Classification Notes
advertisement

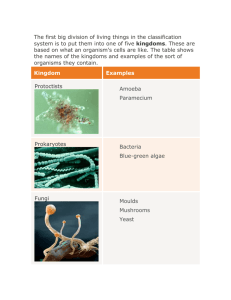
• • • • • • • • • • 121. Evolution Quiz 122. Evolution Notebook check starts 5/9 123. Classification Notes 4/29 and 5/2 124. Dichotomous Key 4/29 and 5/2 125. Prokaryotic VS. Eukaryotic 126. Kingdoms and Domains 127. Classification Review due 5/9 and 5/10 128. Diversity of Life Foldable Rubric 129. Plants 130. Plant Reproduction • Taxonomy = classification of organisms in different categories based on characteristics • How many species are there???? • Carolus Linnaeus: proposed a taxonomic hierarchy to categorize organisms Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Human Wolf Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primata Hominidae Homo sapiens Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Canidae Canis lupus Who is most related? –Binomial nomenclature = naming system • uses two Latin names coming from hierarchy: Genus species • Scientific name for Humans = –Homo sapiens • Why do we classify life? –To understand adaptive radiation (branching evolution on cladograms) 1. Lutra lutra 2. Felis catus 3. Ursa horribilis 4. Dionaea muscipula 5. Panthera pardus 6. Apis mellifera 7. Canis familiaris 8. Equus caballus 9. Agkistrodon contortrix 10. Toxicodendron radicans 11. Streptococcus pyogenes 12. Canis latrans 13. Orcinus orca 14. Rana catesbeiana a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) l) m) n) Cat Copperhead snake Poison Ivy Coyote Horse Killer whale Otter Dog Bullfrog Honeybee Grizzly Bear Venus Fly-Trap Strep-throat-causing Bacteria Leopard • A device that can be used to easily identify an unknown organism. • Comes from two Greek words that mean "divided in two parts“ • Gives you two choices in each step. 1. a. Has pointed ears .............................................. go to 3 b. Has rounded ears .............................................go to 2 2. a. Has no tail ........................................Norno Kentuckyus b. Has tail ....................................................Norno Dakotus 3. a. Ears point upward ............................................go to 5 b. Ears point downward .......................................go to 4 4. a. Engages in waving behavior ......................Norno Dallus b. Has hairy tufts on ears .........................Norno Californius 5. a. Engages in waving behavior ................Norno WalaWala b. Does not engage in waving behavior ................go to 6 6. a. Has hair on head ...................................Norno Beverlus b. Has no hair on head (may have ear tufts) ......go to 7 7. a. Has a tail .................................................Norno Yorkio b. Has no tail, aggressive ..................................Norno Rajus Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic #125 • Make a VENN diagram • Pg 173 in text • A new taxonomic category • Domains are more-inclusive than kingdoms 1. Bacteria – unicellular, prokaryotic, very diverse 2. Archaea – unicellular, prokaryotic, live in extreme environments 3. Eukarya – consists of all organisms whose cells contain a nucleus 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Animalia Plantae Fungi Protista Archaebacteria Eubacteria = contain eukaryotic cells = prokaryotic cell ANIMALIA PLANTAE FUNGI PROTISTA Archaebacteria Eubacteria Domain Cell Type Cell Wall Present Cell Wall Content # of Cells Mode of Nutrition Examples Part 1: Part 2: Look at page 467 in your textbook. Write the answers to the questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Part 3: Use Chapter 18.3 Review 1. In which domain would you classify the following organism: autotrophic, no nucleus, has peptidoglycan in its cells walls? 2. How many cells do Archaea organisms have? 3. What makes fungi different from protists? 4. What sets Animalia apart from all other kingdoms? 5. Which kingdom is most closely related to plants? 6. Which kingdom is the “least satisfying classification?” Why? 7. Why was the original bacteria kingdom of Monera divided into 2 separate kingdoms? 8. Which two kingdoms contain organisms that are non-motile (unable to move from place to place)? 9. As the only prokaryotic kingdoms, how Eubacteria and Archaebacteria differ from the other 4 kingdoms? 10.Which 2 kingdoms only includes heterotrophs? Part 4: Look at page 463 in your textbook. Identify the leaves using the given dichotomous key. I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. • ARTHROPODS #128 Foldable Rubric • ANNELIDS • BACTERIA VS. VIRUSES • PROTISTS • VERTEBRATE ANIMALS • PLANTS (on back) • Provide base for food chains • Provide oxygen • Multi-cellular • Eukaryotes • Contain cell walls made of cellulose • Autotrophic (contain chloroplasts) • 2 Main Divisons 1. Vascular – contain tissues that carry water/food through plant 2. Non-vascular – no vascular tubes, rely on diffusion, live near water, small, short • Vascular Tissue = carry materials –Xylem = carries water through plant –Phloem = carries food/nutrients through plant • Leaves – make food • Roots – absorb water and nutrients from soil • Stems – supports plant; connects leaves and roots • Seeds – created when pollen fertilizes ovule; protect developing embryo 1. Mosses – seedless, non-vascular (Bryophytes) 2. Ferns – seedless, reproduce using spores, vascular 3. Gymnosperms –produce seeds on CONES, vascular 4. Angiosperms – flowering plants, vascular – Produce seeds INSIDE the plant – FLOWERS = Reproductive organs – Seeds are protected by OVARY (becomes the fruit) • Reproduce asexually – vegetative propagation: new individuals arise without production of seeds or spores • Or mainly sexually using pollen and ovules – Alternation of generations • Sporophyte – diploid plant, makes haploid spores by meiosis • Gametophyte – haploid plant, makes gametes (pollen or ovule) which will fuse to make new sporophyte • See drawing on board! • • • • • • • Plant Reproduction Video Use Page 6 for Reproductive Structures Label next slide with name & function. 1. Peduncle: attaches stem to flower 2. Receptacle: expanded flower stalk 3. Sepals 4. Petals Label the reproductive parts of the flower and list the function of each •Carpel? •Sepal? •Stamen? •Peduncle? •Stigma? •Sepal? •Anther? •Ovary? •Petals? •Style? •Nectar? •Ovary? •Filament? •Style? •Stigma? •Anther? •Filament? •Style? •Stigma? •Anther?