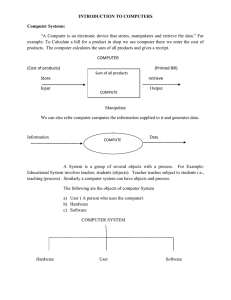
Chapter 6
advertisement

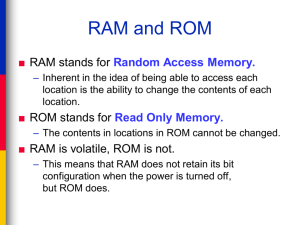
Discovering Computers 2008 Fundamentals Fourth Edition Chapter 6 Storage Chapter 6 Objectives Describe the characteristics of magnetic disks Describe the characteristics of a hard disk Discuss various types of miniature, external, and removable hard disks Describe the characteristics of optical disks Differentiate among various CD and DVD formats Identify the uses of tape Discuss PC Cards, ExpressCard modules and the various types of miniature mobile storage media Identify uses of microfilm and microfiche Next Storage What is storage? Holds data, instructions, and information for future use Storage medium is physical material used for storage Also called secondary storage p. 220 - 221 Fig. 6-1 Next Storage What is capacity? Number of bytes (characters) a storage medium can hold Kilobyte (KB) 1 thousand Megabyte (MB) 1 million p. 222 Gigabyte (GB) 1 billion Terabyte (TB) 1 trillion Petabyte (PB) 1 quadrillion Exabyte (EB) 1 quintillion Zettabyte (ZB) 1 sextillion Yottabyte (YB) 1 septillion Next Storage What is a storage device? Reading Process of transferring items from storage media to memory Hardware that records and retrieves items to and from storage media Functions as source of input p. 222 Writing Process of transferring items from memory to storage media Creates output Next Storage What is access time? p. 222 Time it takes storage device to locate item on storage medium Time required to deliver item from memory to processor Next Magnetic Disks What are tracks and sectors? Track is narrow recording band that forms full circle on disk p. 222 Fig. 6-3 Sector stores up to 512 bytes of data Next Magnetic Disks What is a hard disk? hard disk installed in system unit High-capacity storage Consists of several inflexible, circular platters that store items electronically Components enclosed in airtight, sealed case for protection Longitudinal recording Click to view Web Link, click Chapter 6, Click Web Link from left navigation, then click Perpendicular Recording below Chapter 6 p. 223 Fig. 6-4 Perpendicular recording Next Magnetic Disks What are characteristics of a hard disk? Sample Hard Disk Characteristics Advertised capacity Platters Read/write heads Cylinders Bytes per second Sectors per track Sectors per drive Revolutions per minute Transfer rate Access time p. 224 Fig. 6-5 500 GB 4 8 16,383 512 63 973,773,168 7,200 300 MB per second 8.5 ms actual disk capacity Next Magnetic Disks How does a hard disk work? Step 3. Step 2. When software requests a disk access, read/write heads determine current or new location of data. Small motor spins platters while computer is running. Step 4. Step 1. Circuit board controls movement of head actuator and a small motor. p. 224 Fig. 6-6 Head actuator positions read/write head arms over correct location on platters to read or write data. Next Magnetic Disks platter What is a cylinder? Vertical section of track through all platters Single movement of read/write head arms accesses all platters in cylinder track sector read/write head platter sides p. 225 Fig. 6-7 cylinder Next Magnetic Disks What is a head crash? Occurs when read/write head touches platter surface Spinning creates cushion of air that floats read/write head above platter p. 225 Fig. 6-8 Clearance between head and platter is approximately two-millionths of an inch A smoke particle, dust particle, or human hair could render drive unusable Next Magnetic Disks What is RAID? p. 226 Redundant Array of Independent Disks Connects multiple smaller disks into a single unit that acts as a single large hard disk Next Magnetic Disks What is a miniature hard disk? Provide greater storage capacities than flash memory Smaller than notebook computer hard disks A pocket hard drive is a self-contained unit Click to view Web Link, click Chapter 6, Click Web Link from left navigation, then click Miniature Hard Disks below Chapter 6 p. 226 Fig. 6-9 and 6-10 Next Magnetic Disks What are external hard disks and removable hard disks? Used to back up or transfer files Removable hard disk—hard disk that you insert and remove from hard disk drive External hard disk—freestanding hard disk that connects to system unit p. 226 Fig. 6-11 Next Magnetic Disks What is a disk controller? Chip and circuits that control transfer of items from disk SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) controller uses serial signals to transfer data, instructions, and information EIDE (Enhanced Integrated Drive SCSI controller supports up to fifteen Electronics) controller supports four devices including hard disks, CD hard disks, provides connections for and DVD drives, tape drives, printers, CD and DVD drives scanners, network cards p. 227 Next Magnetic Disks What is online storage? Service on Web that provides storage for minimal monthly fee Files can be accessed from any computer with Web access Others can be authorized to access your data Click to view Web Link, click Chapter 6, Click Web Link from left navigation, then click Online Storage below Chapter 6 p. 227 - 228 Fig. 6-12 Next Magnetic Disks What is a floppy disk? Portable, inexpensive storage medium (also called diskette) Thin, circular, flexible film enclosed in 3.5” wide plastic shell p. 228 Next Magnetic Disks What is a floppy disk drive? Device that reads from and writes to floppy disk One floppy drive, named drive A Also called secondary storage External floppy disk drive attaches to a computer with a cable Floppy disk drive built into a desktop computer p. 228 Fig. 6-13 Next Optical Discs What are optical discs? Flat, round, portable metal discs made of metal, plastic, and lacquer Can be read only or read/write Most PCs include an optical disc drive p. 229 Fig. 6-14 Push the button to slide out the tray. Insert the disc, label side up. Push the same button to close the tray. Next Optical Discs How should you care for an optical disc? p. 230 Fig. 6-15 Next Optical Discs What is a CD-ROM? Compact disc read-only memory Cannot erase or modify contents Typically holds 650 MB to 1 GB Commonly used to distribute multimedia and complex software Click to view Web Link, click Chapter 6, Click Web Link from left navigation, then click CD-ROMs below Chapter 6 p. 231 Fig. 6-17 Next Optical Discs What is a Picture CD? Stores digital versions of roll of film Film developers offer Picture CD service Can be modified using photo editing software Step 1. Drop off film to be developed. Mark the Picture CD box on the film-processing envelope. Click to view Web Link, click Chapter 6, Click Web Link from left navigation, then click Picture CDs below Chapter 6 p. 232 Fig. 6-18 Step 3. Step 2. When you pick up prints and negatives, a Picture CD contains digital images of each photograph. At home, print images from Picture CD on your ink-jet photo printer. At a store, print images to Picture CD at kiosk. Next Optical Discs What are CD-Rs and CD-RWs? Must have CD recorder or CD-R drive CD-R (compact disc-recordable) — disc you can write on once c Cannot erase disc’s contents CD-RW (compact disc-rewritable) — erasable disc you can write on multiple times ce Must have CD-RW software and CD-RW drive p. 232 Next Optical Discs Video: Got Your Video Right Here CLICK TO START Next Optical Discs What is a DVD-ROM (digital versatile disc-ROM or digital video disc-ROM)? Must have DVD-ROM drive or DVD player to read DVD-ROM Stores databases, music, complex software, and movies Blu-ray discs have storage capacity of up to 100 GB HD-DVD discs have storage capacity of up to 60 GB UMD can store up to 1.8 GB p. 233 Fig. 6-19 Next Optical Discs How does a DVD-ROM store data? Two layers of pits are used, lower layer is semitransparent so laser can read through Some are double-sided Many types of recordable and rewritable DVDs are available DVD-R and DVD+R DVD-RW and DVD+RW Click to view Web Link, click Chapter 6, Click Web Link from left navigation, then click Blu-ray and HD DVD below Chapter 6 p. 233 - 234 Fig. 6-20 Next Tape What is tape? Magnetically coated plastic ribbon capable of storing large amounts of data at low cost Primarily used for backup p. 234 Fig. 6-21 Next Tape How is data stored on a tape? p. 235 Sequential access Reads and writes data consecutively, like music tape Unlike direct access — used on hard disks, CDs, and DVDs — which can locate particular item immediately Next PC Cards and ExpressCard Modules What are PC Cards and ExpressCard Modules? Adds capabilities to computer Credit-card-sized device commonly used in notebook computers p. 235 Figs. 6-22 Next Miniature Mobile Storage Media What is miniature mobile storage media? Storage for small mobile devices CompactFlash Secure Digital Memory Stick xD Picture Card Memory Stick PRO Duo Click to view Web Link, click Chapter 6, Click Web Link from left navigation, then click Flash Memory Cards below Chapter 6 p. 236 Fig. 6-23 Next Miniature Mobile Storage Media What is a USB Flash Drive? Plugs in a USB port on a computer or mobile device Storage capacities up to 64 GB Making the floppy disk obsolete p. 236 Fig. 6-24 Next Miniature Mobile Storage Media What is a smart card? Stores data on microprocessor embedded in small card Input, process, output, and storage capabilities Click to view Web Link, click Chapter 6, Click Web Link from left navigation, then click Smart Cards below Chapter 6 p. 237 Fig. 6-25 Next Microfilm and Microfiche What are microfilm and microfiche? Store microscopic images of documents on roll or sheet of film Images recorded using computer output microfilm recorder Microfilm — 100- to 215-foot roll of film p. 238 Fig. 6-26 Microfiche — small sheet of film, usually 4” 6” Next Microfilm and Microfiche How do life expectancies of various media compare? Microfilm and microfiche have longest life of any storage media p. 238 Fig. 6-27 Next Putting It All Together What are recommended storage devices for home users? p. 239 Fig. 6-28 250 GB hard disk Online storage CD or DVD drive Card reader/writer USB flash drive Next Putting It All Together What are recommended storage devices for small office/home office (SOHO) users? p. 239 Fig. 6-28 500 GB hard disk Online storage CD or DVD drive External hard drive for backup USB flash drive Next Putting It All Together What are recommended storage devices for mobile users? p. 239 Fig. 6-28 100 GB hard disk Online storage CD or DVD drive Card reader/writer Portable hard disk for backup USB flash drive Next Putting It All Together What are recommended storage devices for power users? p. 239 Fig. 6-28 1.5 TB hard disk Online storage CD or DVD drive Portable hard disk for backup USB flash drive Next Putting It All Together What are recommended storage devices for large business users? Desktop computer 500 GB hard disk CD or DVD drive Smart card reader Tape drive USB flash drive Server or Mainframe Network storage server 40 TB hard disk system CD-ROM or DVD-ROM server Microfilm or microfiche p. 239 Fig. 6-28 Next Summary of Storage Internal hard disks Recordable and rewritable DVDs External and Removable hard disks Tape Floppy disks PC Cards and ExpressCard Modules CD-ROMs Flash memory cards Recordable and Rewritable CDs USB Flash Drives DVD-ROMs Smart Cards Blu-ray Discs and HD DVD discs Microfilm and microfiche Chapter 6 Complete