lot of heat and STILL be hot. The oceans help maintain a small range of temperature on Earth that is compatible with life by absorbing heat in the day and releasing it at night with little change in the ocean’s temperature. Weather along the Coastline • Coastal regions do not experience a large change in temperature because the water absorbs solar radiation in the day and releases it at night • In contrast, in a desert there's a wide daily range of temperature because no water is available to absorb heat in the day and release it at night Table of Specific Heat • The average specific heat capacity of a human body is approximately 3500. Substance Specific Heat Capacity (J.kg-1.K-1) water 4200 ice 2100 ethanol 2400 copper 390 aluminium 900 glass 840 mercury 140 wood 1700 lead 130 Heat transfer and temperature change As heat, Q, flows into or out of a substance, its temperature change, DT, will depend on the mass, m, of the substance and its specific heat capacity, “c”. Q = mcDT Example: How much heat, Q, is required to raise the temperature of a 3 kg pan of water from 15°C to boiling temperature? (specific heat of water = 4186 J/kg·K) Q = mcDT What is DT? Final – original = 100° – 15° = 85° Q = 3 (4186) 85 = Q = 1,067,430 J Q = mcDT A 0.2 kg block of metal absorbs 1500 J of heat when its temperature changes from 20 to 35 degrees Celsius. What is the specific heat capacity of the metal? c = Q ÷ (mDT) c = 1500 ÷ (0.2 • 15) c = 500 J/kg·K Q = mcDT What is the change in the temperature of 3.5 kg water if 950,000 J of heat are added? C = 4186 J/kg·K DT = Q ÷ (mc) DT = 950,000 ÷ (3.5 • 4186) DT = 64.9°