Hypertension Results
advertisement

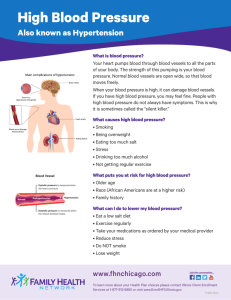
Chronic Care Management Hypertension Results: Represents Health Disparities Collaborative for Hypertension Overall CAP Results HYPERTENSION FACTS Uncontrolled high blood pressure increases the risk of heart failure by 200 percent, compared with those who do not have hypertension. Moreover, the degree of risk appears directly related to the severity of the high blood pressure. * More than 50 million Americans have high blood pressure. (American Heart Association, 2000 Heart and Stroke Statistical Update) * One-third of those with the disease don't know that they have it. (Mayo Clinic Report, "Hypertension," November 6, 1997) * Only 27% of people with hypertension (13.5 million) are treated and have their high blood pressure controlled. (American Heart Association, 2000 Heart and Stroke Statistical Update) Enrollment Facility (Table) Facility Cumulative Frequency Valid Percent Valid Percent Percent Cabin Creek 240 30.2 30.2 30.2 Family Care Charleston 283 35.6 35.6 65.7 Family Care Teays Valley 84 10.6 10.6 76.3 New River Health Center 110 13.8 13.8 90.1 5 .6 .6 90.7 74 9.3 9.3 100.0 796 100.0 100.0 North Fayette Family Health Center Riverside Health Center Total Blood Pressure Check Within Past 6 Months 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 A B C D Average Systolic Pressure 138 137 136 135 134 133 132 131 130 129 128 A B C D Average Diastolic Pressure 90 88 86 84 82 80 78 76 74 A B C D Documented Patient Self-Management 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 A B C D Blood Pressure < 140/90 as % 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 A B C D HYPERTENSION FACTS * High blood pressure can lead to strokes, heart attack, heart failure, kidney failure, and visual impairment. (Mayo Clinic, "Track Your Blood Pressure, January 24, 2000, * The incidence of high blood pressure (HBP) increases with age: * 44% of men and women aged 55-64 have HBP * 60% of men and women aged 65 to 74 have HBP * 64% of men and 77% of women over 75 have HBP (Supplement 2 to the Journal of the American Society of Consultant Pharmacists 1999/ vol. 14) HYPERTENSION FACTS * 32% of African Americans have high blood pressure. (Burt et. al, "Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the adult US population: data from the health examination surveys, 1960-1991. Hypertension 1995: 26:60-9) * High blood pressure costs $24.5 billion in direct costs in this country each year. (American Heart Association: 2000 Heart and Stroke Statistical Update) Compiled by The National Council on the Aging, March 2000. Health Disparities Collaborative for Hypertension Typical Levels Target Levels BP <140/90 mmHg 20-30% >50% BP Documented 2 times/year 50-70% >90% Depression screening (within last 12 months) <20% >70%> Self management goal setting (within last 12 months) <20% >50% Smoking cessation <20% >30% West Virginia Healthy People Year 2010 OBJECTIVE 12.3. Decrease the proportion of adults who have high blood pressure to no more than 22%. (Baseline: 28.3% in 1997) Data Source: WVBPH, OEHP, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) Women & Heart Disease * Heart disease is the #1 killer of American women * One of every three deaths for American women is from heart disease—one in every thirty deaths is from breast cancer * Women's heart disease risk starts to rise in middle age * One in eight American women aged 45-64—and one in three women over 65—has some form of heart disease * In 2002, more than 40 million American women are over age 50 * Nearly two-thirds of American women who die suddenly of a heart attack had no prior symptoms * About two-thirds of American woman women who have a heart attack do not make a full recovery * According to a National Council on the Aging survey: Only 9 percent of American women view heart disease their main health concern—but 61 percent see breast cancer as their chief health concern Internet Links for further information Health Disparities Collaborative – Cardiovascular Disease http://www.healthdisparities.net/collaboratives_cardio.html West Virginia Healthy People 2010 Objectives http://www.wvdhhr.org/bph/hp2010/objective/contents.html Cardiovascular Self-Management Tool http://www.healthdisparities.net/resources.html Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines http://www.guideline.gov/index.asp Improving Chronic Illness Care http://www.improvingchroniccare.org