Hypertension In Children - Coordinated School Health
advertisement

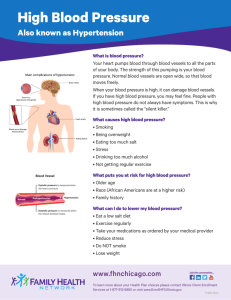
BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT IN CHILDREN Mohammad Ilyas, M.D. Director Hypertension Clinic Arkansas Children’s Hospital Division of Nephrology, Department of Pediatrics. UAMS Little Rock School Health Conference, Little Rock Little Rock is the capitol of State of Arkansas 7/19/07 A. B. False True Distribution of Hypertensive Patients Adults Children 2.5 million 47.5 million 7/19/07 Tracking of Blood Pressure Bogalusa Heart Study showed 40% individuals with SBP > 80th percentile at baseline had levels above that 15 years later The ability to predict BP levels in adulthood from measurements in childhood would provide the opportunity to intervene before hypertension is established, thereby reducing the CVD risk. (Lane et al. J Human Hypertension 2004) 7/19/07 Overweight and Hypertension in Children Prevalence of Overweight in Children Prevalence of Hypertension in School Children 4.50% 14% 4.00% 12% 3.50% 10% 1971-1974 1999-2000 8% 6% Prevalence Prevalence 5.00% 16% 3.00% 2.50% 1989 2004 2.00% 1.50% 4% 1.00% 2% 0.50% 0% 0.00% 6 to 11 years 12 to 19 years Year Age Group Ogden CL et al. JAMA 2002 7/19/07 Sorof JM et al. Pediatrics 2004 Blood Pressure, in children, is most commonly measured by: A. B. 7/19/07 Physicians Nurses Blood Pressure Measurement Training Why to train already trained personnel? 7/19/07 Effect of Training on Observer Errors 7/19/07 Bruce NG et al. J Hypertens 1988; 6:375- 380 Outline History (brief) Blood pressure measurement devices Procedure Definition of hypertension Practice cases 7/19/07 Blood Pressure Measurement Stephen Hales 1733 Hollow glass tube in neck artery of horse Blood rose 9 feet in glass tube 7/19/07 Medicine, an Illustrated History 1987 History of Blood Pressure Measurement 1896. Scipione RivaRocci Only Systolic BP measured by palpation 7/19/07 Medicine, an Illustrated History 1987 Blood Pressure Measurement - History Cook and Briggs 1903 Residents, Johns Hopkins Single size rubber bladder Arm size a “small factor” Systolic BP Children Adults korotkoff 7/19/07 75-90 (<2 yr) 90-110 (childhood) 130 (men) 120 (women) Devices 7/19/07 7/19/07 Which blood pressure apparatus is the “Gold standard” for BP measurement in children above age 3 7/19/07 A. B. C. D. E. DINAMAP Oscillometric wrist BP monitor Ambulatory BP monitor Mercury sphygmanometer Aneroid BP monitor Mercury Sphygmomanometer 7/19/07 Mercury Sphygmomanometry 1998: EPA and the American Hospital Association agreed to virtually eliminate mercury from hospitals by 2005 7/19/07 In the absence of a mercury manometer, which is preferred method to measure BP in children above age 3 A. B. C. D. 7/19/07 Oscillometric wrist BP monitor Auscultatory aneroid BP monitor Oscillometric arm BP monitor DINAMAP Aneroid Manometer Mercury pressure gauge replaced by mechanical spring Gauges are often small Accuracy varies among manufacturers Requires frequent calibration 7/19/07 Aneroid Manometers 7/19/07 Mercury and Aneroid Manometer 7/19/07 How often should an aneroid BP monitor be calibrated? A. B. C. D. E. 7/19/07 Once a day Once a week Once every 6 months Once a year Once every 5 years Testing the Aneroid Manometer Does the needle rest at zero? Inflate to 200 mm Hg. Wait for 1 minute, if lower than 170 suspect leak Using the Y connector, connect to mercury device and check readings If any reading is off by >4 mm, remove from service Date the calibration 7/19/07 Which is preferred method to measure BP in neonates and infants? A. B. C. D. E. 7/19/07 Oscillometric wrist BP monitor Auscultatory aneroid BP monitor Oscillometric finger BP monitor DINAMAP Mercury sphygmanometer Oscillometric Devices Office Use Expensive (approximately $3000) Many have been validated (BHS, AAMI) Recommended for children of all ages Home Use Relatively inexpensive Few have been validated in children Not recommended for ages < 4 years 7/19/07 Dinamap Oscillometric Device ® 7/19/07 Dinamap® is an acronym for: Device for Indirect Noninvasive Mean Arterial Pressure Dinamap Oscillometric Device ® 7/19/07 Dinamap® has been widely used in pediatrics Detects MAP and estimates SBP and DBP Proprietary algorithms Accuracy decreases with increased arterial “stiffness” Possible systematic errors in diabetics What is being measured? Auscultatory method: relies on relationship between audible Korotkoff sounds and pressure at systole and diastole Oscillometric method: relies on the amplitude of oscillations in the arterial wall to determine MAP (maximum amplitude); complex and proprietary algorithms used to estimate SBP and DBP 7/19/07 Evaluation of the Dinamap 8100 Rose et al (2000)* Noted from review of data from NHLBI studies that Dinamap algorithm skipped certain values ARIC Study: More than 180,000 individual BP measurements Never recorded SBP of 89, 119, 124, 125, 130, 140, 141, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 200 mmHg No skip pattern for DBP Skipped HR of 95, 99, 103, 106, 109 bpm Rose KM et al Hypertens (2000); 35:1032-1036 7/19/07 Oscillometric Devices 7/19/07 Validated Monitors British Hypertension Society Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) www.hyp.ac.uk/bhs/blood_pressure_list www.aami.org dabl Educational trust 7/19/07 www.dableducational.com Ambulatory BP Monitoring Oscillometric or acoustic methods 24 hour monitoring Individual measurements not more accurate Readings downloaded into PC Cost: $2500-4500 7/19/07 Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring 7/19/07 White Coat Hypertension 7/19/07 Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring 7/19/07 Procedure 7/19/07 What effect would you expect when taking the blood pressure on an obese child with a small BP cuff? A. No effect B. Higher blood pressure C. Lower blood pressure 7/19/07 Case History 12 years old boy Admitted for cellulitis of left lower leg BP= 210/110 mm Hg Blood pressure rechecked Physical examination, Wt. 587 pounds 7/19/07 Blood Pressure Cuff size 7/19/07 Blood Pressure Cuff Size Index line Cuff length = 80% of MAC Bladder length (80%) 20% MAC Largest allowable mid arm circumference for bladder (100%) 7/19/07 Cuff width = 40% of MAC Blood Pressure Cuff Size NHANES 99-2002 Children Child Adult Large adult Thigh 80 70 60 71 57 50 (%) 51 40 37 30 20 10 0 30 25 3 0.5 3-8 yrs 11 0.7 9-14 yrs 9 4 15-19 yrs 35% of 4th and 8th graders needed large adult cuff in Marianna 7/19/07 Recommended Dimensions for BP Cuff Bladders Age range Width (cm) 4 Length (cm) 8 Max. AC (cm) 10 Infant 6 12 15 Child 9 18 22 Small adult 10 24 26 Adult 13 30 34 Large adult 16 38 44 Thigh 20 42 52 Newborn 7/19/07 Blood pressure is measured in children preferably on A. B. C. D. E. 7/19/07 Right lower leg Left upper arm Right upper arm Left wrist Right wrist What is the optimal position for a patient’s arm to be in when taking the blood pressure? A. B. C. 7/19/07 D. Cubital fossa at the heart level Elbow at heart level Elbow supported with midpoint of upper arm at heart level Elbow by the side of the body Auscultatory Method Fourth Report on BP in Children 2004 Sitting quietly for 5 minutes Back supported and feet on the floor Right arm supported, cubital fossa at heart level Estimate systolic BP by palpation, reinflate cuff to 20 mmHg higher Pediatrics. August 2004 7/19/07 What is the optimal rate of deflation of blood pressure cuff? A. B. C. D. 7/19/07 1 mm Hg / sec 2-3 mm Hg / sec 5 mm Hg / sec 10 mm Hg / sec Auscultatory Method Fourth Report on BP in Children 2004 Deflate cuff at 2-3 mmHg/sec Systolic BP= onset tapping sounds* Diastolic BP= disappearance of sounds (fifth Korotkoff sound) Record BP twice on each occasion as right arm, sitting, SBP/DBP(K5), average used to estimate BP level Pediatrics1996;98:649-658 7/19/07 Auscultatory Sounds 7/19/07 Auscultatory Method Fourth Report on BP in Children 2004 DBP is determined by disappearance of Krotkoff sounds (K5) Sometime Krotkoff sounds heard till 0 mm Hg Try less pressure on the head of stethoscope If K5 still persists K4 should be recorded as DBP Fourth report on BP. Pediatrics August 2004 7/19/07 Blood Pressure In Children Auscultation is preferred method Elevated BP must be confirmed on repeated visits BP readings >90th obtained by oscillometric devices, should be repeated by auscultation Fourth report on BP. Pediatrics August 2004 7/19/07 Definition 7/19/07 Hypertension- Definition Normal blood pressure: less than 120/ 80 mmHg Pre-hypertension: 120 – 139/ 80 - 89 mmHg Hypertension: Stage 1: 140 to 159 /90 to 99 mmHg Stage 2: 160 mmHg / 100 mmHg The JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003; 289:2560. 7/19/07 Pediatric BP Standards Blood pressure correlates with: Age Gender Height percentile Standards Ages 1-12 months: 1987 task force Ages 1-17 years: Fourth BP report Fourth report on BP. Pediatrics August 2004 7/19/07 Definitions Normal Pre-hypertension SBP and DBP <90th percentiles for gender, age, and height Average SBP or DBP between 90th and 95th percentiles or > 120/80 mm Hg Hypertension 7/19/07 Average SBP and/or DBP > 95th for gender, age, and height on more than 3 occasions Fourth Report on BP. Pediatrics August 2004 5 yrs old Girl BP 121/80 Height 90th percentile 90th : 109/69 95th : 112/73 Fourth Report on BP. Pediatrics August 2004 7/19/07 Definitions Stage I hypertension Average SBP and/or DBP between 95th and 99th percentile plus 5 mm Hg Stage II hypertension Average SBP and/or DBP > 99th percentile plus 5 mm Hg Fourth Report on BP. Pediatrics August 2004 7/19/07 5 yrs old Girl BP 121/80 Height 90th percentile 90th : 109/69 95th : 112/73 99th : 120/81 Stage II: >125/86 Fourth Report on BP. Pediatrics August 2004 7/19/07 A 7 years old boy had average BP 110/60 mm Hg. Similar BP readings were documented on three separate occasions. His height is at 95th percentile. This boy has A. B. C. D. 7/19/07 Normal blood pressure Pre-hypertension Stage I hypertension Stage II hypertension A 8 years old girl has average BP 130/90 mm Hg. Similar BP readings were documented on three separate occasions. Her height is at 75th percentile This girl has A. B. C. D. 7/19/07 Normal blood pressure Pre-hypertension Stage I hypertension Stage II hypertension A 11 years old boy had average BP 140/95 mm Hg. Similar BP readings were documented on three separate occasions. His height is at 5th percentile This boy has A. B. C. D. 7/19/07 Normal blood pressure Pre-hypertension Stage I hypertension Stage II hypertension A 18 years old young man had average BP 150/95 mm Hg. Similar BP readings were documented on three separate occasions. His height is at 50th percentile This young man has A. B. C. D. 7/19/07 Normal blood pressure Pre-hypertension Stage I hypertension Stage II hypertension Blood Pressure Screening in Marianna May 2005 Volunteers and school nurse was trained for BP measurement 81, 4th grader (89% AA) First screening Normal 80% Pre-htn 9% Hypertension 11% Third screening 7/19/07 Hypertension 3.7% School Blood Pressure Screening Purpose To find undiagnosed hypertensive school children and adolescents Refer these children to primary care physicians Help primary care physicians in the management of these children if required 7/19/07 Summary Accurate blood pressure measurement is the corner stone of diagnosis of hypertension in children Oscillatory method can be used for screening but elevated blood pressure should be confirmed with auscultatoy method Appropriately sized cuff is mandatory and measure mid arm circumference to choose the cuff size Calibrate BP measurement apparatus semiannually 7/19/07 Thanks Ms. Paula Smith Department of Pediatrics-UAMS Office of education Minority Health Commission Marianna School 7/19/07 Hypertension Clinic-ACH Dr. Karen McNiece, M.D Dr. Thomas Wells, M.D. Dr. Mohammad Ilyas, M.D. Jona Plummer, RNP Wendy Davis, RN Contact Number (501) 364-1847 7/19/07